The Actual Treatment Algorithm Of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension

The Actual Treatment Algorithm Of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) carries a poor prognosis if not promptly diagnosed and appropriately treated. the development and approval of 14 medications over the last several decades have led to a rapidly evolving approach to therapy, and have necessitated periodic updating of evidence based treatment guidelines. this guideline statement, which now includes a visual algorithm to. Eur heart j 2022;aug 26: [epub ahead of print]. the following are key points to remember from the 2022 european society of cardiology european respiratory society (esc ers) guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: pulmonary hypertension (ph) is now defined by a mean pulmonary arterial pressure >20 mm hg at rest. the.
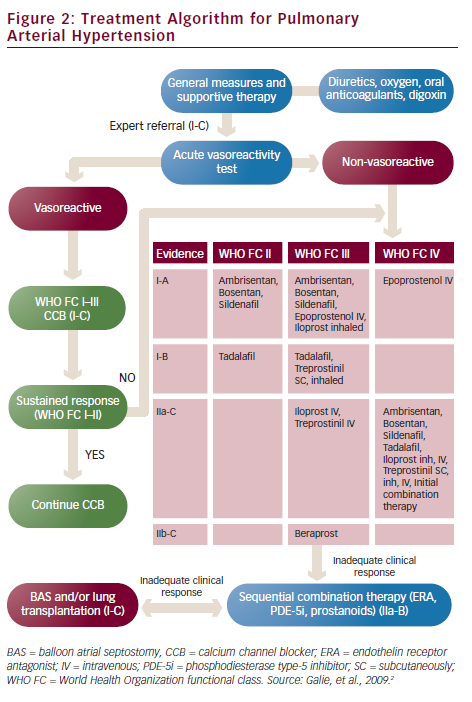
Treatment Algorithm For Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Radcliffe Introduction. the complexity of the treatment algorithm for pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) has progressively increased since the 2nd world symposium on pulmonary hypertension (wsph) in evian, france in 1998 when, apart from calcium channel blockers (ccbs) for vasoreactive patients, the only approved therapy was epoprostenol administered by continuous intravenous infusion . Pulmonary hypertension (ph) is a heterogeneous and highly morbid disease encountered commonly in general medicine, cardiology, and pulmonary medicine clinical practices. 1 the original definition of ph used mean pulmonary artery pressure (mpap) ≥25 mm hg, but this was derived from expert consensus opinion originally reported 45 years ago in the absence of sufficiently powered clinical data. Background: pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) carries a poor prognosis if not promptly diagnosed and appropriately treated. the development and approval of 14 medi cations over the last several decades have led to a rapidly evolving approach to therapy, and have necessitated periodic updating of evidence based treatment guidelines. this. There are five ph clinical subgroups, 1) pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah); 2) ph due to left heart disease; 3) ph due to respiratory disease, hypoxia, or hypoventilatory syndromes; 4) ph due to pulmonary arterial obstructions (e.g., chronic thromboembolic ph [cteph]); and 5) a constellation of ph etiologies that vary widely by pathogenesis, including sickle cell disease, sarcoidosis, and.

Treatment Algorithm Pah Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Ipah Background: pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) carries a poor prognosis if not promptly diagnosed and appropriately treated. the development and approval of 14 medi cations over the last several decades have led to a rapidly evolving approach to therapy, and have necessitated periodic updating of evidence based treatment guidelines. this. There are five ph clinical subgroups, 1) pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah); 2) ph due to left heart disease; 3) ph due to respiratory disease, hypoxia, or hypoventilatory syndromes; 4) ph due to pulmonary arterial obstructions (e.g., chronic thromboembolic ph [cteph]); and 5) a constellation of ph etiologies that vary widely by pathogenesis, including sickle cell disease, sarcoidosis, and. Abstract. pulmonary arterial hypertension leads to significant impairment in haemodynamics, right heart function, exercise capacity, quality of life and survival. current therapies have mechanisms of action involving signalling via one of four pathways: endothelin 1, nitric oxide, prostacyclin and bone morphogenetic protein activin signalling. The demands on a pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) treatment algorithm are multiple and in some ways conflicting. the treatment algorithm usually includes different types of recommendations with varying degrees of scientific evidence.

2022 Esc Ers Guidelines For The Diagnosis And Treatment Of Pulmonary Abstract. pulmonary arterial hypertension leads to significant impairment in haemodynamics, right heart function, exercise capacity, quality of life and survival. current therapies have mechanisms of action involving signalling via one of four pathways: endothelin 1, nitric oxide, prostacyclin and bone morphogenetic protein activin signalling. The demands on a pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) treatment algorithm are multiple and in some ways conflicting. the treatment algorithm usually includes different types of recommendations with varying degrees of scientific evidence.

Treatment Of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Nejm

Comments are closed.