Trophic Level Chart
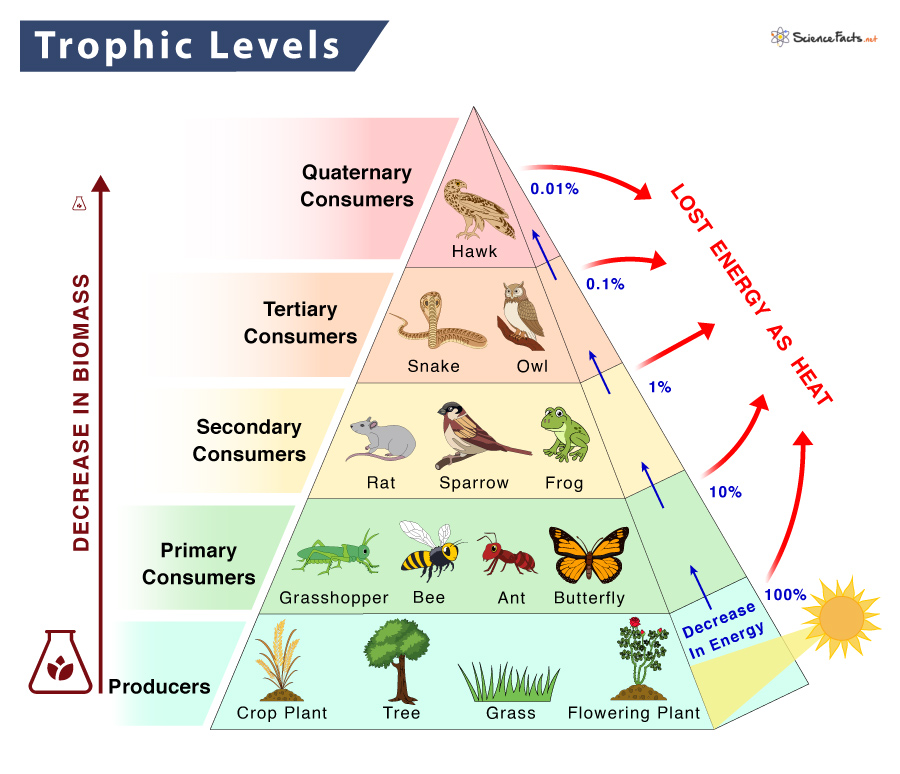
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram Learn what trophic level means and how it relates to the position of organisms in the food chain. see the five trophic levels with examples and a diagram of energy and biomass pyramids. Learn what trophic level is and how it relates to the food chain and energy flow in ecosystems. find out the five main trophic levels and their characteristics, with examples of organisms and diagrams.

Trophic Level Definition Examples Facts Britannica The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. within a food web, a food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. the trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it is from the start of the chain. a food web starts at trophic level 1 with primary. Trophic level, any step in a nutritive series, or food chain, of an ecosystem. organisms are classified into levels on the basis of their feeding behavior. the lowest level contains the producers, green plants, which are consumed by second level organisms, herbivores, which, in turn, are consumed by carnivores. Trophic levels. the feeding positions in a food chain or web are called trophic levels. the different trophic levels are defined in the table below. examples are also given in the table. all food chains and webs have at least two or three trophic levels. generally, there are a maximum of four trophic levels. A trophic level refers to a level or a position in a food chain, a food web, or an ecological pyramid. it is occupied by a group of organisms that have a similar feeding mode. in an ecological pyramid, the various trophic levels are primary producers (at the base), consumers (primary, secondary, tertiary, etc.), and predators (apex).
