Urinary Catheters Uses Types And Complications Cathet Vrogue Co
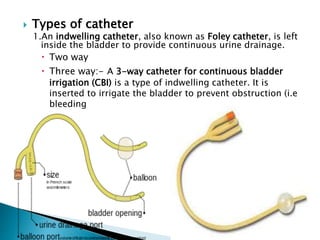
Urinary Catheters Uses Types And Complications Atelier Yuwa Ciao Jp Cloudy urine due to pus. burning of the urethra or genital area. leaking of urine out of the catheter. blood in the urine. foul smelling urine. low back pain and achiness. other complications from. The average urinary catheter size for adult men is 14 fr, while female patients typically have 12 fr catheters, and children can have anywhere from 6 fr to 10 fr, on average. length – in terms of length, catheters can range from around 6 inches long to 18 inches or even more. typically, adult male patients require the longest catheters, as.
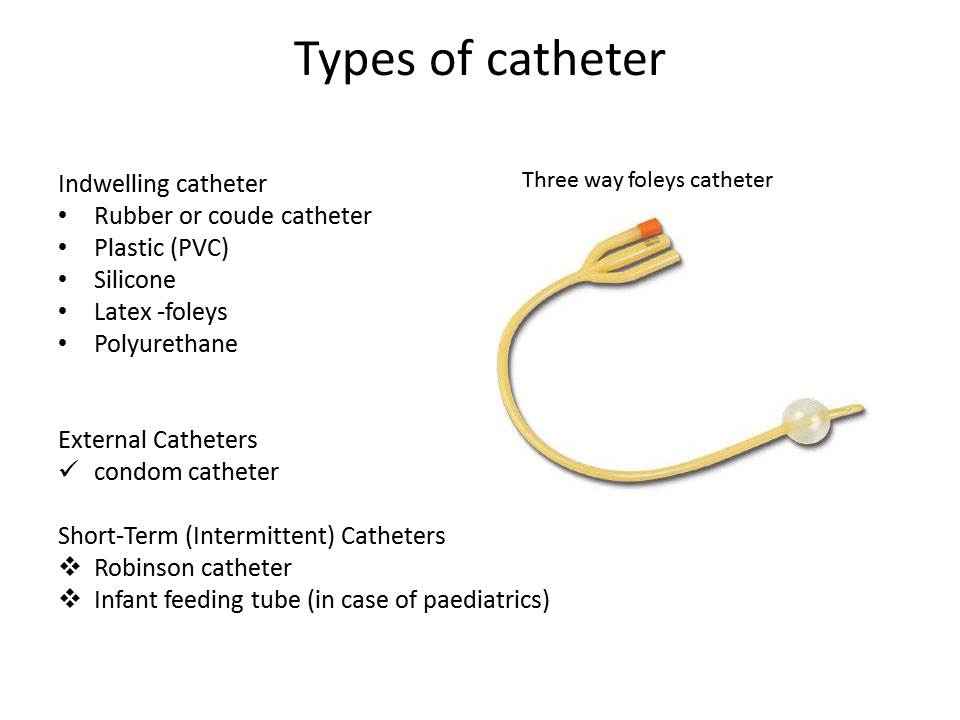
Urinary Catheters Uses Types And Complications 50 Off General complications. bacteriuria and urinary tract infection — the presence of bacteria in the urine is almost universal in patients with catheters in place for over one week. rates vary depending upon the type of catheter and duration of use. the evaluation of bacteriuria and diagnosis of catheter associated urinary tract infection is. There are a few things to watch when you use urinary catheters other than external and condom catheters. infection. this is the most common problem. the catheter may let germs into your body. Our recommendations for urinary catheter placement and care are generally consistent with major guidelines that focus on prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infection [1 3]. this topic will discuss the use and management of urinary catheters. management of bacteriuria and catheter associated urinary tract infection is discussed. Tumors within the urinary tract or reproductive organs. a healthcare provider may also insert a urinary catheter: to accurately measure urine output in critically ill people. to drain the bladder.

Urinary Catheters Uses Types And Complications Owl Classroom Our recommendations for urinary catheter placement and care are generally consistent with major guidelines that focus on prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infection [1 3]. this topic will discuss the use and management of urinary catheters. management of bacteriuria and catheter associated urinary tract infection is discussed. Tumors within the urinary tract or reproductive organs. a healthcare provider may also insert a urinary catheter: to accurately measure urine output in critically ill people. to drain the bladder. Clinical indicators of catheter associated urinary tract infection (cauti) include pyrexia, tachycardia, abdominal pain and changes in urine characteristics, such as aroma and appearance. in older people the signs and symptoms may be less specific and include confusion, disorientation and falls (royal college of nursing, 2021). Avoid contact with the connector of the bag as this helps to reduce the risk of cauti. open the catheter valve once the bag is attached, so urine can drain into the bag. leg bags that are used during the day should be secured onto the leg (fig 2f). overnight, a night drainage bag should be attached to a catheter stand.

Urinary Catheters Uses Types And Complications Catheter Bladder Clinical indicators of catheter associated urinary tract infection (cauti) include pyrexia, tachycardia, abdominal pain and changes in urine characteristics, such as aroma and appearance. in older people the signs and symptoms may be less specific and include confusion, disorientation and falls (royal college of nursing, 2021). Avoid contact with the connector of the bag as this helps to reduce the risk of cauti. open the catheter valve once the bag is attached, so urine can drain into the bag. leg bags that are used during the day should be secured onto the leg (fig 2f). overnight, a night drainage bag should be attached to a catheter stand.

Comments are closed.