Trajectories Of Projectiles Launched At Different Elevation Angles But

Trajectories Of Projectiles Launched At Different Elevation Angles But Trajectories of projectiles launched at different elevation angles but the same speed of 10 m s in a vacuum and uniform downward gravity field of 10 m s 2. points are at 0.05 s intervals and length of their tails is linearly proportional to their speed. Projectile trajectories: the launch angle determines the range and maximum height that an object will experience after being launched.this image shows that path of the same object being launched at the same speed but different angles.

Projectile Motion Boundless Physics Note from figure 4.16 that if the two projectiles were launched at the same speed but at different angles, the projectiles would have the same range as long as the angles were less than 90 °. 90 °. the launch angles in this example add to give a number greater than 90 ° . 90 ° . Trajectories of projectiles launched at different elevation angles but at the same speed (g = 10 m s²). attribution: cmglee , cc by sa 3.0 , via wikimedia commons. did you find out when distance is maximal?. [ latex] the projectile launched with the smaller angle has a lower apex than the higher angle, but they both have the same range. figure 4.15 trajectories of projectiles on level ground. (a) the greater the initial speed [latex] {v} {0}, [ latex] the greater the range for a given initial angle. The initial speed for the shot at [latex]70^\circ[ latex] is greater than the initial speed of the shot at [latex]30^\circ.[ latex] note from figure that two projectiles launched at the same speed but at different angles have the same range if the launch angles add to [latex]90^\circ.[ latex] the launch angles in this example add to give a.
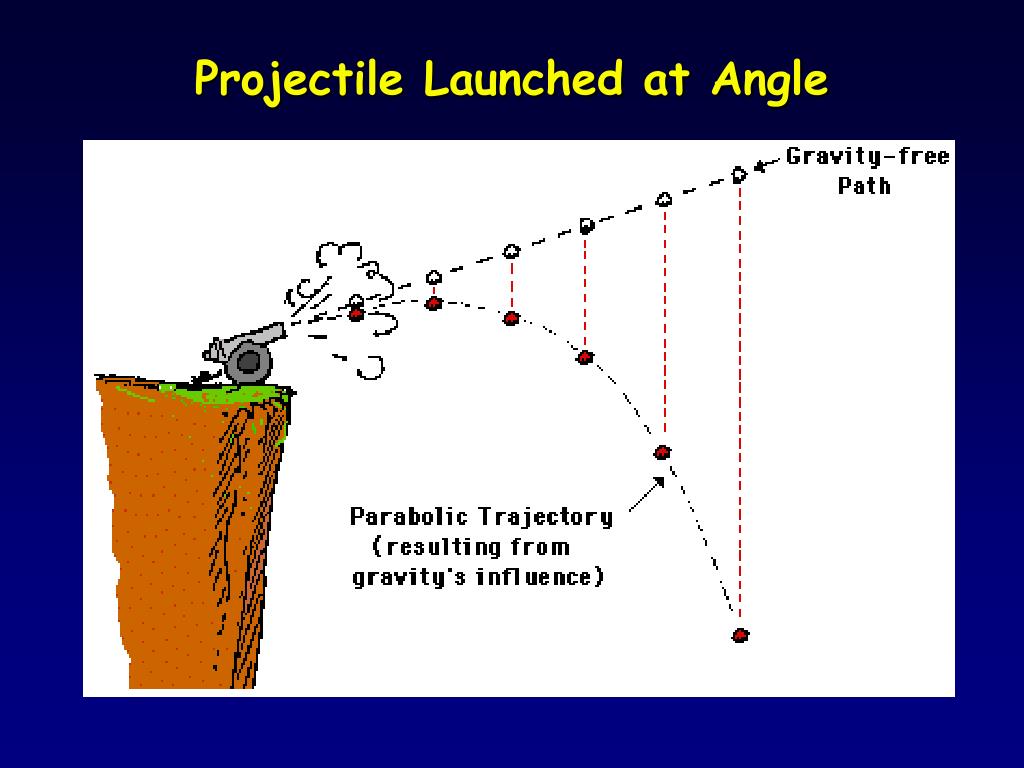
Ppt Projectile Motion Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 341073 [ latex] the projectile launched with the smaller angle has a lower apex than the higher angle, but they both have the same range. figure 4.15 trajectories of projectiles on level ground. (a) the greater the initial speed [latex] {v} {0}, [ latex] the greater the range for a given initial angle. The initial speed for the shot at [latex]70^\circ[ latex] is greater than the initial speed of the shot at [latex]30^\circ.[ latex] note from figure that two projectiles launched at the same speed but at different angles have the same range if the launch angles add to [latex]90^\circ.[ latex] the launch angles in this example add to give a. This is the time of flight for a projectile both launched and impacting on a flat horizontal surface. equation \ref{4.24} does not apply when the projectile lands at a different elevation than it was launched, as we saw in example 4.8 of the tennis player hitting the ball into the stands. the other solution, t = 0, corresponds to the time at. The most important concept in projectile motion is that when air resistance is ignored, horizontal and vertical motions are independent, meaning that they don’t influence one another. figure 5.27 compares a cannonball in free fall (in blue) to a cannonball launched horizontally in projectile motion (in red). you can see that the cannonball in.

Projectiles Moving Along Its Trajectories With Different Launch Angles This is the time of flight for a projectile both launched and impacting on a flat horizontal surface. equation \ref{4.24} does not apply when the projectile lands at a different elevation than it was launched, as we saw in example 4.8 of the tennis player hitting the ball into the stands. the other solution, t = 0, corresponds to the time at. The most important concept in projectile motion is that when air resistance is ignored, horizontal and vertical motions are independent, meaning that they don’t influence one another. figure 5.27 compares a cannonball in free fall (in blue) to a cannonball launched horizontally in projectile motion (in red). you can see that the cannonball in.

4 3 Projectile Motion University Physics Volume 1

Projectiles Launched At An Angle

Comments are closed.