State And Its Elements

Essential Elements Of State University Of Political Science Learn the definition, elements and characteristics of the state, a natural and universal social institution. compare and contrast the state with society and nation, and understand the concepts of sovereignty, government and territory. State, political organization of society, or the body politic, or, more narrowly, the institutions of government.the state is a form of human association distinguished from other social groups by its purpose, the establishment of order and security; its methods, the laws and their enforcement; its territory, the area of jurisdiction or geographic boundaries; and finally by its sovereignty.

State And Its Elements Learn the definition, history and elements of state in political science. the web page explains the concepts of population, territory, government and sovereignty with examples and references. The former is a much more comprehensive intellectual history of the state as an idea in western european thought; the latter a history of normative political interpretations of the state. a more recent intellectual history is nelson 2006, which makes an explicit attempt to embed the western tradition in its social context. 4. sovereignty. 1. population is an essential elements of state. two conclusions flow from the discussion on the meaning and nature of the state: (i) that the state is a human institution the product of man’s gregarious nature and the result of necessities of human life, and. (2) population and land are the starting point of any study of man. Anarchism. anarchism is a political philosophy that considers states immoral and instead promotes a stateless society, anarchy. anarchists believe that the state is inherently an instrument of domination and repression, no matter who is in control of it. anarchists believe that the state apparatus should be completely dismantled and an.
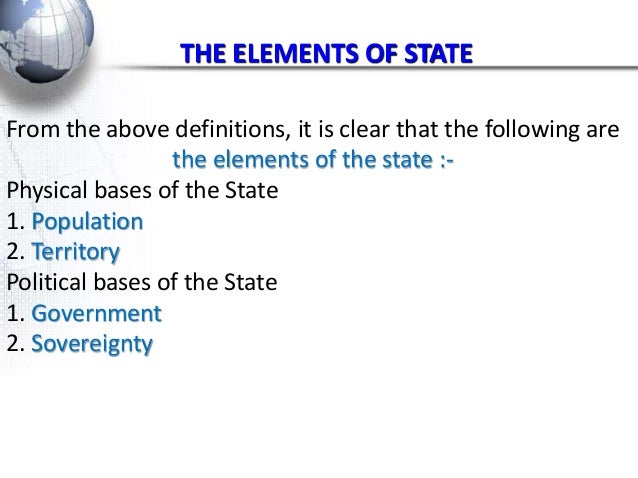
State And Its Elements 4. sovereignty. 1. population is an essential elements of state. two conclusions flow from the discussion on the meaning and nature of the state: (i) that the state is a human institution the product of man’s gregarious nature and the result of necessities of human life, and. (2) population and land are the starting point of any study of man. Anarchism. anarchism is a political philosophy that considers states immoral and instead promotes a stateless society, anarchy. anarchists believe that the state is inherently an instrument of domination and repression, no matter who is in control of it. anarchists believe that the state apparatus should be completely dismantled and an. A state is a political entity that regulates society and the population within a territory. [1] government is considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states. [2][3] a country often has a single state, with various administrative divisions. a state may be a unitary state or some type of federal union; in the latter type, the. The basic principle is that of continuity in the identity of the state, a principle whose intensity depends on the changes that may occur in its constituent elements: 1. variations in sovereignty over the territory. 2. changes in the population, by modifying the sovereignty in a territory, or by migratory movements. 3.

State And Its Elements Ppt A state is a political entity that regulates society and the population within a territory. [1] government is considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states. [2][3] a country often has a single state, with various administrative divisions. a state may be a unitary state or some type of federal union; in the latter type, the. The basic principle is that of continuity in the identity of the state, a principle whose intensity depends on the changes that may occur in its constituent elements: 1. variations in sovereignty over the territory. 2. changes in the population, by modifying the sovereignty in a territory, or by migratory movements. 3.

Comments are closed.