Tundra Food Chain Examples And Diagram 40 Off

Tundra Food Chain Examples And Diagram 40 Off In tundra, the primary consumers are herbivores. they eat plants such as lemmings, musk ox, reindeer, squirrels, voles, and arctic hares. mosquitoes, flies, moths, grasshoppers, arctic bumble bees, other insects, and birds such as ravens, falcons, and gulls are also found in this trophic level. primary consumers reside in the second food chain. The middle of alpine tundra food chains are predominantly made up of grass eaters in one form or another. they include alpacas, llamas, mountain goats, sheep, elk, grouse, chinchillas, and pikas. this is not even close to a full count of the animals one would find at the tip top of mountains.
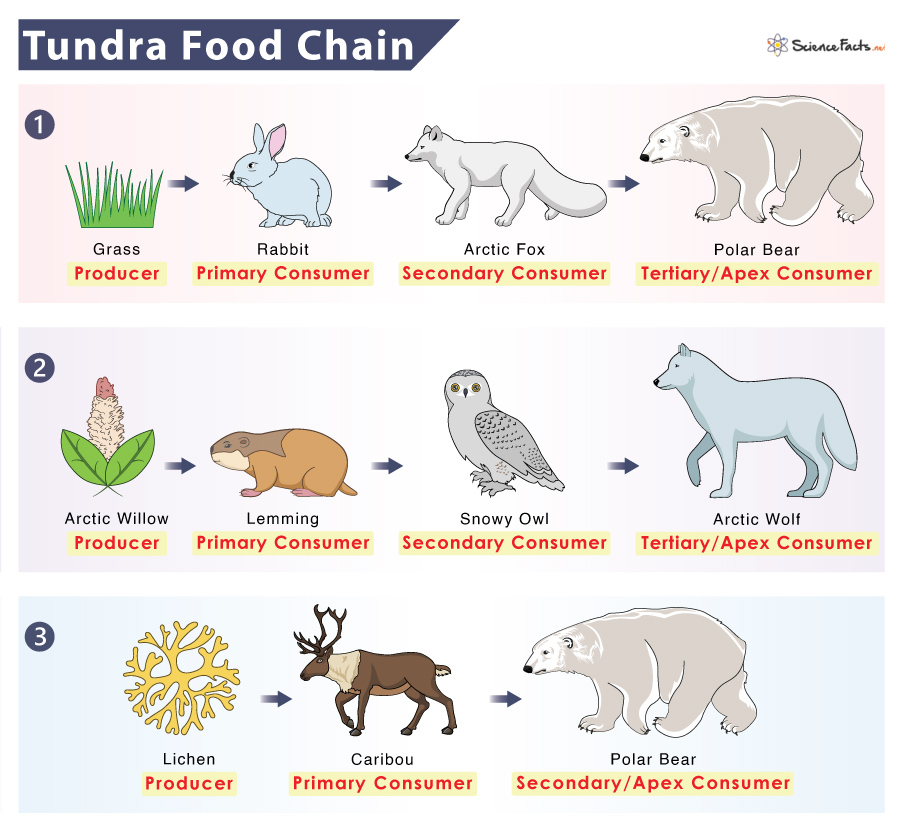
Tundra Food Chain Examples And Diagram Food chains are a conceptual description of energy flow in any ecosystem. most ecosystems are supported by primary production. the primary producers are vascular plants and algae that produce organic material from inorganic materials like nutrients, atmospheric gases, and water. the energy that fuels this process comes from the sun. The tundra biome is characterized by a cold, dry climate. the plants and animals in tundra ecosystems form communities based on the transfer of energy between organisms. a food chain shows how energy is transferred from one living thing to another. food chains intersect to form food webs. The example below shows the energy flow in a basic food chain in the tundra. this food chain is part of a more complex food web involving producers and consumers (herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores). producers here include grasses, lichens, and caribou moss. herbivores that eat these plants include the musk ox, arctic hare, and lemmings. Learn about the tundra food web, also known as the tundra food chain. discover the producers and consumers in the tundra ecosystem and how they survive. updated: 11 21 2023.
