What Are Consumers In Biology

Consumer Biology Britannica A consumer is an animal that cannot make its own energy and relies on other organisms to survive. consumers are categorized into four levels based on their food source: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. herbivore. noun. organism that eats mainly plants and other producers. molecule.

Consumers In Ecosystem Definition Classifications Lesson Study Types of consumer. 1. primary consumers. herbivores are the dominant consumers. their food source is the first trophic level in the food web, which consists of plants. plants are also considered autotrophs. autotrophs make their own energy from sunlight and basic nutrients through photosynthesis; the phrases producer and autotroph have the same. Learn what consumers are in biology and how they obtain their energy from producers or other consumers. explore the four types of consumers: herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and decomposers, with examples and videos. Animals are called consumers because they ingest plant material or other animals that feed on plants, using the energy stored in this food to sustain themselves. lastly, the organisms known as decomposers, mostly fungi and bacteria, break down plant and animal material and return it to the environment…. read more. A primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers, which are autotrophic plants that produce their own food through photosynthesis. learn about the different types of primary consumers, their feeding strategies, adaptations and examples, such as ruminants, zooplankton and herbivorous birds.

Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary Animals are called consumers because they ingest plant material or other animals that feed on plants, using the energy stored in this food to sustain themselves. lastly, the organisms known as decomposers, mostly fungi and bacteria, break down plant and animal material and return it to the environment…. read more. A primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers, which are autotrophic plants that produce their own food through photosynthesis. learn about the different types of primary consumers, their feeding strategies, adaptations and examples, such as ruminants, zooplankton and herbivorous birds. Learn the definitions and examples of producers and consumers in biology, and how they interact in ecosystems. producers are organisms that make their own food, while consumers are organisms that need to eat other organisms to get energy. Consumers are organisms that obtain their energy and nutrients by consuming other organisms, either directly or indirectly. they play a crucial role in ecosystems by forming the second trophic level and above, connecting producers to higher trophic levels and facilitating the flow of energy through food webs. by interacting with both producers and decomposers, consumers contribute to nutrient.
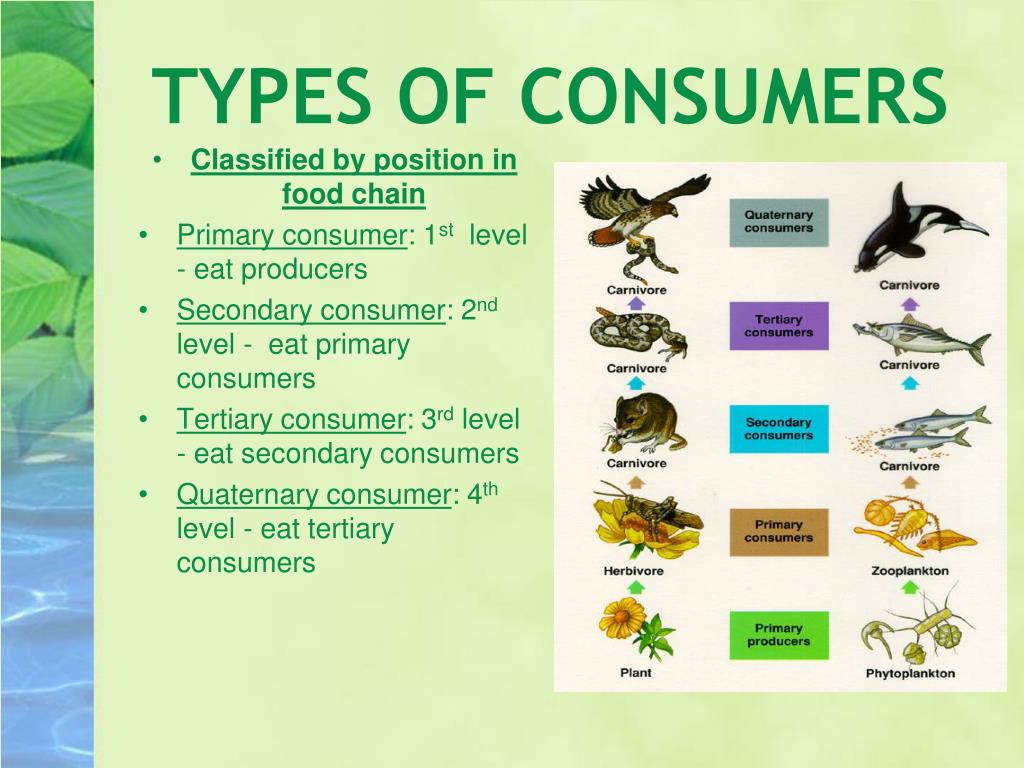
Types Of Consumer Tribes At Shirley Bull Blog Learn the definitions and examples of producers and consumers in biology, and how they interact in ecosystems. producers are organisms that make their own food, while consumers are organisms that need to eat other organisms to get energy. Consumers are organisms that obtain their energy and nutrients by consuming other organisms, either directly or indirectly. they play a crucial role in ecosystems by forming the second trophic level and above, connecting producers to higher trophic levels and facilitating the flow of energy through food webs. by interacting with both producers and decomposers, consumers contribute to nutrient.

