Trophic Levels Study Guide Inspirit
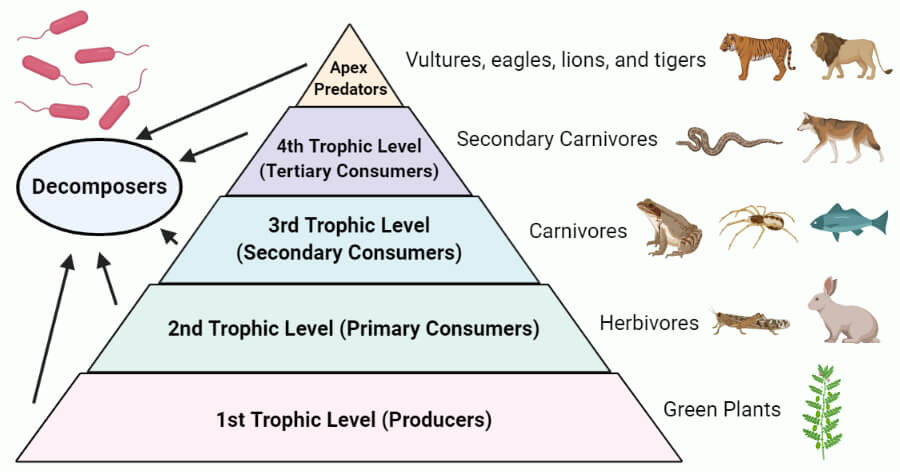
Trophic Levels Study Guide Inspirit Trophic levels comprise the nutritive arrangement or food chain of the ecosystem. here, the organisms are ranked based on their food requirements. 1. first trophic level: autotrophs. the first level consists of green algae and plants (the producers), also known as autotrophs. they utilize solar energy through photosynthesis and don’t depend. Introduction: the plants absorb as little as 1% of the emitted sunlight from the sun, convert it into a form of energy sufficient to power and support life on the earth. this occurs in a sequence of nutrient flow cycles amongst the living and nonliving components of the ecosystem. this guide helps to understand the energy flow in an ecosystem.
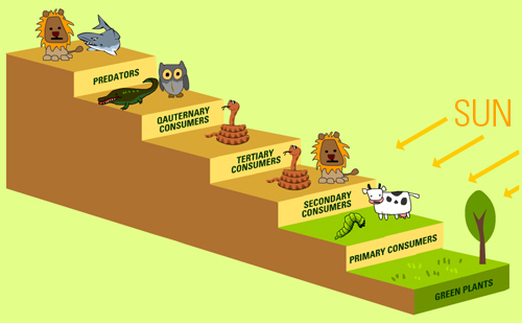
Trophic Levels Study Guide Inspirit Trophic levels study guide by inspirit learning inc. march 28, 2023 check out awesome, educational vr rooms on inspirit’s mobile app (available for ios and android devices) 🤩 introduction trophic levels make up the different steps in the food chain in an ecosystem, where one organism feeds on the other for survival. Trophic levels make up the different steps in the food chain in an ecosystem, illustrating the feeding behavior of different groups of organisms. organisms are ranked based on their food requirements in the nutritive arrangement or food chain of the ecosystem. different trophic levels. first trophic level: autotrophs; second trophic level. Trophic levels represent the levels of organisms in an ecosystem based on their feeding relationships. tertiary consumers are carnivores that feed on secondary consumers, forming the top of the food chain. example: bald eagles are tertiary consumers that primarily feed on fish, making them an example of this trophic level. energy moves through. Herbivores primarily eat plants and plant products, placing them in the trophic level of primary consumers. energy transfer and food chains. energy pyramid: represents the transfer of energy between trophic levels, with approximately 10% of energy transferred between each level.
