The Radial Nerve Course Motor Sensory Teachmeanatomy
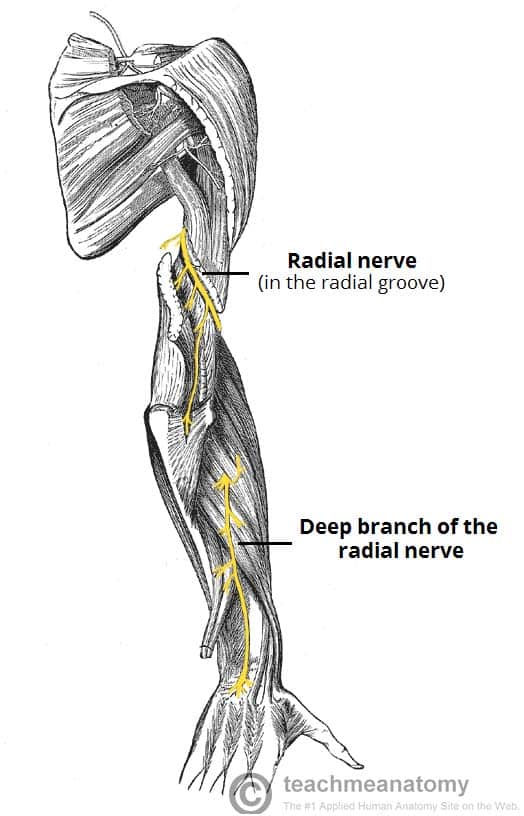
The Radial Nerve Course Motor Sensory Teachmeanatomy Anatomical course. the radial nerve is the terminal continuation of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. it therefore contains fibres from nerve roots c5 – t1. the nerve arises in the axilla region, where it is situated posteriorly to the axillary artery. it exits the axilla inferiorly (via the triangular interval), and supplies. Anatomical course. the median nerve is derived from the medial and lateral cords of the brachial plexus. it contains fibres from roots c6 t1 and can contain fibres from c5 in some individuals. after originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla, the median nerve descends down the arm, initially lateral to the brachial artery.
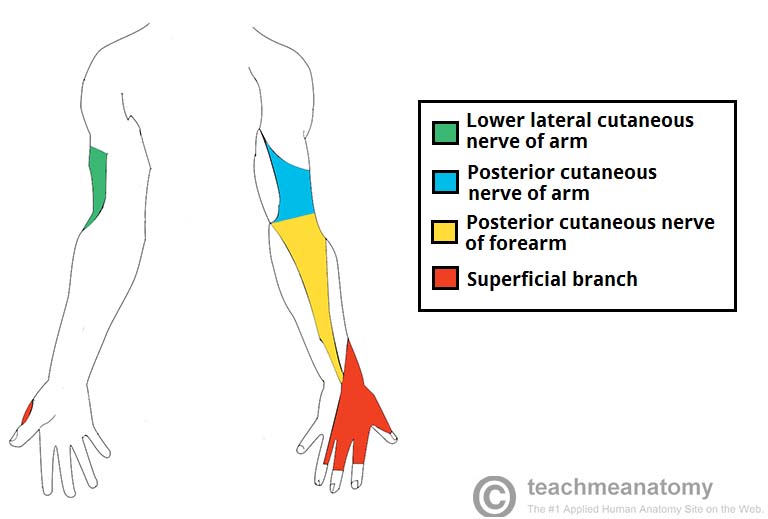
The Radial Nerve Course Motor Sensory Teachmeanatomy Anatomical course. the ulnar nerve arises from the brachial plexus within the axilla region. it is a continuation of the medial cord and contains fibres from spinal roots c8 and t1. after arising from the brachial plexus, the ulnar nerve descends in a plane between the axillary artery (lateral) and the axillary vein (medial). Origin and course. the radial nerve is the largest terminal branch of the brachial plexus. it originates from the posterior cord along with the axillary nerve, carrying fibers from ventral roots of spinal nerves c5 c8 and t1. the radial nerve arises in the axilla, immediately posterior to the axillary artery, between coracobrachialis and teres. Radial nerve originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus (c5 t1) behind axillary artery. course. posterior wall axilla. courses on the posterior wall of the axilla (on subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, teres major) 3 branches in axilla. posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm. branch to long head of triceps. The function of your radial nerve is to supply movement (motor) and sensory information between your brain and parts of your arm, wrist and hand. the motor branch of your radial nerve stimulates the: triceps muscles on the back of your upper arm to straighten your elbow. muscles in the outer part of your forearm that rotate your forearm and.
