Step 4 We Determine The Resultant Vector By Using The Parallelogram

Step 4 We Determine The Resultant Vector By Using The Parallelogram To find their sum: step 1: draw the vectors p and q such that their tails touch each other. step 2: complete the parallelogram by drawing the other two sides. step 3: the diagonal of the parallelogram that has the same tail as the vectors p and q represents the sum of the two vectors. i.e., p q = r. The resultant vector is the vector that 'results' from adding two or more vectors together. there are a two different ways to calculate the resultant vector. methods for calculating a resultant vector: the head to tail method to calculate a resultant which involves lining up the head of the one vector with the tail of the other.

Step 4 We Determine The Resultant Vector By Using The Parallelogram Yes, there is a specific formula to calculate the resultant vector using the parallelogram method. the formula is r = sqrt (a^2 b^2 2abcosθ), where r is the magnitude of the resultant vector, a and b are the magnitudes of the two vectors being added, and θ is the angle between them. in conclusion, the parallelogram method is a powerful. This video explains how to use the parallelogram method to find the resultant sum of two vectors. you need to be familiar with law of cosines formula in ord. Step 1: if adding two vectors u → v →, graph both vectors on the coordinate plane with the initial points at the origin. if subtracting two vectors u → − v →, rewrite to u → (− v. Let θ be the angle between p and q and r be the resultant vector. then, according to parallelogram law of vector addition, diagonal ob represents the resultant of p and q. so, we have. r = p q. now, expand a to c and draw bc perpendicular to oc. from triangle ocb, in triangle abc, also, magnitude of resultant: substituting value of ac and bc.

Using The Parallelogram Method Find The Resultant Vector Step 1: if adding two vectors u → v →, graph both vectors on the coordinate plane with the initial points at the origin. if subtracting two vectors u → − v →, rewrite to u → (− v. Let θ be the angle between p and q and r be the resultant vector. then, according to parallelogram law of vector addition, diagonal ob represents the resultant of p and q. so, we have. r = p q. now, expand a to c and draw bc perpendicular to oc. from triangle ocb, in triangle abc, also, magnitude of resultant: substituting value of ac and bc. The following steps are used to find the resultant vector. step 1: as the first step, we draw a line, at the head of vector , parallel to vector . we then repeat this for the other vector. step 2: next, we draw a line from the point of concurrency of the two vectors to the point of intersection of the two parallel lines. This video shows how to find the resultant force of two vectors using the parallelogram method. we draw a parallelogram to help us find the resultant force.
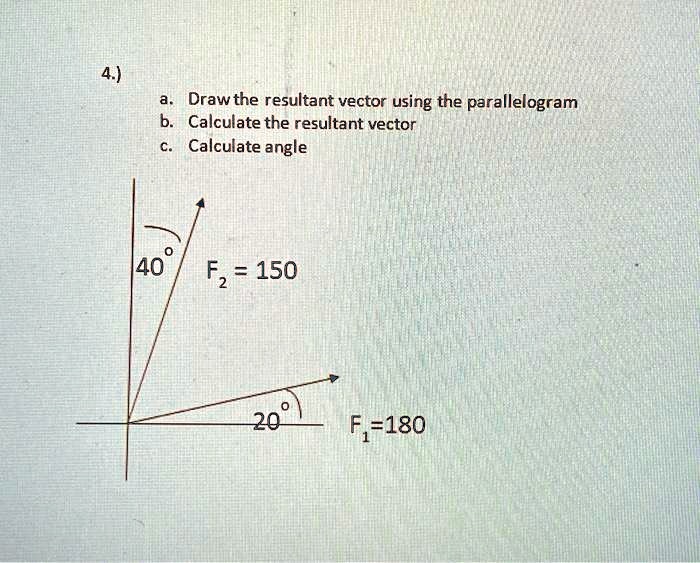
Solved Pls Need Step By Step Solution 4 A Draw The Resultant Vector The following steps are used to find the resultant vector. step 1: as the first step, we draw a line, at the head of vector , parallel to vector . we then repeat this for the other vector. step 2: next, we draw a line from the point of concurrency of the two vectors to the point of intersection of the two parallel lines. This video shows how to find the resultant force of two vectors using the parallelogram method. we draw a parallelogram to help us find the resultant force.

Comments are closed.