What Are Consumers Heterotrophs In A Food Chain

Heterotroph Examples In Food Chains A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores. The food chain is a way of describing how different organisms on earth interact with each other. the food chain starts with the producers, who make their own food using sunlight or chemicals. the producers are eaten by the consumers, who are either herbivores or carnivores. the carnivores are eaten by the omnivores, and the top of the food.

Food Pyramid For Animals Heterotrophs are known as consumers because they consume producers or other consumers. dogs, birds, fish, and humans are all examples of heterotrophs . heterotrophs occupy the second and third levels in a food chain , a sequence of organisms that provide energy and nutrients for other organisms. By studying food chains, ecologists better understand ecosystem dynamics, including the flow of energy, population control, and the impact of human activities on natural habitats. key points. food chains are linear models that illustrate energy transfer from producers to top consumers. each organism in a food chain contributes to ecosystem balance. Heterotroph definition. a heterotroph is an organism that cannot manufacture its own food by carbon fixation and therefore derives its intake of nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. in the food chain, heterotrophs are secondary and tertiary consumers. carbon fixation is the process of converting. Heterotrophs in the food chain heterotrophs form the various levels of consumers in the ecological food chain, directly or indirectly relying on the organic matter produced by autotrophs. they play vital roles in transferring energy from one trophic level to another, ensuring the flow of nutrients through ecosystems.

