Ultrasound Guided Median And Ulnar Nerve Blocks In The Forearm To
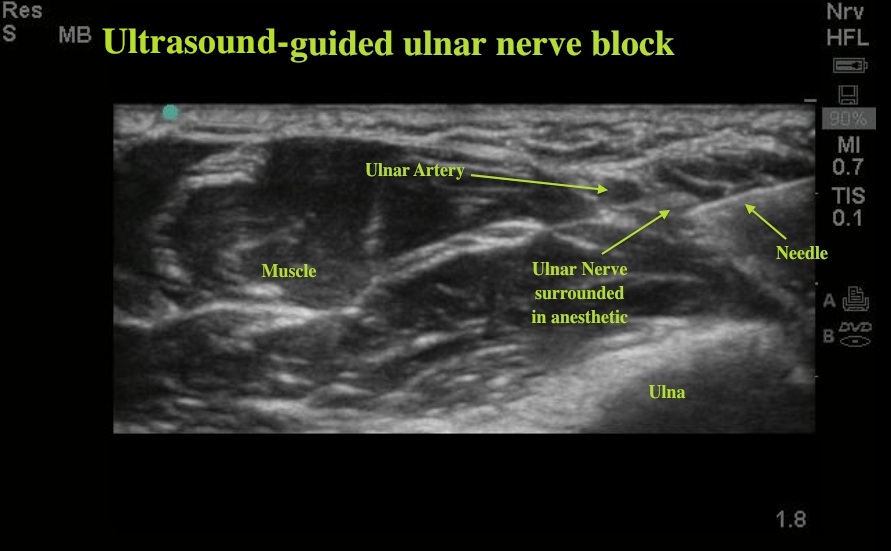
Ultrasound Guided Ulnar Nerve Block Emory School Of Medicine Figure 1. anatomic relationship of the radial, median, ulnar, and musculocutaneous nerves, at the level of the elbow. ultrasonographic assessment shows that a median nerve block using nerve stimulation alone is commonly associated with intraneural injection. some authors have suggested additional indications for forearm blocks, in combination. Unfortunately, the forearm nerve blocks do not provide anesthesia to the volar forearm ( musculocutaneous nerve, medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve ) or the wrist ( musculocutaneous, ain and pin are missed with forearm blocks). this means forearm blocks of the ulnar, median, radial nerve will provide incomplete anesthesia for distal radius or.

Forearm Blocks вђ Highland Em Ultrasound Fueled Pain Management Feasibility of forearm ultrasonography guided nerve blocks of the radial, ulnar, and median nerves for hand procedures in the emergency department. ann emerg med 2006;48:558 62. stone mb, price dd, wang r. ultrasound guided supraclavicular block for the treatment of upper extremity fractures, dislocations, and abscesses in the emergency department. This review is devoted to peripheral nerve blocks of the distal upper extremity, specifically, those of the median, radial and ulnar nerves. these blocks are fairly simple to perform even by a beginner to produce anesthesia or analgesia for surgery of the forearm, wrist and hand. they may be done when blockade of the entire brachial plexus is. Summary. the three main nerves of the forearm – median, radial and ulnar – can easily be blocked using ultrasound guidance with or without nerve stimulation. an in plane needle approach is recommended. the volume of local anaesthetic required is usually 5 8ml per nerve. Nerve blocks of the ulnar, median, and radial nerves at the wrist and elbow provide effective anesthesia for a wide range of medical procedures in the upper extremity. ultrasound guided nerve.

Comments are closed.