Soil Formation What Is Soil Made Of How Do Soils Form
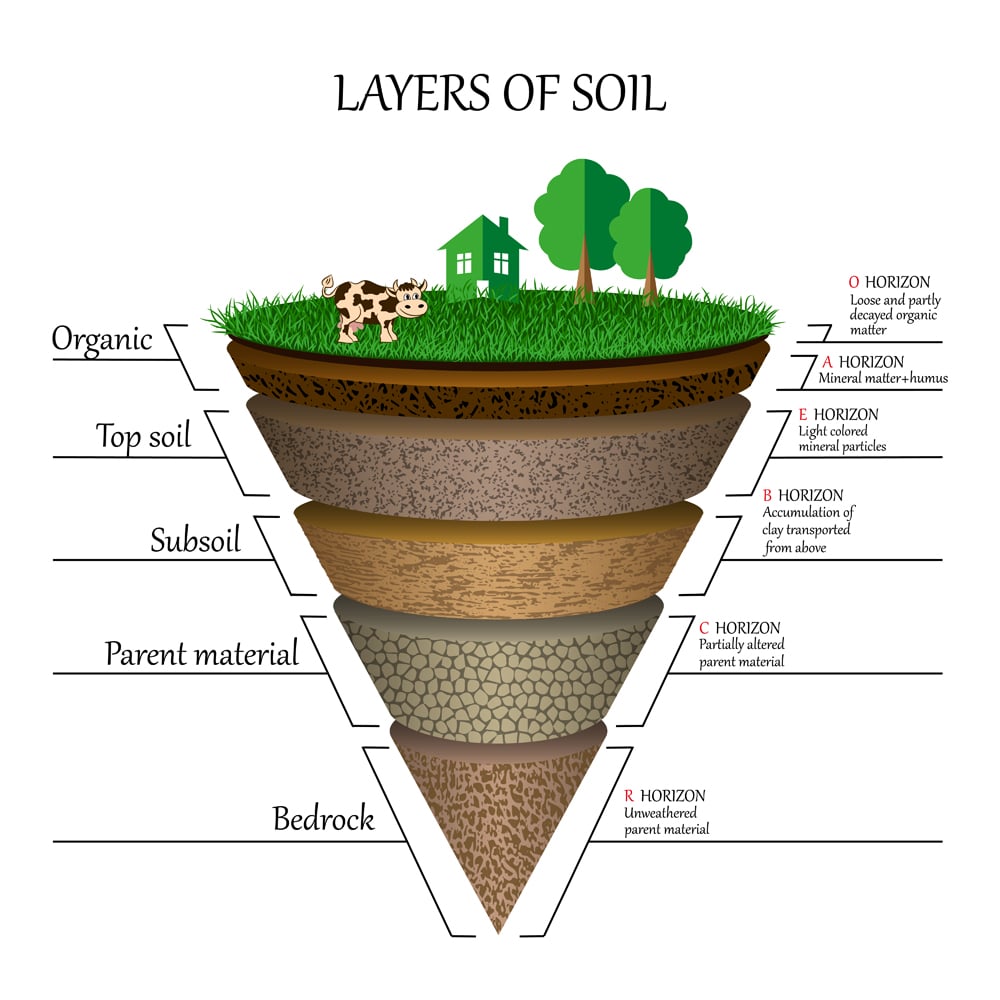
Soil Formation What Is Soil Made Of How Do Soils Form Soil formation, composition, structure: as stated at the beginning of this article, soils evolve under the action of biological, climatic, geologic, and topographic influences. the evolution of soils and their properties is called soil formation, and pedologists have identified five fundamental soil formation processes that influence soil properties. these five “state factors” are parent. Soil formation. soil formation, also known as pedogenesis, is the process of soil genesis as regulated by the effects of place, environment, and history. biogeochemical processes act to both create and destroy order (anisotropy) within soils.
