The Multiplication Rule Of Probability Explained
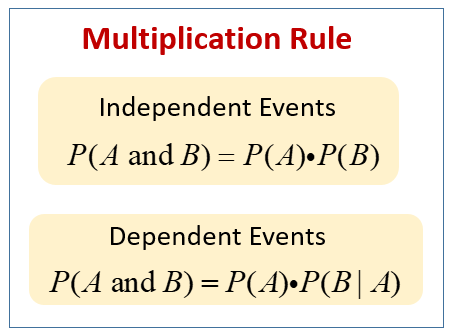
Multiplication Rule For Probability Examples Solutions Lessons The addition rule. if a and b are defined on a sample space, then: p (a or b) = p (a) p (b) − p (a and b) if a and b are mutually exclusive, then. p(a and b) = 0. and equation 4.3.2 becomes. p (a or b) = p (a) p (b). example 4.3.1. klaus is trying to choose where to go on vacation. We have already learned the multiplication rules we follow in probability, such as; p (a∩b) = p (a)×p (b|a) ; if p (a) ≠ 0. p (a∩b) = p (b)×p (a|b) ; if p (b) ≠ 0. let us learn here the multiplication theorems for independent events a and b. if a and b are two independent events for a random experiment, then the probability of.

Ppt Unit 4 Probability Simple Probability Examples Powerpoint To use this rule, multiply the probabilities for the independent events. with independent events, the occurrence of event a does not affect the likelihood of event b. this rule is not valid for dependent events. using probability notation, the specific multiplication rule is the following: p (a ∩ b) = p (a) * p (b) or, the joint probability. The general multiplication rule states that the probability of any two events, a and b, both happening can be calculated as: p (a and b) = p (a) * p (b|a) the vertical bar | means “given.”. thus, p (b|a) can be read as “the probability that b occurs, given that a has occurred.”. if events a and b are independent, then p (b|a) is simply. Any time you want to know the chance of two events happening together, you can use the multiplication rule of probability. independent events:p(a and b) = p(. The multiplication rule of probability states that the probability of the events, a and b, both occurring together is equal to the probability that b occurs times the conditional probability that a occurs given that b occurs. the multiplication rule can be written as p (a∩b)=p (b)⋅p (a|b). the general multiplication rule of probability can.

Multiplication Law Rule Of Probability Explained Statistics Tutor Any time you want to know the chance of two events happening together, you can use the multiplication rule of probability. independent events:p(a and b) = p(. The multiplication rule of probability states that the probability of the events, a and b, both occurring together is equal to the probability that b occurs times the conditional probability that a occurs given that b occurs. the multiplication rule can be written as p (a∩b)=p (b)⋅p (a|b). the general multiplication rule of probability can. Step 2: we want to start computing probabilities, starting with the first stage. the probability that the first card is a suspect is 6 21 = 2 7. the probability that the first card is a weapon is the same: 2 7. finally, the probability that the first card is a room is 9 21 = 3 7. The question asks us to find the probability of rolling at least one 4 out of three total rolls of an eight sided die, so we know we need to use the multiplication rule. however, trying to find at least one 4 is complicated, so it would be easier for us to find the complement and subtract from 1, which is the total probability.
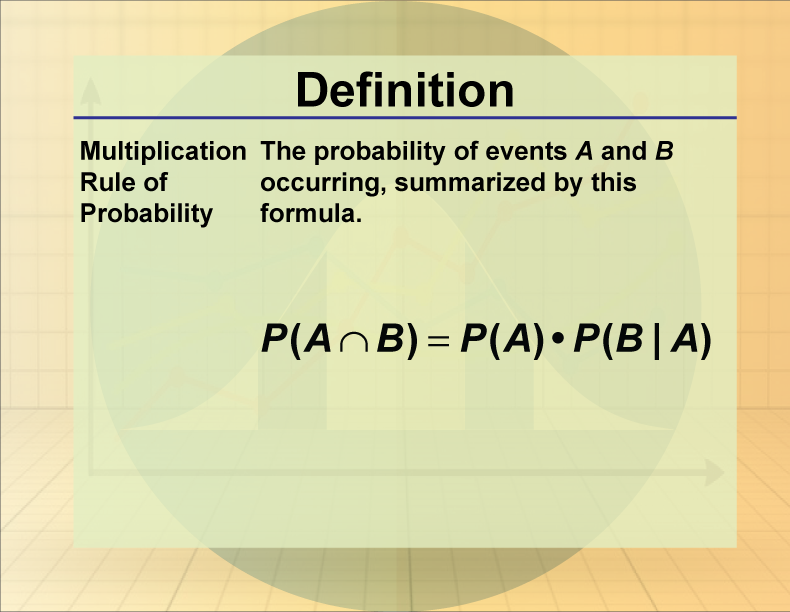
Definition Statistics And Probability Concepts Multiplication Rule Of Step 2: we want to start computing probabilities, starting with the first stage. the probability that the first card is a suspect is 6 21 = 2 7. the probability that the first card is a weapon is the same: 2 7. finally, the probability that the first card is a room is 9 21 = 3 7. The question asks us to find the probability of rolling at least one 4 out of three total rolls of an eight sided die, so we know we need to use the multiplication rule. however, trying to find at least one 4 is complicated, so it would be easier for us to find the complement and subtract from 1, which is the total probability.

The Multiplication Rule Of Probability Explained Youtube

Multiplication Rule Probability And Youtube

Comments are closed.