The Theory Of Consumer Behavior Accounts For Time

Ppt The Theory Of Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Free The theory of consumer behavior accounts for time a. because time can be used to earn money. b. because time is free. c. differently than it accounts for other resources. d. without consideration for the value of time. b. consider the following comment: "want to make millions of dollars? invent a product that saves americans lots of time. Abstract. the chapter focuses on the relationship between time perspective and economy and consists of three parts: i. the first reviews the history of conceptual and empirical research in time and economy, a special attention is paid to the classic marshmallow test (mischel et al.) and to the work of zimbardo and boyd. ii.

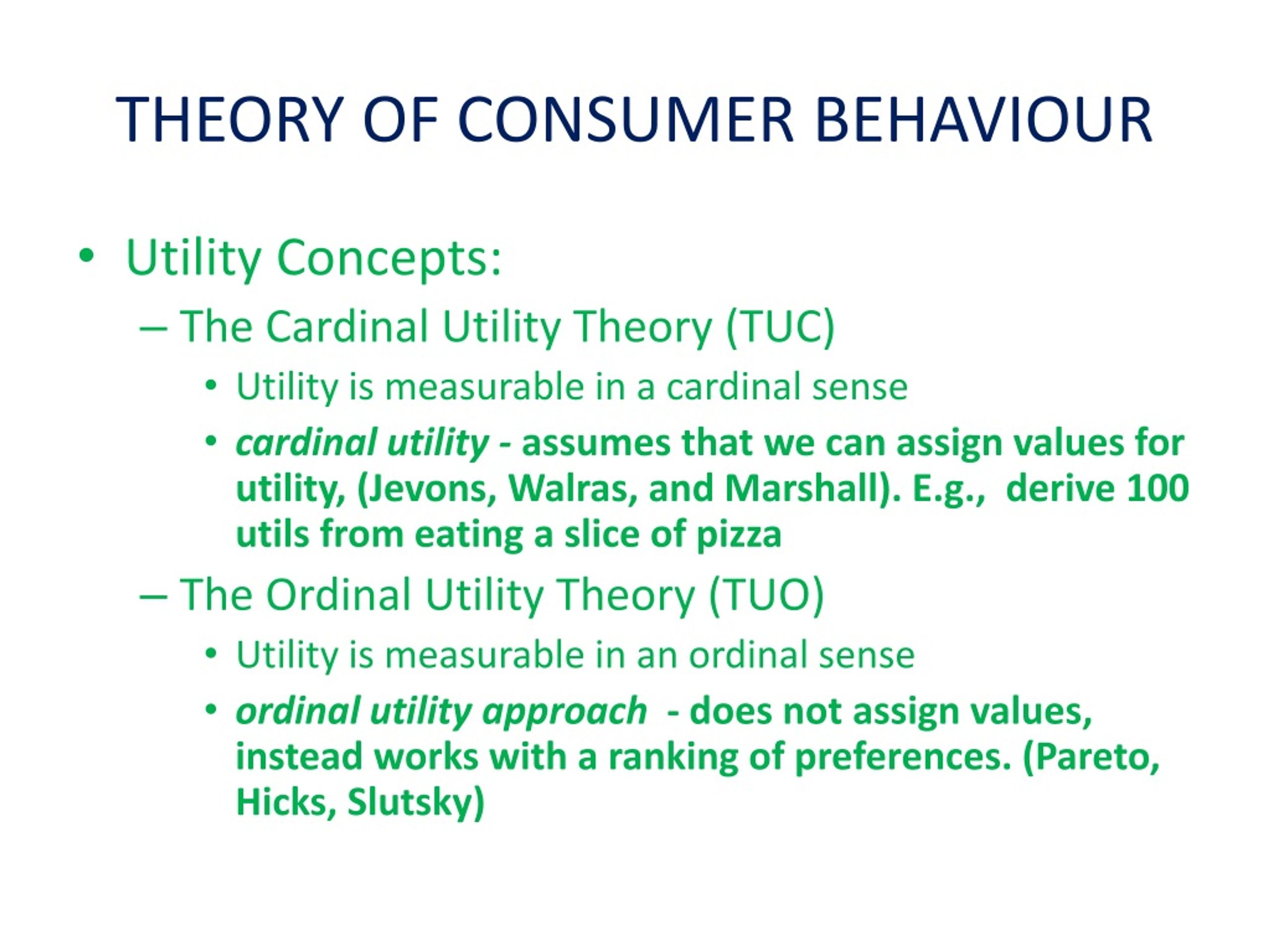
Ppt The Theory Of Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Free On the new theory of consumer behavior 381 havioral decisions involving choices made with limited resources among com peting ends a common definition of economics have been avoided. deci sions about the allocation of a consumer's nonmarket time and decisions about his choice of a religion, a marriage mate, a family size, a divorce, a political. Our objective is to stimulate much needed conceptual and empirical attention regarding the relationships between time and consumer behavior. the approach adopted here is to review what has been published on the subject in the fields of economics, sociology, home economics, psychology, and marketing and to advance a rudimentary terminology. Hornik j (1984) subjective vs. objective time measures: a note on the perception of time in consumer behavior. journal of consumer research 11(1): 615–618. crossref. The theory of consumer behaviour built on both the cardinal and o rdinal approach is attributed to modern economists such as alfred marshal, j. r. hicks and r. g. allen 8 . the cardinal utility.

Ppt Chapter 6 Theory Of Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Hornik j (1984) subjective vs. objective time measures: a note on the perception of time in consumer behavior. journal of consumer research 11(1): 615–618. crossref. The theory of consumer behaviour built on both the cardinal and o rdinal approach is attributed to modern economists such as alfred marshal, j. r. hicks and r. g. allen 8 . the cardinal utility. Abstract. psychological time is one of the most important dimensions for understanding human behaviour. short durations, in particular, have a special role in everyday life and their perception is a factor which explains important aspects of behaviour. these arguments are demonstrated in this article via one of the most important domains of. 1991. lea, tarpy & webley. the model considers that: (1) economic behaviour is subjected to a twofold causation, which means certain types of economic behaviour determine the course of affairs in this matter. at the same time, the economy, as a social reality, exerts a major influence in human behaviour.

Ppt Theory Of Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Free Abstract. psychological time is one of the most important dimensions for understanding human behaviour. short durations, in particular, have a special role in everyday life and their perception is a factor which explains important aspects of behaviour. these arguments are demonstrated in this article via one of the most important domains of. 1991. lea, tarpy & webley. the model considers that: (1) economic behaviour is subjected to a twofold causation, which means certain types of economic behaviour determine the course of affairs in this matter. at the same time, the economy, as a social reality, exerts a major influence in human behaviour.
Ppt Theory Of Consumer Behaviour Powerpoint Presentation Free

Comments are closed.