Types Of Consumers In Economics

Types Of Consumers Who Buys And When Consumers are the basic economic entities of an economy. all the consumers consume goods and services directly and indirectly to maximise satisfaction and utility. consumers have limited income and by which they want to satisfy their maximum utility (utility is the want satisfying capacity of a commodity). generally, consumer means an individual only; however, consumers will consist of a. 1. one that consumes, especially one that acquires goods or services for direct use or ownership rather than for resale or use in production and manufacturing. consumer protection, from the concise encyclopedia of economics: when you buy a good or service, you rarely have perfect knowledge of its quality and safety.

Ppt Economics Key Terms Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id Consumer theory is the study of how people decide to spend their money based on their individual preferences and budget constraints. building a better understanding of individuals’ tastes and. Consumer good, in economics, any tangible commodity produced and subsequently purchased to satisfy the current wants and perceived needs of the buyer. consumer goods are divided into three categories: durable goods, nondurable goods, and services. consumer durable goods have a significant life span, often three years or more (although some. (see consumer good.) neoclassical (mainstream) economists generally consider consumption to be the final purpose of economic activity, and thus the level of consumption per person is viewed as a central measure of an economy’s productive success. the study of consumption behaviour plays a central role in both macroeconomics and microeconomics. In almost all cases, consumer choices are driven by prices. as price goes up, the quantity that consumers demand goes down. this correlation between the price of goods and the willingness to make purchases is represented clearly by the generation of a demand curve (with price as the y axis and quantity as the x axis).
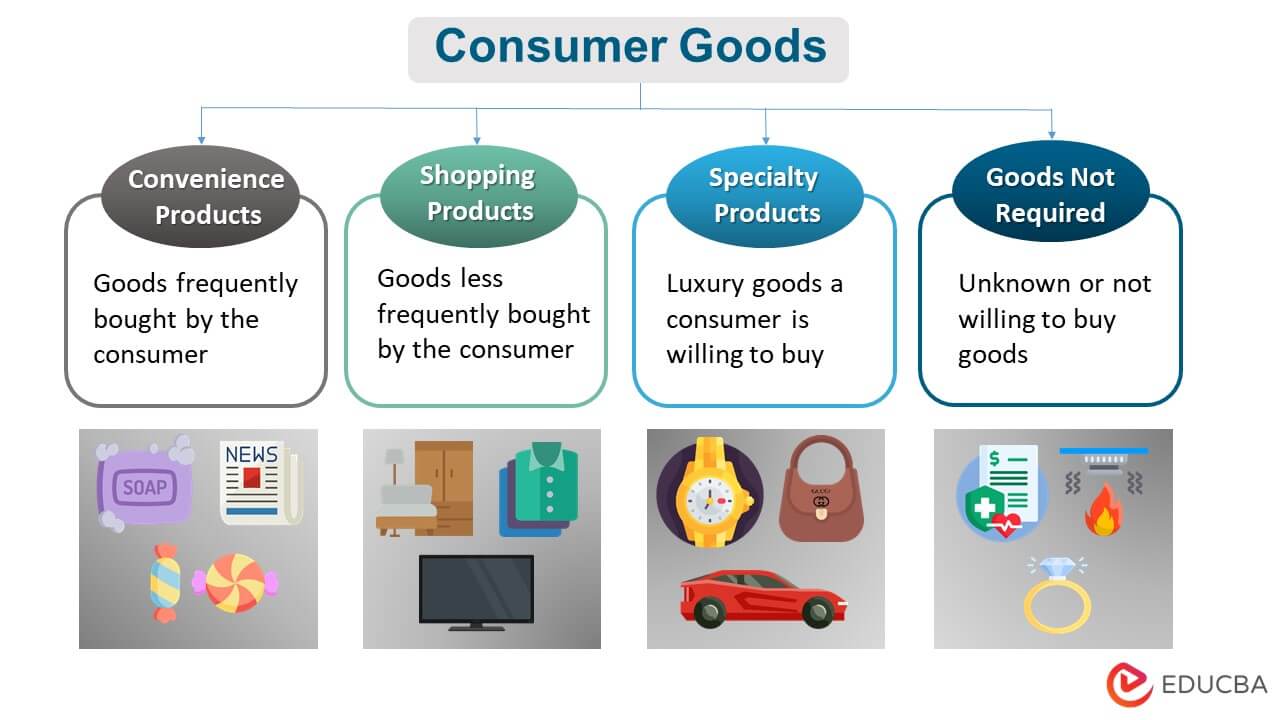
Consumer Goods Meaning Types Examples Benefits (see consumer good.) neoclassical (mainstream) economists generally consider consumption to be the final purpose of economic activity, and thus the level of consumption per person is viewed as a central measure of an economy’s productive success. the study of consumption behaviour plays a central role in both macroeconomics and microeconomics. In almost all cases, consumer choices are driven by prices. as price goes up, the quantity that consumers demand goes down. this correlation between the price of goods and the willingness to make purchases is represented clearly by the generation of a demand curve (with price as the y axis and quantity as the x axis). The theory of consumer choice assumes consumers wish to maximise their utility through the optimal combination of goods given their limited budget. to illustrate how consumers choose between different combinations of goods we can use equi marginal principle and indifference curves and budget lines. consumer equilibrium equimarginal. Economics; consumer goods: meaning, types, and examples. by. the investopedia team. full bio. investopedia contributors come from a range of backgrounds, and over 25 years there have been.
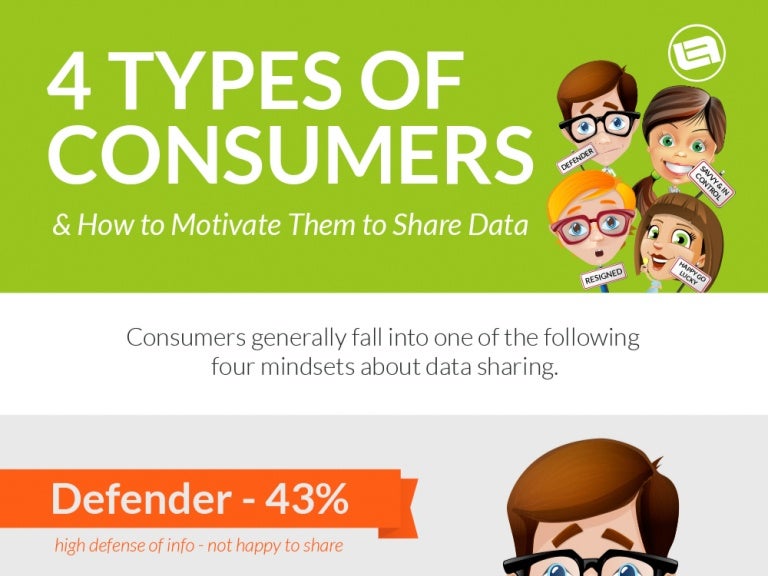
4 Types Of Consumers How To Motivate Them To Share Data Infographi The theory of consumer choice assumes consumers wish to maximise their utility through the optimal combination of goods given their limited budget. to illustrate how consumers choose between different combinations of goods we can use equi marginal principle and indifference curves and budget lines. consumer equilibrium equimarginal. Economics; consumer goods: meaning, types, and examples. by. the investopedia team. full bio. investopedia contributors come from a range of backgrounds, and over 25 years there have been.

Comments are closed.