Soil Basics Soil Profiles
Soil Profile Class 7 Science Soil Soil profiles dig down deep into any soil, and you’ll see that it is made of layers, or horizons. put the horizons together, and they form a soil profile. like a biography, each profile tells a story about the life of a soil. soil changes with age as a soil ages, it gradually starts to look different from its parent material. that’s. This video was created to teach about soil profiles. for more information on soil basics visit: purdue.ag soil basics#purdueextension #soilscience #.

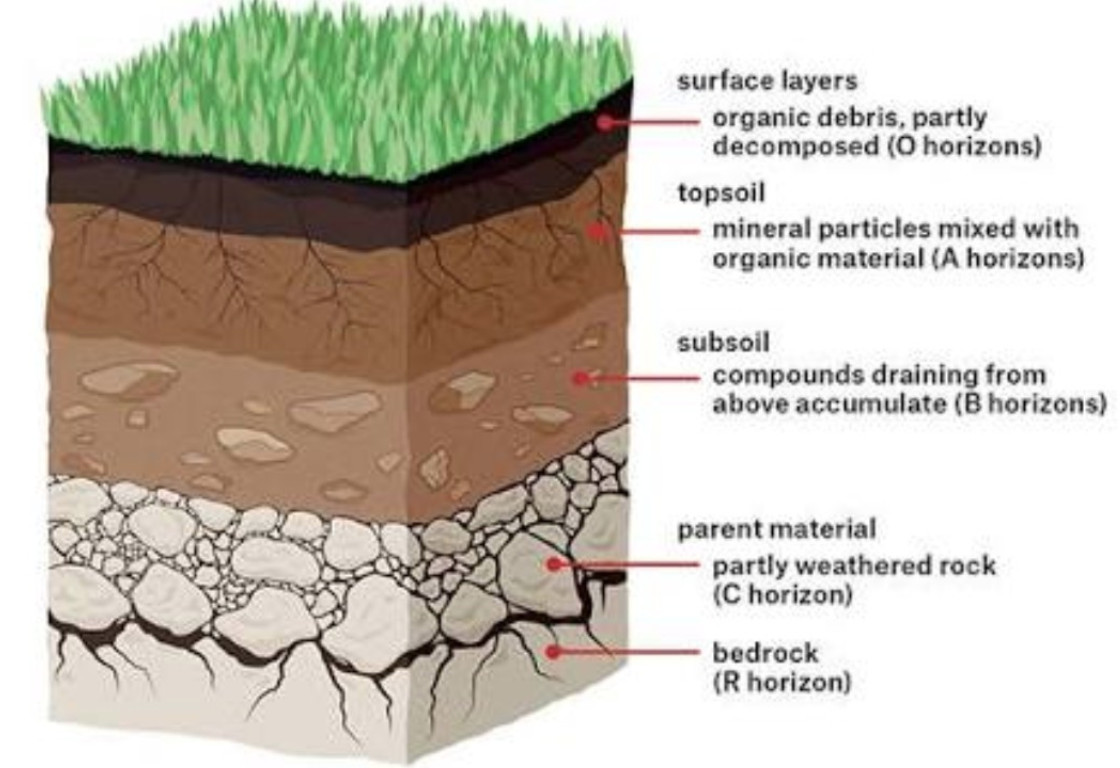
Soil Profile Definition Diagram Layers Of Soil Geeksforgeeks Soil profile cards (114.94 kb) print the soil profile cards (above) onto cardstock paper or draw your own design on a 3" x 5" note card. cut the cards apart. attach a short strip of carpet tape to the card. rolls of double sided tape come in various widths. one inch tape is adequate. Soil profiles. digging through the soil, you may notice the deeper you go, the more it changes. this is because over time soil begins to stratify or form layers. these different layers are called soil horizons. a soil profile is a vertical slice of the soil that shows the different layers. each layer is different both physically and chemically. The particular compositional, structural and chemical composition of the soil depends on the various factors that influence soil formation. this page titled 16.4: soil profiles is shared under a cc by nc sa 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by arnaud temme, kansas state university ( the physical environment ) via source. Illuvial layers are found low in the soil profile. illuvial zones are found closer to the surface in semiarid and arid climates where precipitation is scarce. capillary action brings cations like calcium and sodium dissolved in soil water upwards where they precipitate from the water. figure 11.4.2 11.4. 2: eluviation and illuviation under.
Schematic Drawing Of The Soil Profile Download Scientific Diagram The particular compositional, structural and chemical composition of the soil depends on the various factors that influence soil formation. this page titled 16.4: soil profiles is shared under a cc by nc sa 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by arnaud temme, kansas state university ( the physical environment ) via source. Illuvial layers are found low in the soil profile. illuvial zones are found closer to the surface in semiarid and arid climates where precipitation is scarce. capillary action brings cations like calcium and sodium dissolved in soil water upwards where they precipitate from the water. figure 11.4.2 11.4. 2: eluviation and illuviation under. This is because the first place where water and air come in contact with the soil is at the top. a cut in the side of a hillside shows each of the different layers of soil. all together, these are called a soil profile (figure 3). the simplest soils have three horizons: topsoil (a horizon), subsoil (b horizon), and c horizon. Dig down deep into any soil, and you’ll see that it is made of layers, or horizons (o, a, e, b, c, r). put the horizons together, and they form a soil profile. like a biography, each profile tells a story about the life of a soil. most soils have three major horizons (a, b, c) and some have an organic horizon (o). the horizons are:.

Comments are closed.