T1 2 For A First Order Reaction Is 6 93 S The Value Of Rate Constan

First Order Reaction Plot Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. see answer. question: the half life (t1 2) of a first order reaction is 0.100 s. what is the rate constant? a. 6.93 s 1 b. 0.693 s 1 c. 0.0693 s 1 d. 0.144 s 1 e. 3.01 s 1. the half life (t1 2) of a first order reaction is 0.100 s. The half life period t 1 2 for a first order reaction is 6.93 s, the value of rate constant for the reaction would be 0.1 s − 1 k = 0.693 t 1 2 k = 0.693 6.93 s.

T1 2 For A First Order Reaction Is 6 93 S The Value Of Rate Constant First order chemical reactions. return to kinetics menu. problem #1: calculate half life for first order reaction if 68% of a substance is reacted within 66 s. solution: 1) 68% reacted means 32% remains: ln a = kt ln a o. ln 0.32 = k (66 s) ln 1. k = 0.0172642 s 1. note that this calculation is done with how much substance remains, not. Figure 4.5.1 4.5. 1: the half life of a first order reaction. this plot shows the concentration of the reactant in a first order reaction as a function of time and identifies a series of half lives, intervals in which the reactant concentration decreases by a factor of 2. in a first order reaction, every half life is the same length of time. Half lives of first order reactions. the half life (t1 2) is a timescale on which the initial population is decreased by half of its original value, represented by the following equation. [a] = 1 2[a]o. after a period of one half life, t = t1 2 and we can write. [a]1 2 [a]o = 1 2 = e − kt1 2. Second order reaction: rate = − Δ[a] Δt = k[a]2 1 [a] = 1 [a]0 kt. the reaction rate of a zeroth order reaction is independent of the concentration of the reactants. the reaction rate of a first order reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of one ….
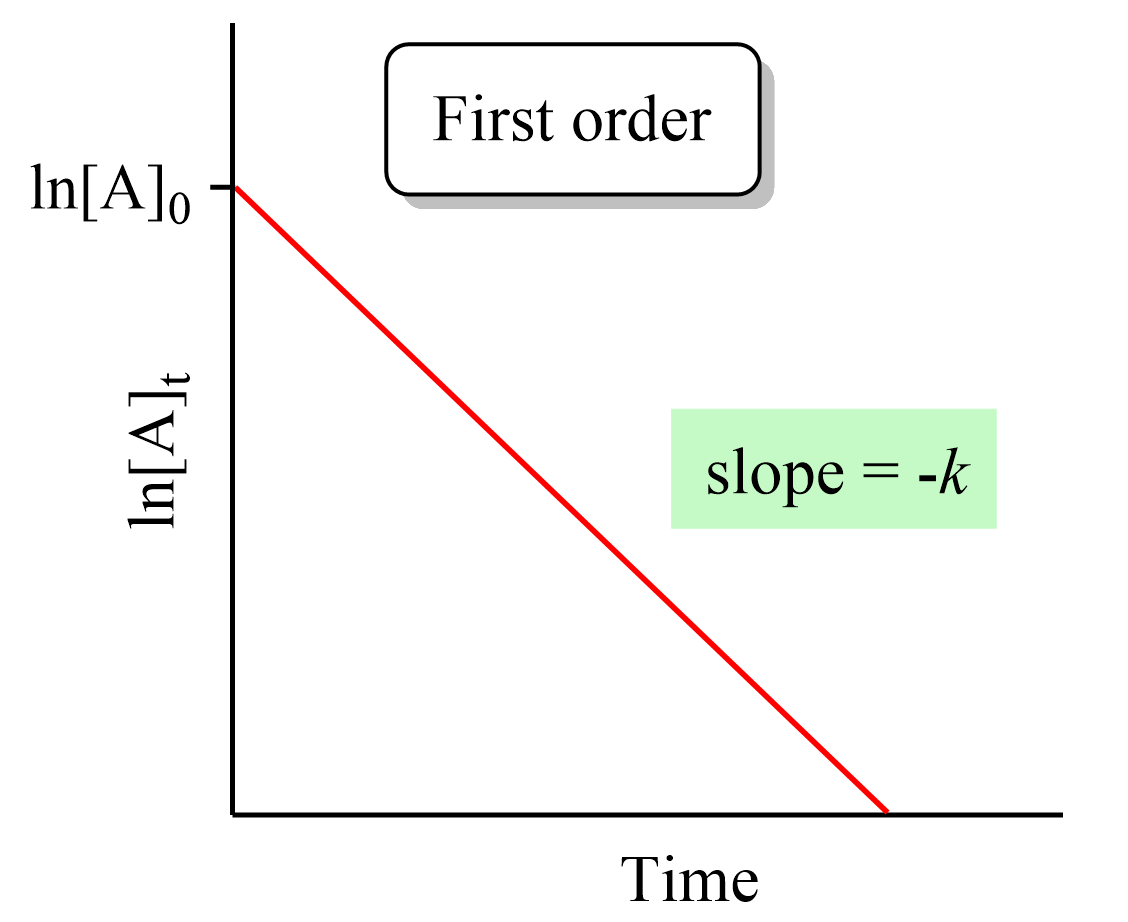
First Order Reactions Chemistry Steps Half lives of first order reactions. the half life (t1 2) is a timescale on which the initial population is decreased by half of its original value, represented by the following equation. [a] = 1 2[a]o. after a period of one half life, t = t1 2 and we can write. [a]1 2 [a]o = 1 2 = e − kt1 2. Second order reaction: rate = − Δ[a] Δt = k[a]2 1 [a] = 1 [a]0 kt. the reaction rate of a zeroth order reaction is independent of the concentration of the reactants. the reaction rate of a first order reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of one …. Show that for a first order reaction half life is independent of initial concentration. the rate constant for a first order reaction is 1.54 × 10 −3 s −1. calculate its half life time. for the first order reaction, half life is equal to . read the passage given below and answer the following question. Half life equation for first order reactions: t1 2=0.693k . where t1 2 is the half life in seconds (s), and k is the rate constant in inverse seconds (s−1). a. what is the half life of a first order reaction with a rate constant of 8.70×10 −4 s−1? b. what is the rate constant of a first order reaction that takes 533 seconds for the.

