Types And Ecg Features Of Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt

Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis The term supraventricular tachycardia (svt) refers to any tachydysrhythmia arising from above the level of the bundle of his, and encompasses regular atrial, irregular atrial, and regular atrioventricular tachycardias. it is often used synonymously with av nodal re entry tachycardia (avnrt), a form of svt. in the absence of aberrant conduction. Introduction. supraventricular tachycardia (svt) is a dysrhythmia originating at or above the atrioventricular (av) node and is defined by a narrow complex (qrs < 120 milliseconds) at a rate > 100 beats per minute (bpm). atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (avnrt), also known as paroxysmal svt, is defined as intermittent svt without.
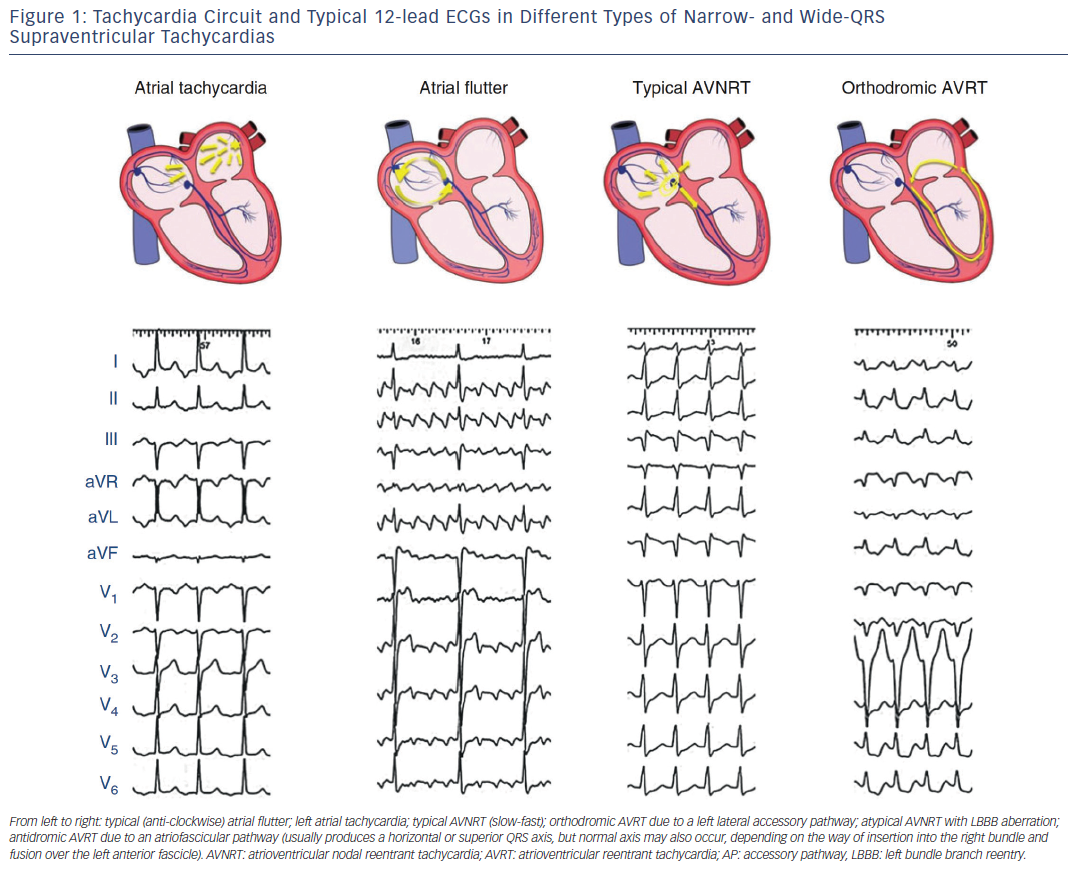
Figure 1 Tachycardia Circuit And Typical 12 Lead Ecgs In Different Types of supraventricular tachycardia margaret r. helton, md, ecg characteristics for the types of svt, 1. most of which have narrow qrs complexes (less than 0.12 seconds). Ia is the most common type of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. in this type, the standard conduction through the atrioventricular node pai. s with a fast retrograde conduction through the. The most common types of supraventricular tachycardia are caused by a reentry phenomenon producing acceler ated heart rates. symptoms may include palpitations (including possible pulsations in the. Basis of supraventricular tachycardia on a cellular basis, svt can either originate from non re entrant mechanisms, such as enhanced automaticity or triggered activity, or from re entry within myocardial tissue perturbing normal sinus rhythm.4 occasionally, sinus rhythm itself will be dysregulated and become tachycardic by.
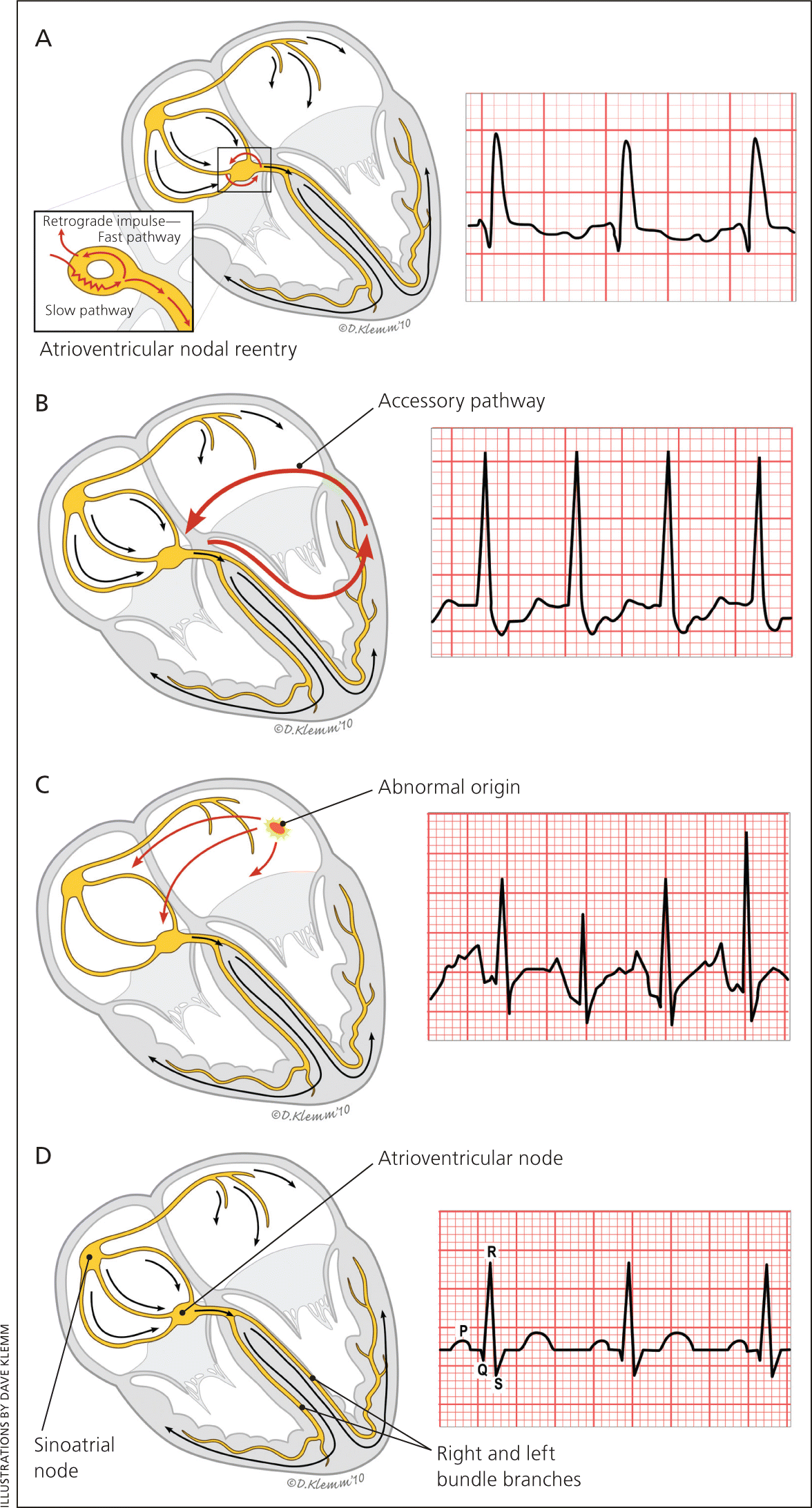
