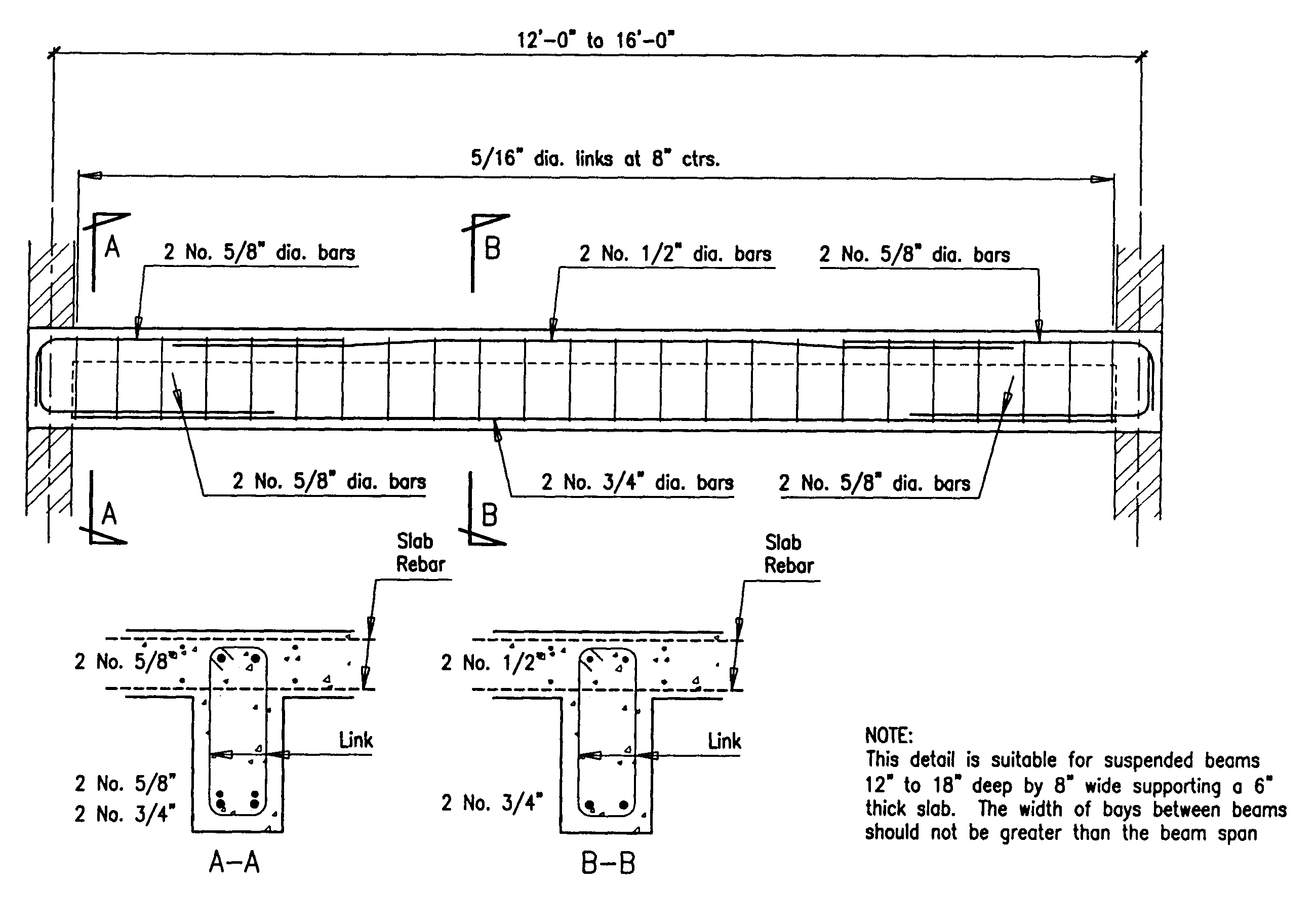
Typical Reinforcement Details Of Perimeter Beams Reinforced Concrete

Typical Reinforcement Details Of Perimeter Beams Reinforced Concrete 92)details and detailing199. the rights of. crete industry are stated more clearly by providing. specifications for . 315 highway bridges,” pg. (in.) for standard end hooks on grade 60 bars in. (in.) for standard end hooks on grade 60 bars in. 1.3 engineering drawings buildings and other struc . Clearly, the detailing of the reinforced concrete members is the key to good design and execution of work at the site.that is why poor detailing of reinforcement makes the structure undergo cracking, excessive deflection, or even collapse. reinforcements resist tensile forces. they may also be required in the compression zones to increase the.
Building Guidelines Drawings Section B Concrete Construction The east (section 5 5) and north (section 3 3) walls are shown in cross section. the column footing and pier reinforcing bars are shown in schedules. in drawing wall elevations where footing steps occur, the detailer refers to the “typical stepped footing” detail on the structural drawing and footing elevations on the plan view. This edition of the reinforced concrete design handbook, sp 17m(14), is dedicated to the memory of daniel w. falconer and his many contributions to the concrete industry. he was managing director of engineering for the american concrete institute from 1998 until his death in july 2015. dan was instrumental in the reorganization of building code. Top bars of perimeter beams [7.13.2.2(a)] figure 3. structural integrity requirements for joist construction [7.13.2.1] figure 5. structural integrity requirements for bottom bars of perimeter beams [7.13.2.2(b)] in joist construction at least one bottom bar must be continuous or must be spliced with class a tension splice or mechanical or. The concrete in order to develop the yield stress. •an average design ultimate bond stress φfb is assumed at the interface between the concrete and the reinforcing bar (φ= 0.6). • φfb depends on ‐type and condition of reinforcing bar; strength and compaction of concrete; concrete cover;.