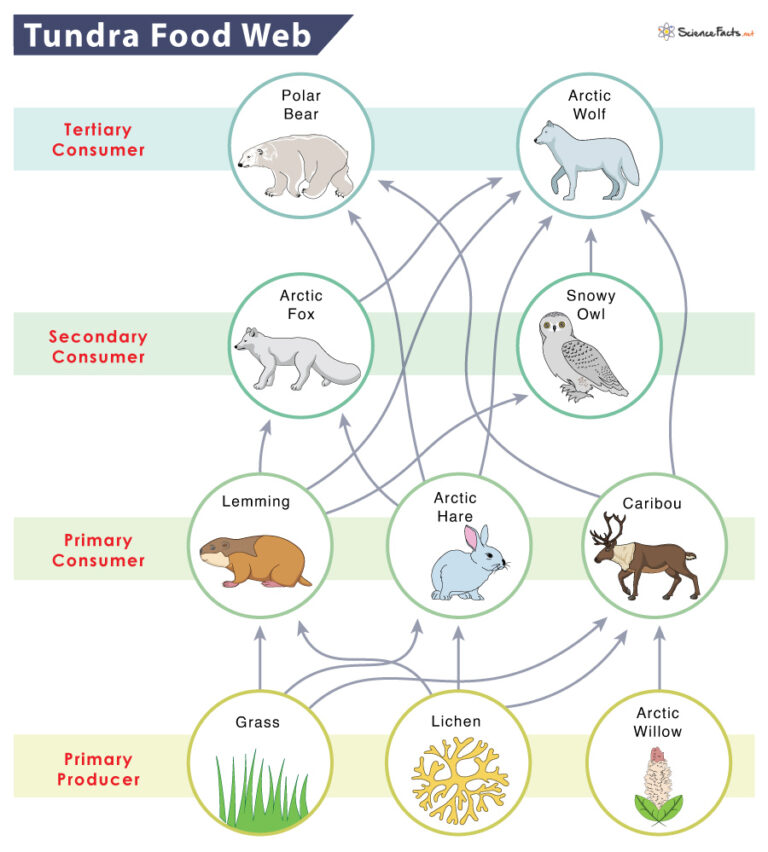
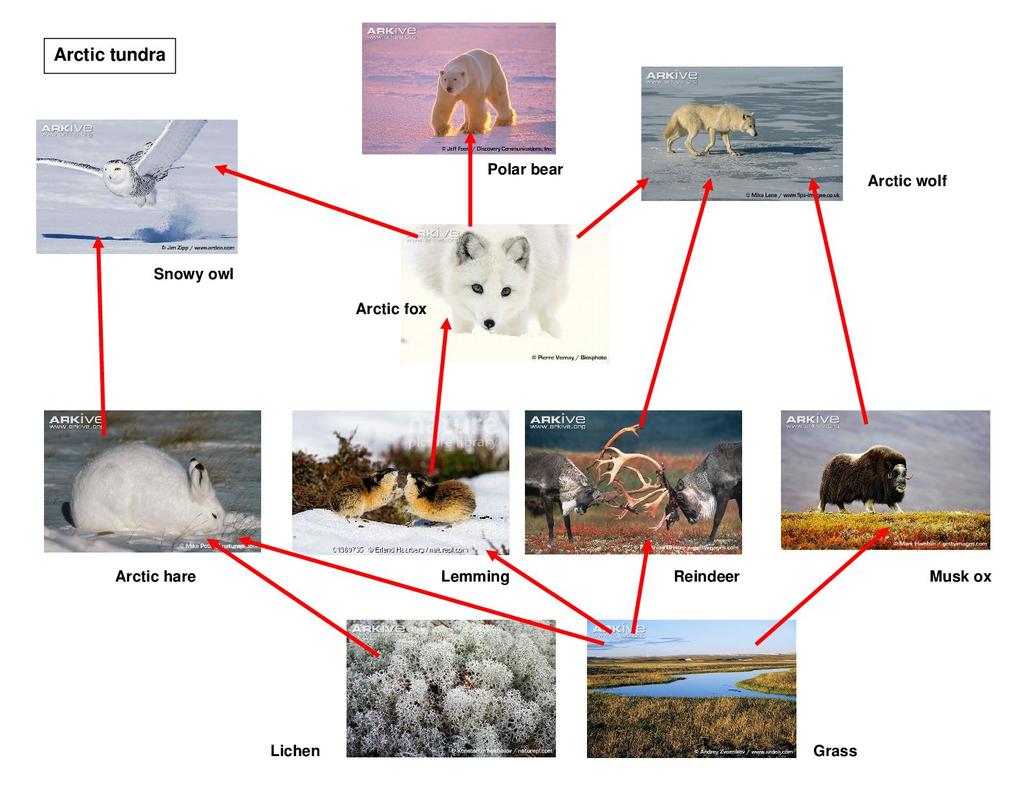
Tundra Food Chain Examples And Diagram The example below shows the energy flow in a basic food chain in the tundra. this food chain is part of a more complex food web involving producers and consumers (herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores). producers here include grasses, lichens, and caribou moss. herbivores that eat these plants include the musk ox, arctic hare, and lemmings. Learn about the tundra food web, also known as the tundra food chain. discover the producers and consumers in the tundra ecosystem and how they survive. updated: 11 21 2023. Producer’s role. food chains basically facilitate the flow of energy from one trophic level to another. in any given food chain, plants (and some species of bacteria) play the role of producers, who harness the sun’s energy and use it to prepare their own food. with deep rooted plants virtually absent, the role of producers is played by. Top consumers are petrels – seabirds and killer whales, which will use almost any other tundra animal as food. decomposers on the land include bacteria, fungi and worms, while some bacteria do their work in the oceans. mosses, algae, lichens and two species of flowering plants are producers on land.