Supraventricular Tachycardia Types Cardiology Outlines The most common types of supraventricular tachycardia are caused by a reentry phenomenon producing acceler ated heart rates. symptoms may include palpitations (including possible pulsations in the. Basis of supraventricular tachycardia on a cellular basis, svt can either originate from non re entrant mechanisms, such as enhanced automaticity or triggered activity, or from re entry within myocardial tissue perturbing normal sinus rhythm.4 occasionally, sinus rhythm itself will be dysregulated and become tachycardic by. Supraventricular tachycardia comprises a group of conditions in which atrial or atrioventricular nodal tissues are essential for sustaining the arrhythmia. common symptoms include palpitations, chest pain, anxiety, light headedness, pounding in the neck, shortness of breath, and uncommonly syncope. they are produced either by disorders of. Supraventricular tachycardia (svt) includes all forms of tachycardia that either arise above the bifurcation of the bundle of his or that have mechanisms dependent on the bundle of his. we conducted a review of the techniques used to differentiate the mechanisms of svt. we searched the pubmed and medline databases for english language literature published from 1970 to 2008. articles were.

Ecg Educator Blog Atrial Rhythms Supraventricular tachycardia comprises a group of conditions in which atrial or atrioventricular nodal tissues are essential for sustaining the arrhythmia. common symptoms include palpitations, chest pain, anxiety, light headedness, pounding in the neck, shortness of breath, and uncommonly syncope. they are produced either by disorders of. Supraventricular tachycardia (svt) includes all forms of tachycardia that either arise above the bifurcation of the bundle of his or that have mechanisms dependent on the bundle of his. we conducted a review of the techniques used to differentiate the mechanisms of svt. we searched the pubmed and medline databases for english language literature published from 1970 to 2008. articles were.

Electrocardiogram Show Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt Pattern Stock

Ecg Educator Blog Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt

Comments are closed.