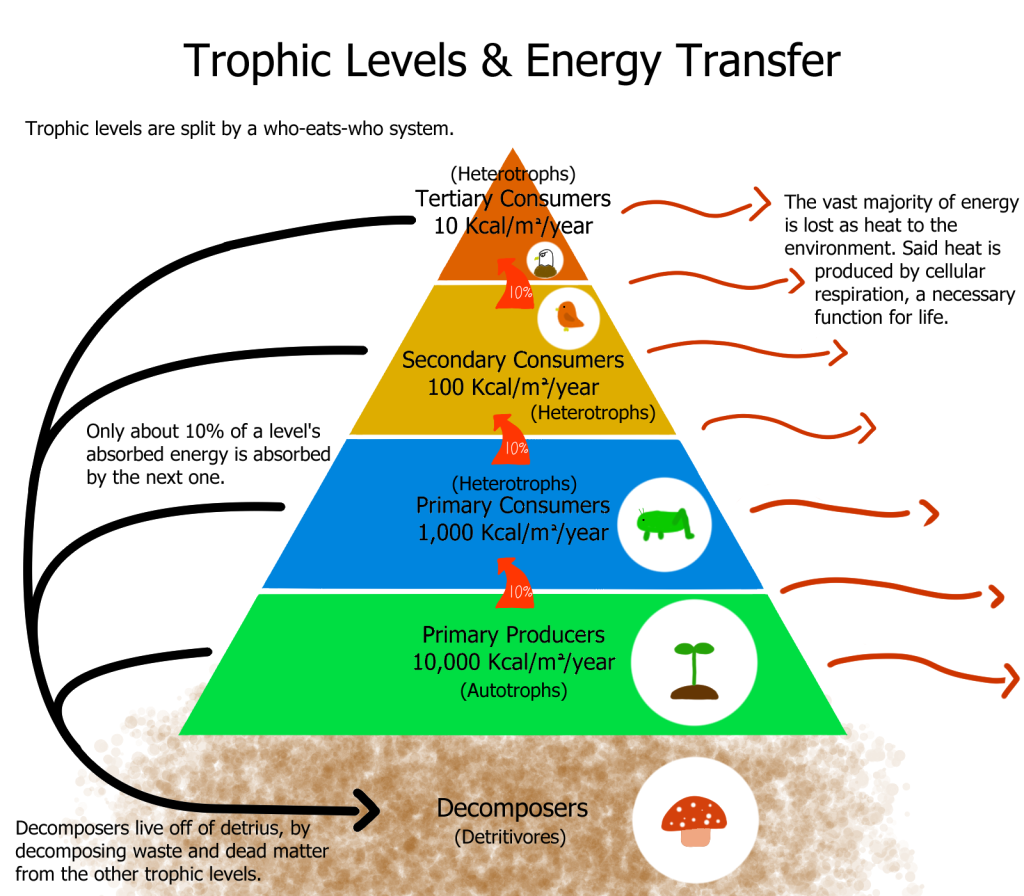
Energy Flow Study Guide Inspirit Trophic levels represent the levels of organisms in an ecosystem based on their feeding relationships. tertiary consumers are carnivores that feed on secondary consumers, forming the top of the food chain. example: bald eagles are tertiary consumers that primarily feed on fish, making them an example of this trophic level. energy moves through. Herbivores primarily eat plants and plant products, placing them in the trophic level of primary consumers. energy transfer and food chains. energy pyramid: represents the transfer of energy between trophic levels, with approximately 10% of energy transferred between each level. Energy flow study guide energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. all living organisms can be organized into producers and consumers, and those producers and consumers can further be organized into a food chain. As we move from the first trophic level to the last, we lose energy. approximately 10% of the energy is passed on from one trophic level to the next. for example, if there are 10,000,000 calories of phytoplankton in the first trophic level, only 1,000,000 calories will be passed on to the second trophic level. food webs.

Trophic Levels In An Ecosystem Study Guide Biology Unit 12 Tpt Energy flow study guide energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. all living organisms can be organized into producers and consumers, and those producers and consumers can further be organized into a food chain. As we move from the first trophic level to the last, we lose energy. approximately 10% of the energy is passed on from one trophic level to the next. for example, if there are 10,000,000 calories of phytoplankton in the first trophic level, only 1,000,000 calories will be passed on to the second trophic level. food webs.

Comments are closed.