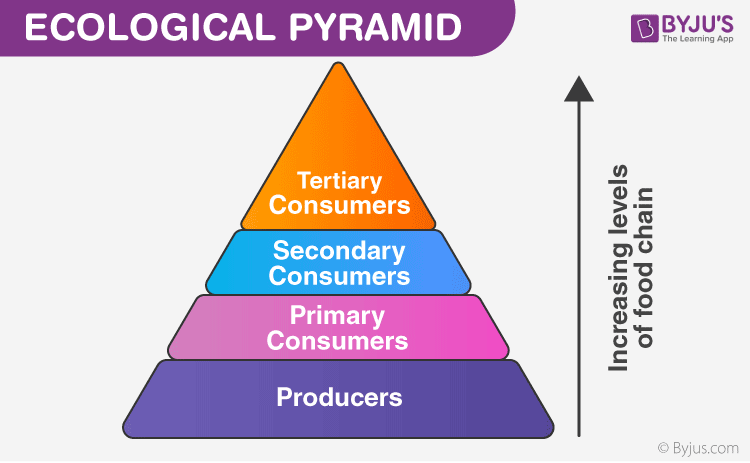
Trophic Level Diagram Ecological Pyramids Trophic levels. the feeding positions in a food chain or web are called trophic levels. the different trophic levels are defined in the table below. examples are also given in the table. all food chains and webs have at least two or three trophic levels. generally, there are a maximum of four trophic levels. A trophic level refers to a level or a position in a food chain, a food web, or an ecological pyramid. it is occupied by a group of organisms that have a similar feeding mode. in an ecological pyramid, the various trophic levels are primary producers (at the base), consumers (primary, secondary, tertiary, etc.), and predators (apex). Trophic level is the position within a food chain that is occupied by a group of organisms in an ecosystem. the classification of organisms into the different food chains is based on their feeding behavior. trophic level is a step in the nutritive series of food chains which in some cases might form a complicated path called a food web. Trophic levels are distinct stages in the food chain of an ecosystem, representing the flow of energy from one group of organisms to another. starting from the primary producers at the base, moving up to consumers, and culminating with apex predators, each level plays a pivotal role in the ecosystem’s health and functionality.
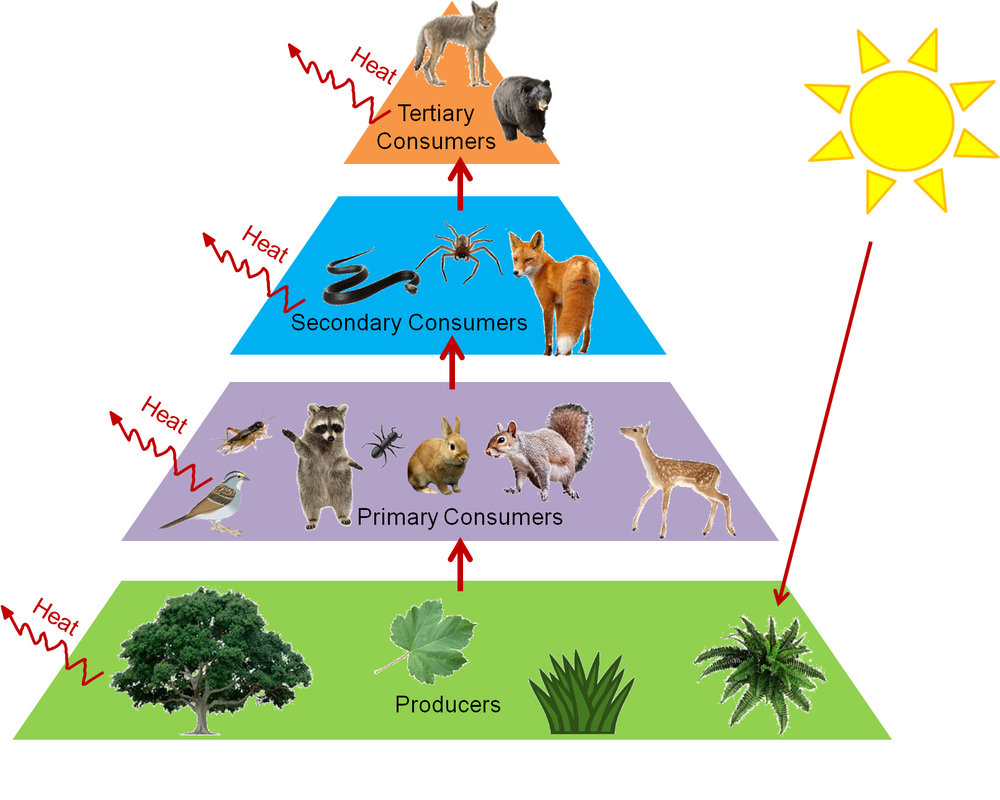
Trophic Levels And Ecological Pyramids Online Science Notes Trophic level is the position within a food chain that is occupied by a group of organisms in an ecosystem. the classification of organisms into the different food chains is based on their feeding behavior. trophic level is a step in the nutritive series of food chains which in some cases might form a complicated path called a food web. Trophic levels are distinct stages in the food chain of an ecosystem, representing the flow of energy from one group of organisms to another. starting from the primary producers at the base, moving up to consumers, and culminating with apex predators, each level plays a pivotal role in the ecosystem’s health and functionality.

Comments are closed.