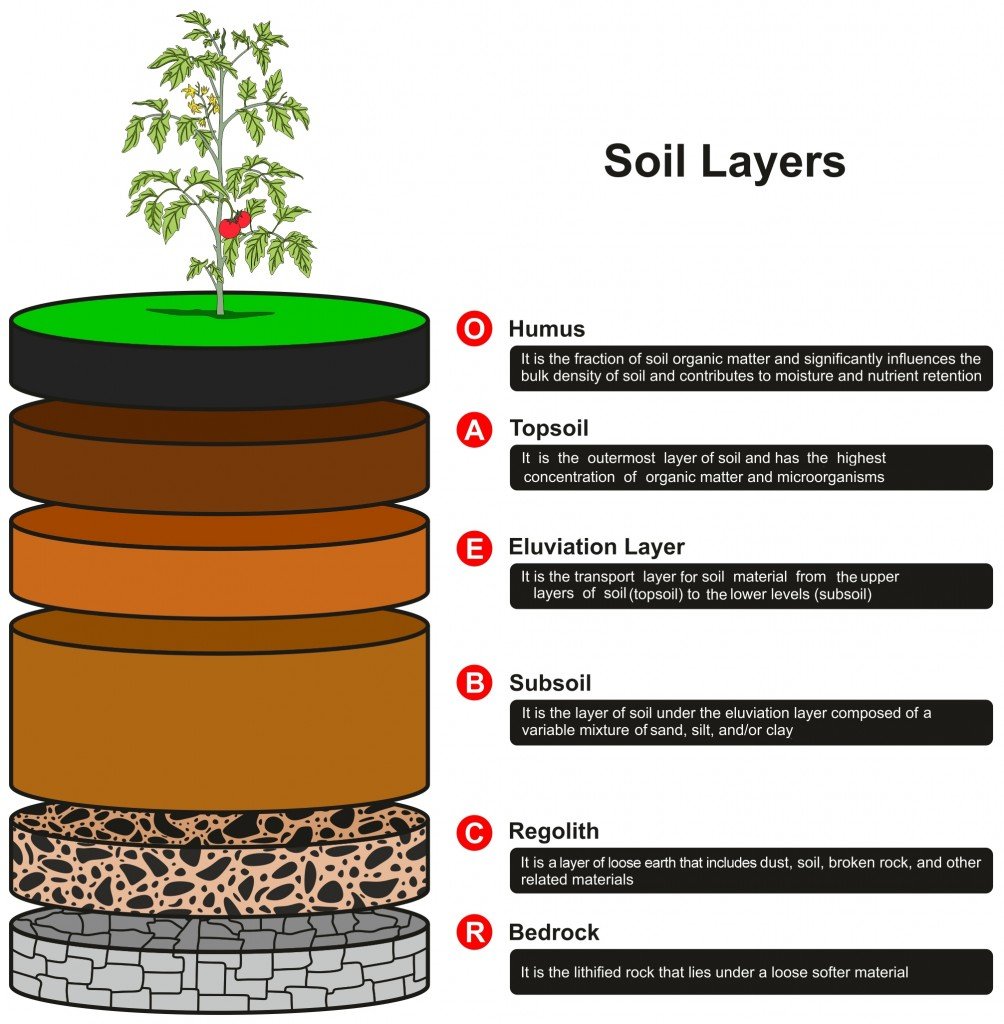
Soil Formation What Is Soil Made Of How Do Soils Form Time is responsible for horizon formation. the longer the soil is exposed to the soil forming factors mentioned above, the greater will be the development and composition of the soil. soils found on steep slopes and windy areas take more time to form, due to continuous erosion, as compared to older and more physically stable areas. How do soils form? soil profiles dig down deep into any soil, and you’ll see that it is made of layers, or horizons. put the horizons together, and they form a soil profile. like a biography, each profile tells a story about the life of a soil. soil changes with age as a soil ages, it gradually starts to look different from its parent. How do soils form? the early phase of soil formation starts by disintegrating the rock under the influence of climate. rainwater will dissolve rock elements, temperature fluctuations will cause cracks and fissures in the rocks. freezing and thawing of water captured in the rock will widen existing cracks and cavities. Water erodes rocks, wind transports sand, and freezing temperatures can create permafrost. a climate is an area in which weather patterns are consistent, and each climate can sway the soil formation process. the weather in a climate can not only determine how the soil forms, but also govern whether wild plants can grow fruitfully in the area.
