Types Of Data Cross Sectional Time Series And Panel Data Data

Types Of Data Cross Sectional Time Series And Panel Data Data Definition. cross sectional data refers to data collected at a single point in time from multiple individuals, groups, or companies. this type of data provides a snapshot of a population at a specific moment. on the other hand, panel data, also known as longitudinal data, involves collecting data from the same individuals, groups, or companies. Based on the collection method, data can be divided into cross section, time series, and panel data. a good understanding of the differences between the three types and how to collect the three types of data will lead to the right choice of analysis.

Time Series Vs Cross Sectional Data Infographics Handout #17 on two year and multi year panel data 1 the basics of panel data we’ve now covered three types of data: cross section, pooled cross section, and panel (also called longitudi nal). in a panel data set we track the unit of observation over time; this could be a state, city, individual, rm, etc to help you visualize these types of. Panel data allows for the analysis of both cross sectional and time series variations, controlling for unobserved heterogeneity and capturing dynamic relationships. on the other hand, time series data focuses on the analysis of a single entity over time, exploiting temporal dependence and identifying seasonality. Time series data is data collected at regular intervals over time. on the other hand, cross sectional data is a snapshot of a group of things or people at the same point in time. for example, a time series dataset of the number of cars sold each month over the course of 5 years consists of 60 data points (one for each month). In conclusion, both cross sectional data and time series data offer valuable insights into different aspects of a phenomenon. cross sectional data provides a snapshot of a population or sample at a specific point in time, allowing for comparisons and analysis of different groups. on the other hand, time series data captures the evolution of a.
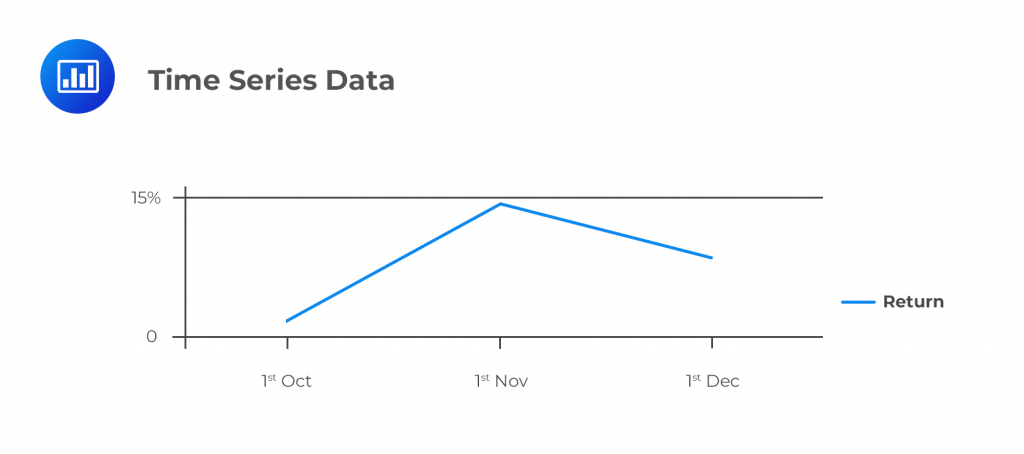
Time Series Cross Sectional Data Examples Cfa Level 1 Analystprep Time series data is data collected at regular intervals over time. on the other hand, cross sectional data is a snapshot of a group of things or people at the same point in time. for example, a time series dataset of the number of cars sold each month over the course of 5 years consists of 60 data points (one for each month). In conclusion, both cross sectional data and time series data offer valuable insights into different aspects of a phenomenon. cross sectional data provides a snapshot of a population or sample at a specific point in time, allowing for comparisons and analysis of different groups. on the other hand, time series data captures the evolution of a. Panel data is usually called as cross sectional time series data as it is a combination of the above mentioned types (i.e., collection of observations for multiple subjects at multiple instances). panel data or longitudinal data is multi dimensional data involving measurements over time. Cross sectional data differs from time series data, in which the same small scale or aggregate entity is observed at various points in time. another type of data, panel data (or longitudinal data ), combines both cross sectional and time series data aspects and looks at how the subjects (firms, individuals, etc.) change over a time series.