Primary Consumers Lesson For Kids Definition Examples Lesson
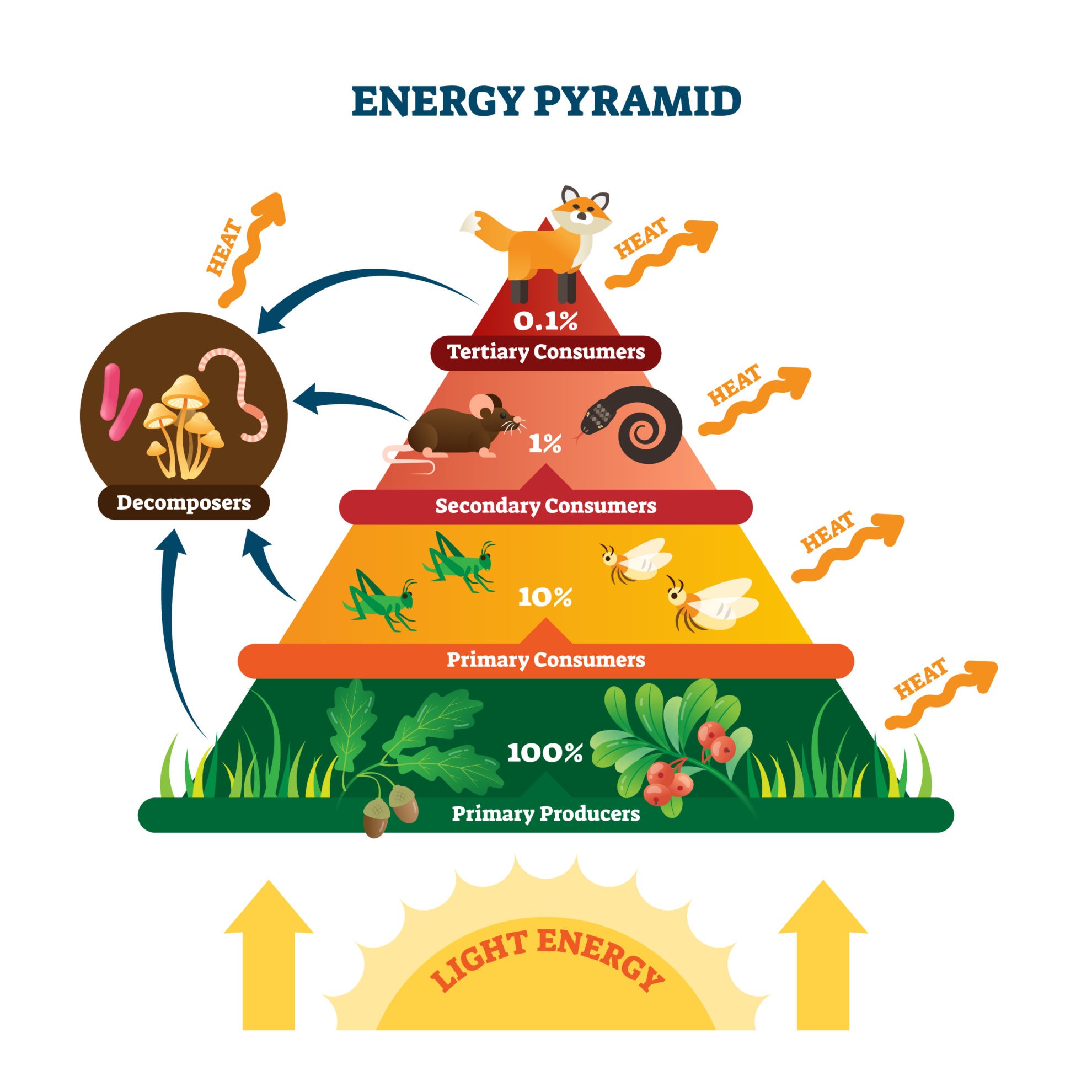
Freshwater Community Energy Relationships Producers Consumers

Comments are closed.