Tundra Food Chain Examples And Diagram 40 Off Producer’s role. food chains basically facilitate the flow of energy from one trophic level to another. in any given food chain, plants (and some species of bacteria) play the role of producers, who harness the sun’s energy and use it to prepare their own food. with deep rooted plants virtually absent, the role of producers is played by. Top consumers are petrels – seabirds and killer whales, which will use almost any other tundra animal as food. decomposers on the land include bacteria, fungi and worms, while some bacteria do their work in the oceans. mosses, algae, lichens and two species of flowering plants are producers on land.
Tundra Food Chain Examples And Diagram 40 Off
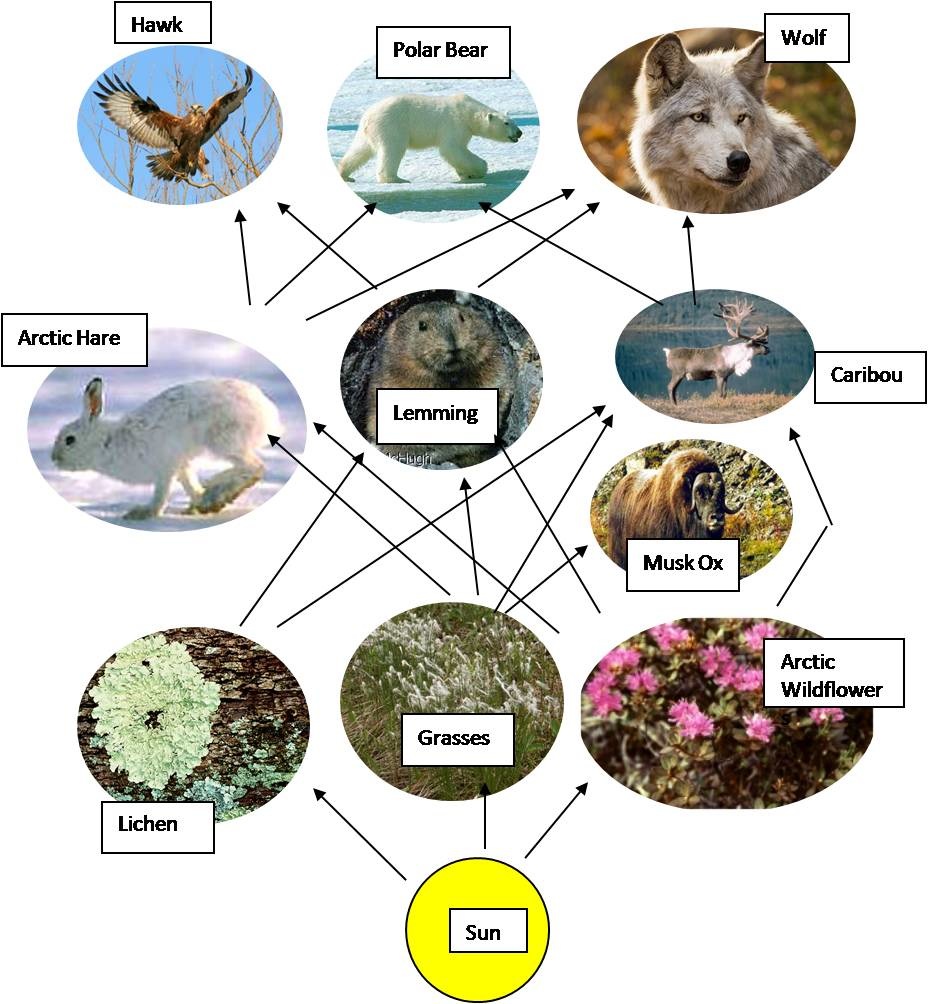
Food Web Tundra Biome

Comments are closed.