Difference Between Time Series Panel Cross Sectional Data Ppt Panel data is usually called as cross sectional time series data as it is a combination of the above mentioned types (i.e., collection of observations for multiple subjects at multiple instances). panel data or longitudinal data is multi dimensional data involving measurements over time. Cross sectional data differs from time series data, in which the same small scale or aggregate entity is observed at various points in time. another type of data, panel data (or longitudinal data ), combines both cross sectional and time series data aspects and looks at how the subjects (firms, individuals, etc.) change over a time series.
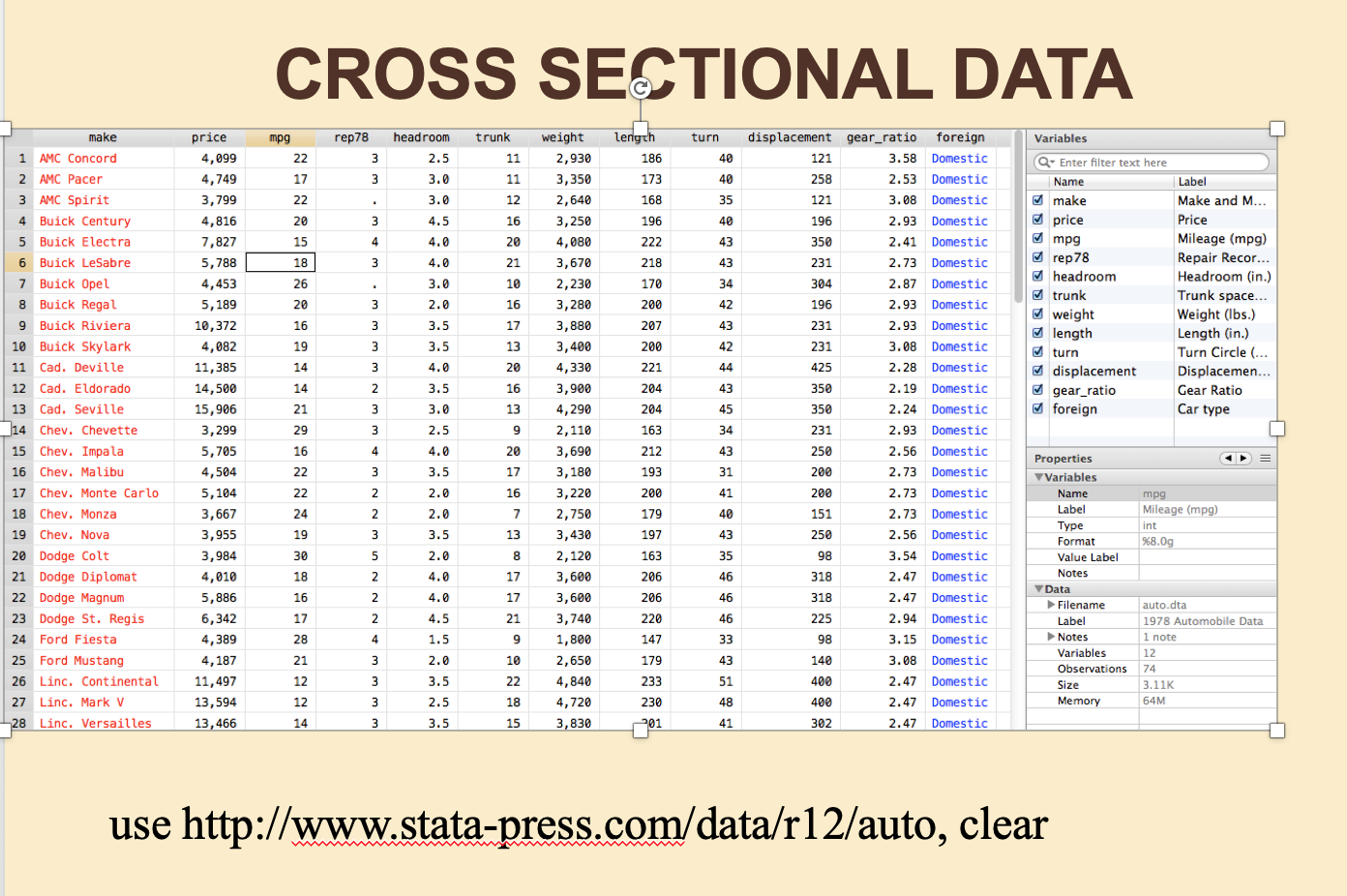
7 Data Please Researching And Writing For Economics Students

Panel Data Schematic A Cross Sectional Data B Time Series Data

Comments are closed.