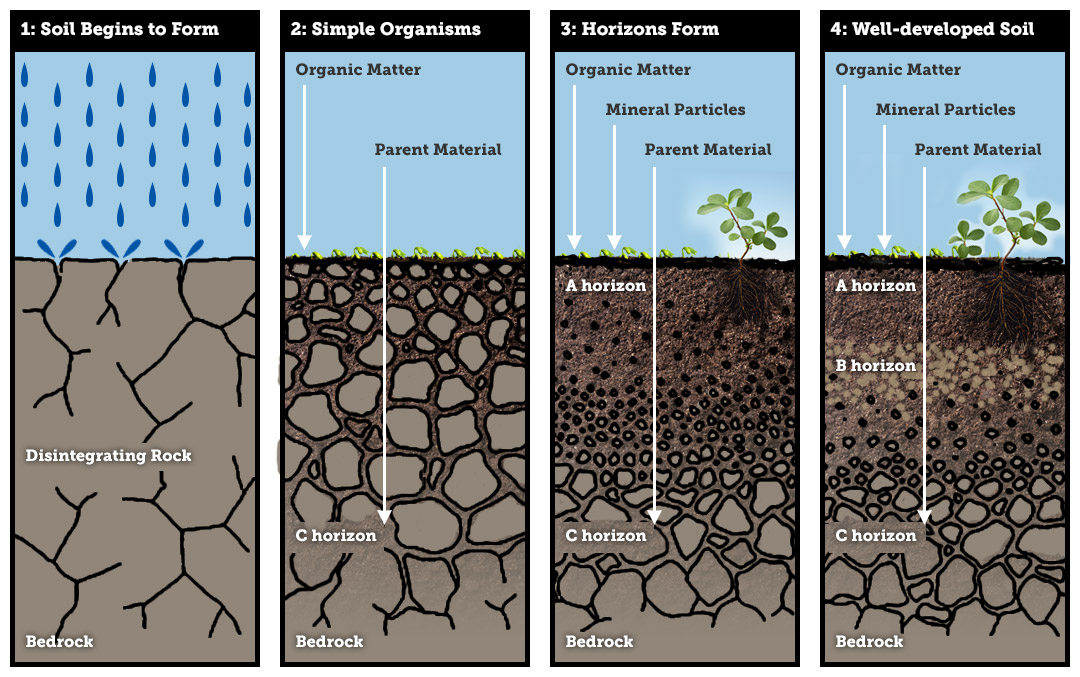
Soil Formation And Soil Types Civilarc How do soils form? the early phase of soil formation starts by disintegrating the rock under the influence of climate. rainwater will dissolve rock elements, temperature fluctuations will cause cracks and fissures in the rocks. freezing and thawing of water captured in the rock will widen existing cracks and cavities. Water erodes rocks, wind transports sand, and freezing temperatures can create permafrost. a climate is an area in which weather patterns are consistent, and each climate can sway the soil formation process. the weather in a climate can not only determine how the soil forms, but also govern whether wild plants can grow fruitfully in the area. Soil 1. a material composed of minerals, living organisms, soil organic matter, gas, and water. 2. a body composed of soil and other parts such as rocks, roots, and animals that has size, form. Soils develop faster in warm, moist climates and slowest in cold or arid ones. rainfall is one of the most important climate factors in soil formation. organisms: plants root, animals burrow, and bacteria eat – these and other organisms speed up the breakdown of large soil particles into smaller ones. for instance, roots produce carbon.

A Brief Overview Of How Soil Is Formed Including Its Soil Forming Soil 1. a material composed of minerals, living organisms, soil organic matter, gas, and water. 2. a body composed of soil and other parts such as rocks, roots, and animals that has size, form. Soils develop faster in warm, moist climates and slowest in cold or arid ones. rainfall is one of the most important climate factors in soil formation. organisms: plants root, animals burrow, and bacteria eat – these and other organisms speed up the breakdown of large soil particles into smaller ones. for instance, roots produce carbon.

Formation Of Soil Soil Formation Classnotes Ng

Comments are closed.