What Are Consumers In A Food Chain
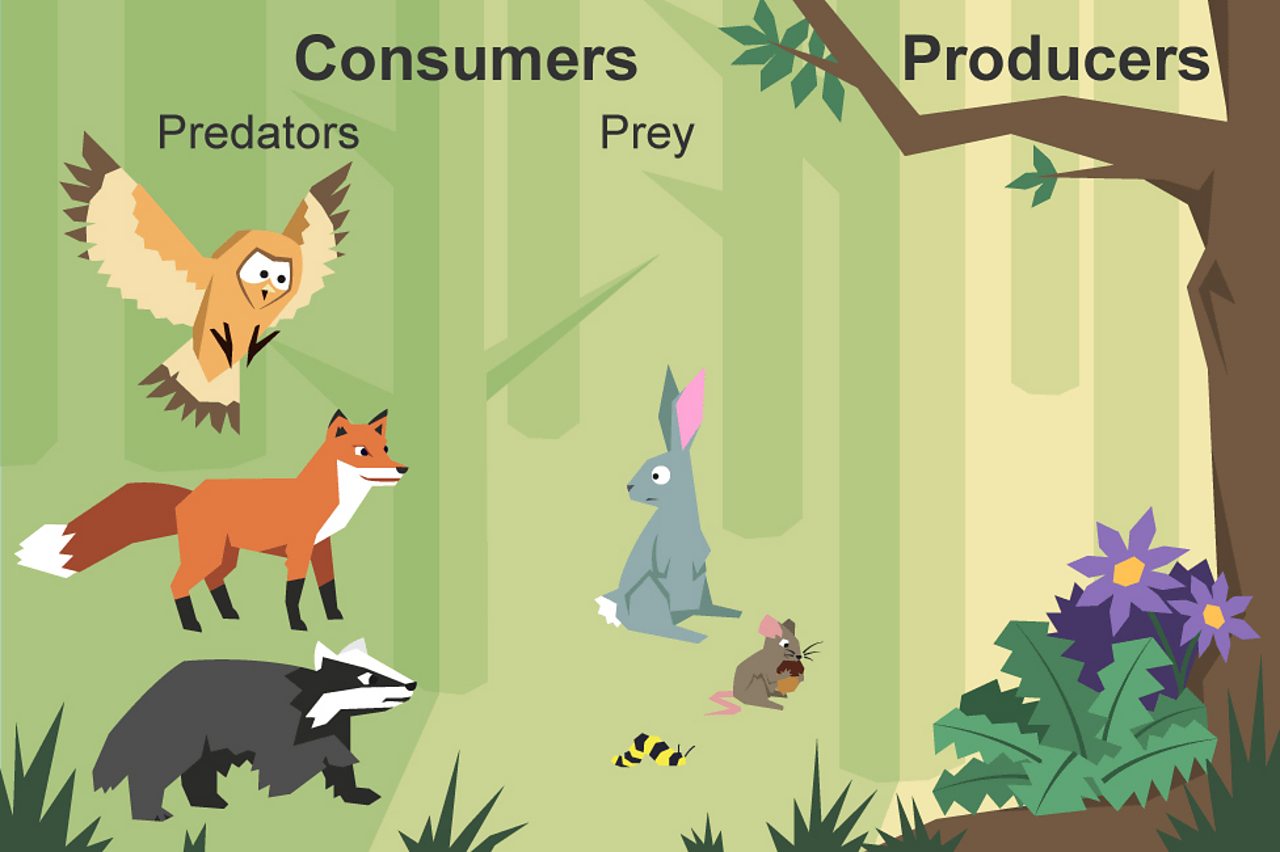
What Is A Food Chain Bbc Bitesize A consumer is an animal that cannot make its own energy and relies on other organisms to survive. consumers are classified into four categories based on their food source: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores.

Food Chain Trophic Levels And Flow Of Energy In Ecosystem Online Organisms in the food chain are divided into trophic levels or feeding levels. the four essential parts are the sun, primary producers, consumers, and decomposers. every food chain originates with the sun providing light and energy for plants to grow and ends with the decomposition of the animals. The cow and human are consumers. a food chain is a list of organisms in a. habitat. that shows their feeding relationship, i.e what eats what. the organisms are joined by arrows which show the. The primary consumer plays an important role in the ecosystem by facilitating the flow of energy through the food chain. its main job is to consume plants, converting the energy stored in them into a form that can be used by other consumers in the ecosystem. primary consumers are vital in the trophic structure as they directly consume. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.

The Food Chain For Kids Hubpages The primary consumer plays an important role in the ecosystem by facilitating the flow of energy through the food chain. its main job is to consume plants, converting the energy stored in them into a form that can be used by other consumers in the ecosystem. primary consumers are vital in the trophic structure as they directly consume. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. In ecology, a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass: primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. there is a single path through the chain. each organism in a food chain occupies what is called a trophic level. Higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain, which are called the apex consumers. some lines within a food web may point to more than one organism; those organisms may occupy different trophic levels depending on their position in each food chain within the web.

Food Chain Pyramid Examples In ecology, a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass: primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. there is a single path through the chain. each organism in a food chain occupies what is called a trophic level. Higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain, which are called the apex consumers. some lines within a food web may point to more than one organism; those organisms may occupy different trophic levels depending on their position in each food chain within the web.

Comments are closed.