Energy For Life An Overview Of Photosynthesis â Opencurriculum Heterotroph definition. a heterotroph is an organism that cannot manufacture its own food by carbon fixation and therefore derives its intake of nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. in the food chain, heterotrophs are secondary and tertiary consumers. carbon fixation is the process of converting. Heterotrophs in the food chain heterotrophs form the various levels of consumers in the ecological food chain, directly or indirectly relying on the organic matter produced by autotrophs. they play vital roles in transferring energy from one trophic level to another, ensuring the flow of nutrients through ecosystems. In ecology, a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass: primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. there is a single path through the chain. food chains do not accurately describe most ecosystems. Heterotroph, in ecology, an organism that consumes other organisms in a food chain. in contrast to autotrophs, heterotrophs are unable to produce organic substances from inorganic ones. they must rely on an organic source of carbon that has originated as part of another living organism.
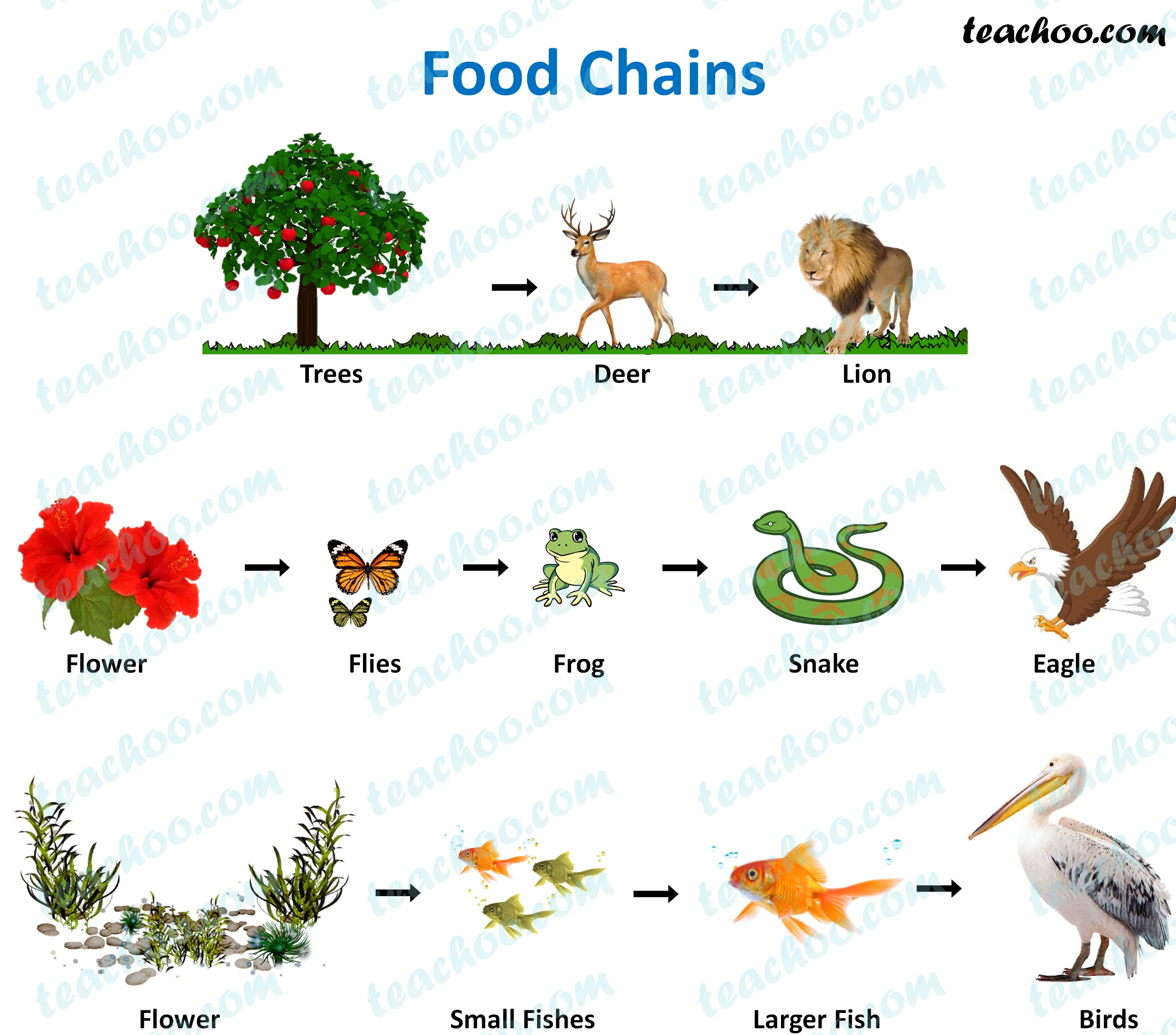
Food Chain And Food Web Meaning Diagrams Examples Teachoo In ecology, a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass: primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. there is a single path through the chain. food chains do not accurately describe most ecosystems. Heterotroph, in ecology, an organism that consumes other organisms in a food chain. in contrast to autotrophs, heterotrophs are unable to produce organic substances from inorganic ones. they must rely on an organic source of carbon that has originated as part of another living organism.
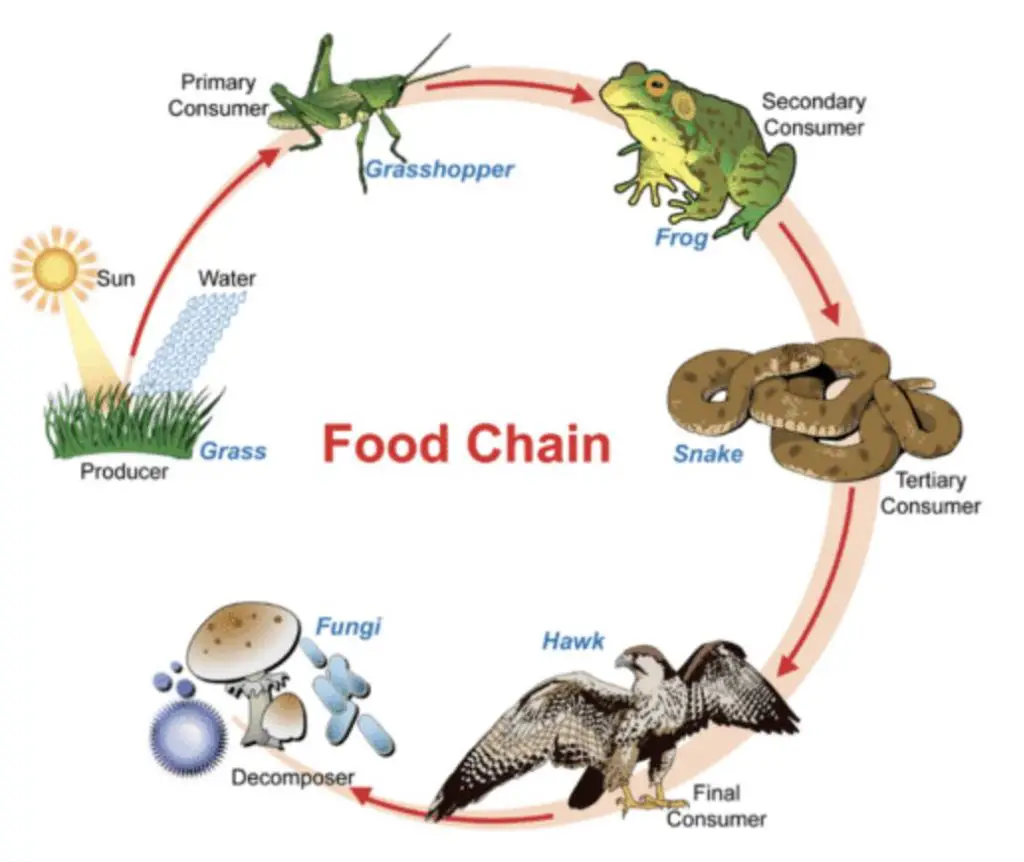
Autotrophs Vs Heterotrophs Definition And Examples Rs Science

Food Chain And Food Webs Explained

Comments are closed.