Vascular Dementia Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Pathology

Vascular Dementia Diagnosis Treatment Clinical Department Cdc Vascular dementia is caused by different conditions that interrupt the flow of blood and oxygen supply to the brain and damage blood vessels in the brain. people with vascular dementia almost always have abnormalities in the brain that can be seen on mri scans. these abnormalities can include evidence of prior strokes, which are often small and. Vascular dementia is among the most common etiologies of major neurocognitive disorder (mnd), affecting primarily older adults (>65), and it is the leading nondegenerative cause of dementia. the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fifth edition (dsm v) subsumes all dementing diseases under the syndromic term mnd. mnd requires an acquired decline in one or more cognitive.

What Is Vascular Dementia Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment But unlike alzheimer's disease, the most significant symptoms of vascular dementia tend to involve speed of thinking and problem solving rather than memory loss. vascular dementia signs and symptoms include: confusion. trouble paying attention and concentrating. reduced ability to organize thoughts or actions. A brain imaging study can help your doctor zero in on more likely causes for your symptoms and rule out other causes. brain imaging procedures your doctor may recommend to help diagnose vascular dementia include: magnetic resonance imaging (mri). an magnetic resonance imaging (mri) uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to produce. Definitions. vascular dementia — vascular dementia refers to any dementia that is primarily caused by cerebrovascular disease or impaired cerebral blood flow, or in which cerebrovascular disease or impaired cerebral blood flow is a contributing causative factor. vascular dementia is typically recognized in either of two clinical scenarios [4]:. Vascular dementia (vad) is widely recognised as the second most common type of dementia. consensus and accurate diagnosis of clinically suspected vad relies on wide ranging clinical, neuropsychological and neuroimaging measures in life but more importantly pathological confirmation. factors defining ….
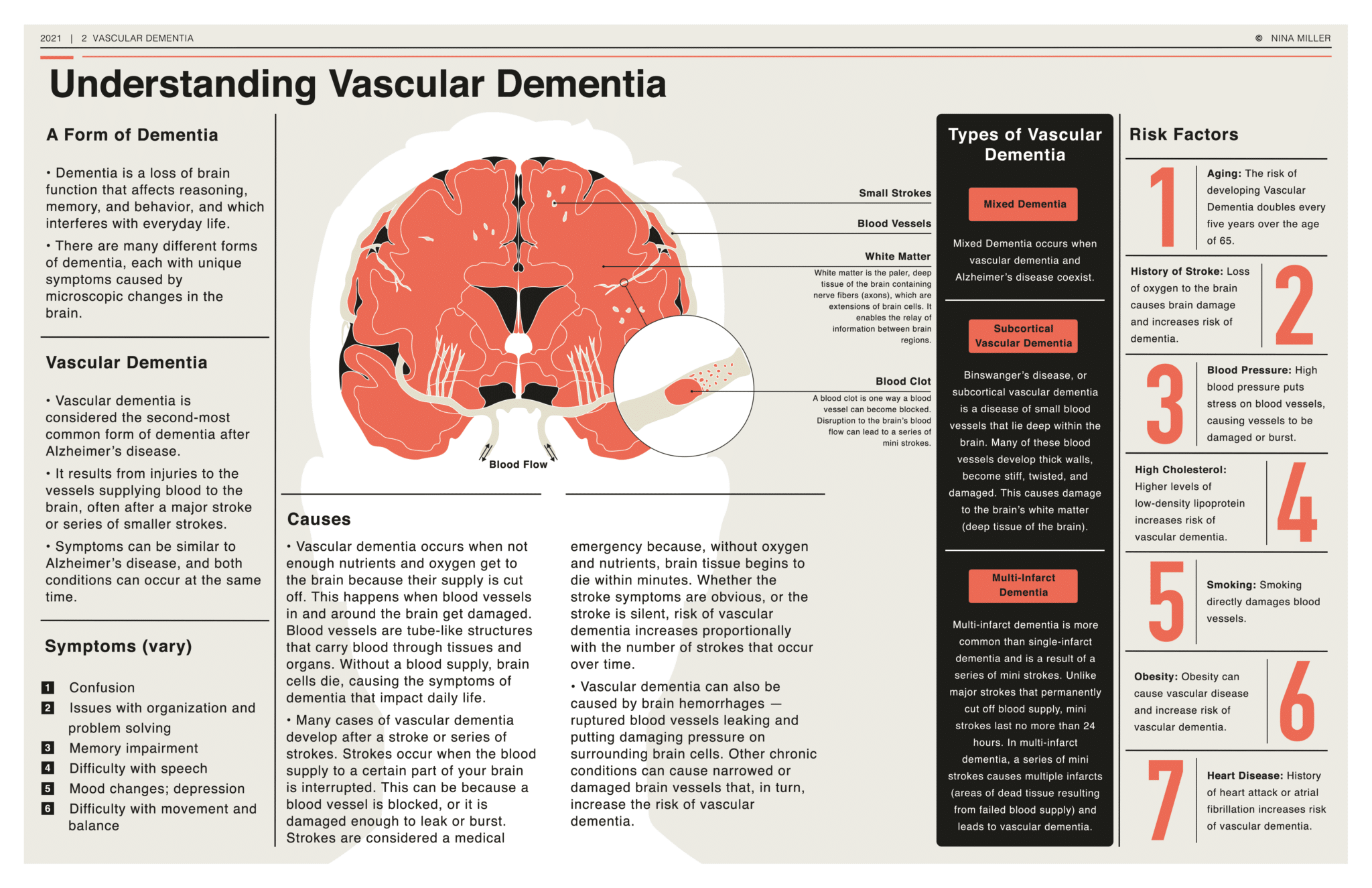
Vascular Dementia Penn Memory Center Definitions. vascular dementia — vascular dementia refers to any dementia that is primarily caused by cerebrovascular disease or impaired cerebral blood flow, or in which cerebrovascular disease or impaired cerebral blood flow is a contributing causative factor. vascular dementia is typically recognized in either of two clinical scenarios [4]:. Vascular dementia (vad) is widely recognised as the second most common type of dementia. consensus and accurate diagnosis of clinically suspected vad relies on wide ranging clinical, neuropsychological and neuroimaging measures in life but more importantly pathological confirmation. factors defining …. Like alzheimer's disease, the symptoms of vascular dementia are often mild for a long time. they may include: problems with short term memory. wandering or getting lost in familiar surroundings. Vascular dementia is a common type of dementia that happens when there’s decreased blood flow to areas of your brain. the resulting lack of oxygen and nutrients damages brain tissue. this leads to a decline in mental (cognitive) functions that’s severe enough to interfere with daily living. several conditions can contribute to a lack of.

Vascular Dementia Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Pathology Like alzheimer's disease, the symptoms of vascular dementia are often mild for a long time. they may include: problems with short term memory. wandering or getting lost in familiar surroundings. Vascular dementia is a common type of dementia that happens when there’s decreased blood flow to areas of your brain. the resulting lack of oxygen and nutrients damages brain tissue. this leads to a decline in mental (cognitive) functions that’s severe enough to interfere with daily living. several conditions can contribute to a lack of.

Comments are closed.