For A First Order Reaction The Value Of Rat Constant For The Reaction A Show that for a first order reaction half life is independent of initial concentration. the rate constant for a first order reaction is 1.54 × 10 −3 s −1. calculate its half life time. for the first order reaction, half life is equal to . read the passage given below and answer the following question. Half life equation for first order reactions: t1 2=0.693k . where t1 2 is the half life in seconds (s), and k is the rate constant in inverse seconds (s−1). a. what is the half life of a first order reaction with a rate constant of 8.70×10 −4 s−1? b. what is the rate constant of a first order reaction that takes 533 seconds for the.
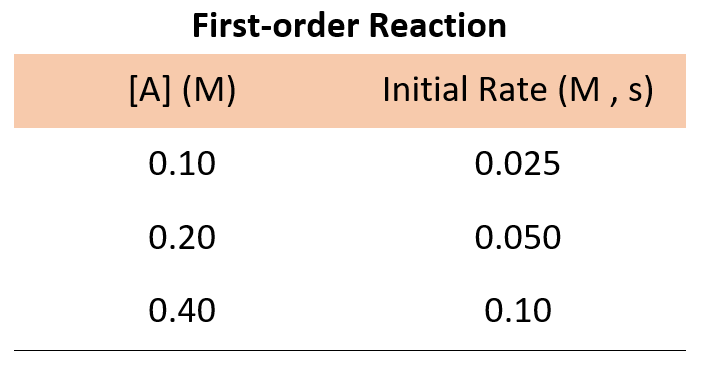
First Order Reaction Rate

First Order Reaction Linear Plot

Comments are closed.