Typical Reinforcement Details Of Beam The Best Picture Of Beam Top bars of perimeter beams [7.13.2.2(a)] figure 3. structural integrity requirements for joist construction [7.13.2.1] figure 5. structural integrity requirements for bottom bars of perimeter beams [7.13.2.2(b)] in joist construction at least one bottom bar must be continuous or must be spliced with class a tension splice or mechanical or. The concrete in order to develop the yield stress. •an average design ultimate bond stress φfb is assumed at the interface between the concrete and the reinforcing bar (φ= 0.6). • φfb depends on ‐type and condition of reinforcing bar; strength and compaction of concrete; concrete cover;. Reinforcement details of concrete beams and slabs should specify clearly about cover to reinforcement, length of reinforcement, curtailment of reinforcement, number and diameter of reinforcement to be provided. for a simply supported beam and slab, the maximum bending moment occurs at the center of the span and shear force at a distance of d 2. 7. choose bars for as and determine spacing and cover, recheck h and weight. make final check of mn using final d, and check that mu ≤ mn. 8. check that . t 0.005 (if not, increase h and reduce as) 9. design shear reinforcement (stirrups) 10.check deflection, crack control, steel development length.

Categories Of Concrete Beam And Their Reinforcement Details Reinforcement details of concrete beams and slabs should specify clearly about cover to reinforcement, length of reinforcement, curtailment of reinforcement, number and diameter of reinforcement to be provided. for a simply supported beam and slab, the maximum bending moment occurs at the center of the span and shear force at a distance of d 2. 7. choose bars for as and determine spacing and cover, recheck h and weight. make final check of mn using final d, and check that mu ≤ mn. 8. check that . t 0.005 (if not, increase h and reduce as) 9. design shear reinforcement (stirrups) 10.check deflection, crack control, steel development length.
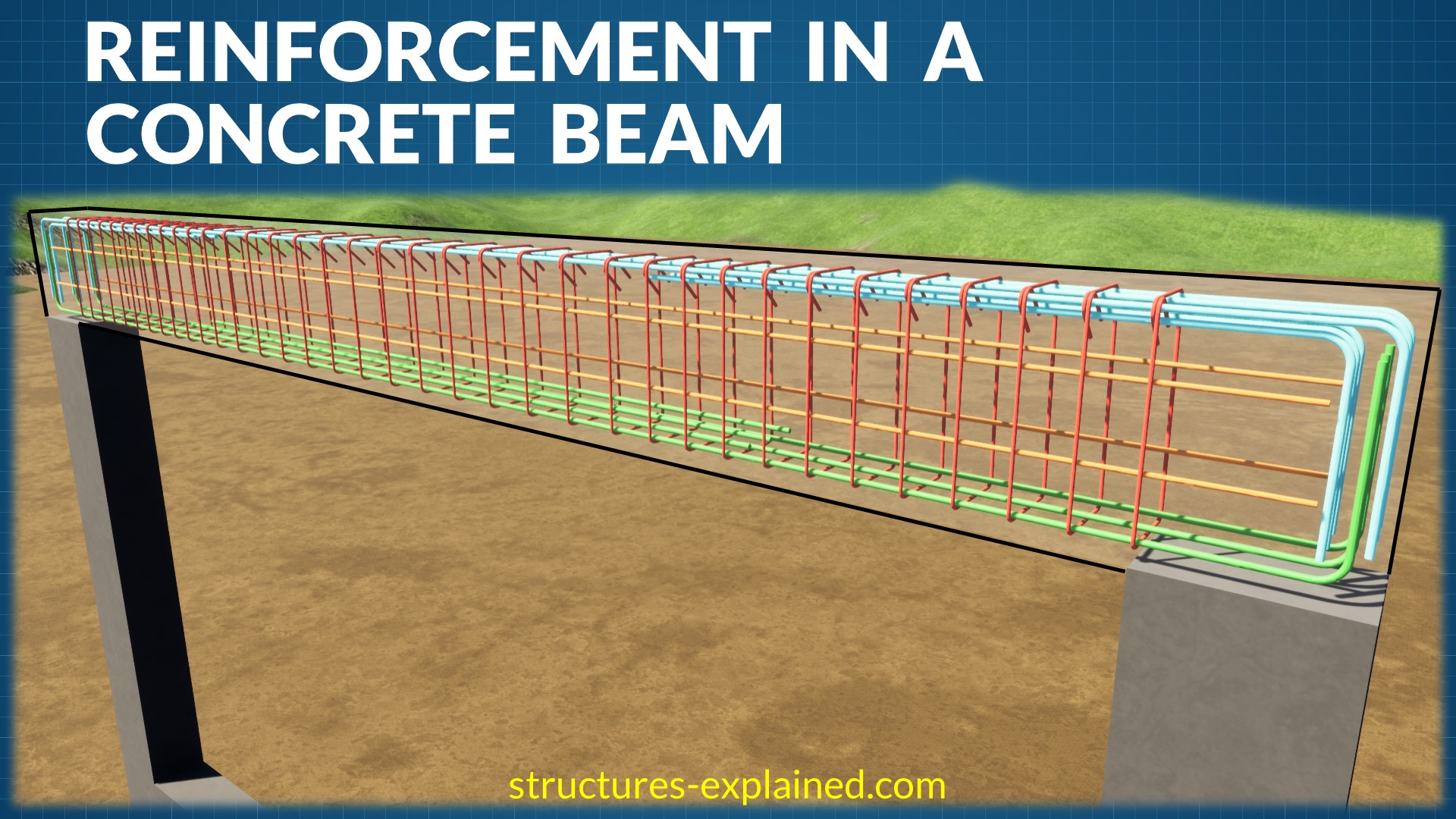
Typical Reinforcement In A Concrete Beam Beam Reinforcement

Comments are closed.