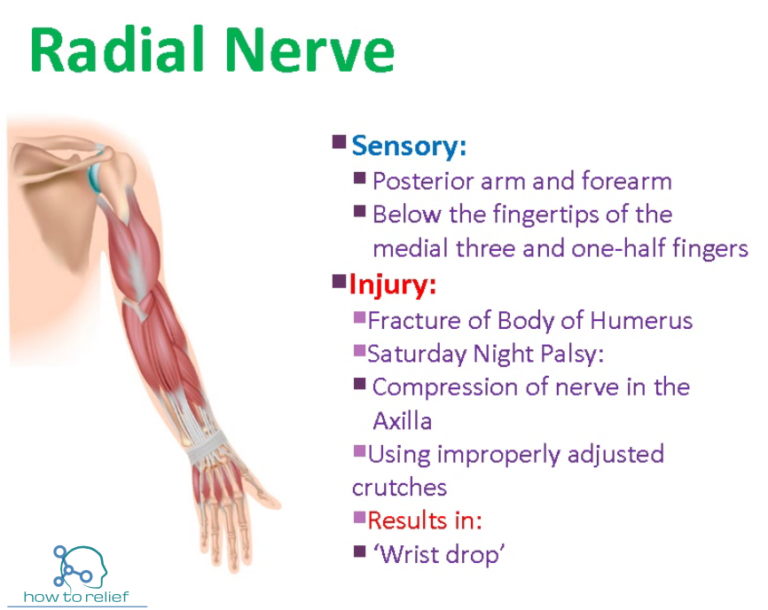
Radial Nerve Course Motor Sensory Common Injuries How To Relief Radial nerve originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus (c5 t1) behind axillary artery. course. posterior wall axilla. courses on the posterior wall of the axilla (on subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, teres major) 3 branches in axilla. posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm. branch to long head of triceps. The function of your radial nerve is to supply movement (motor) and sensory information between your brain and parts of your arm, wrist and hand. the motor branch of your radial nerve stimulates the: triceps muscles on the back of your upper arm to straighten your elbow. muscles in the outer part of your forearm that rotate your forearm and. The radial nerve is the second terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, that contains fibers of spinal nerves c5 t1. this nerve is a mixed nerve that provides motor and sensory innervation to the arm and forearm. the radial nerve provides motor supply to the following: all muscles of the posterior compartment of the arm. The radial nerve is a peripheral nerve supplying specific parts of the arm, forearm, wrist, and hand (see image. posterior upper extremity nerves). this nerve has both motor and sensory functions. the motor branches stimulate the posterior arm muscles, posterior forearm muscles, and extrinsic wrist and hand extensors. the sensory branches supply the skin on the anterolateral arm, distal.

The Radial Nerve Course Motor Sensory Teachmeanatomy 46 Off The radial nerve is the second terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, that contains fibers of spinal nerves c5 t1. this nerve is a mixed nerve that provides motor and sensory innervation to the arm and forearm. the radial nerve provides motor supply to the following: all muscles of the posterior compartment of the arm. The radial nerve is a peripheral nerve supplying specific parts of the arm, forearm, wrist, and hand (see image. posterior upper extremity nerves). this nerve has both motor and sensory functions. the motor branches stimulate the posterior arm muscles, posterior forearm muscles, and extrinsic wrist and hand extensors. the sensory branches supply the skin on the anterolateral arm, distal.

Comments are closed.