What Are Enzymes Cofactor Coenzyme Prosthetic Group Apoenzyme
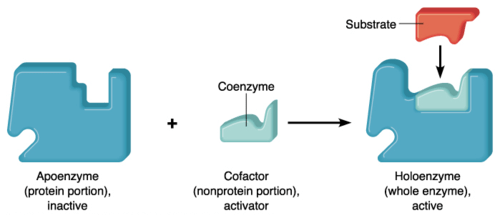
Apoenzyme Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Holoenzyme. the holoenzyme is the combination apoenzyme & cofactor that activated complex of an enzyme for a specific catalytic action. holoenzymes are the active form of an apoenzyme. here co factor may be inorganic ions or organic or metallorganic (coenzyme). Coenzymes. larger organic (carbon containing) cofactors are known as coenzymes. some coenzymes are permanently bound to the enzyme they assist, often in or near the active site. some coenzymes only bind temporarily during the reaction. coenzymes are involved in carrying electrons or chemical groups between enzymes, aiding in catalysis.
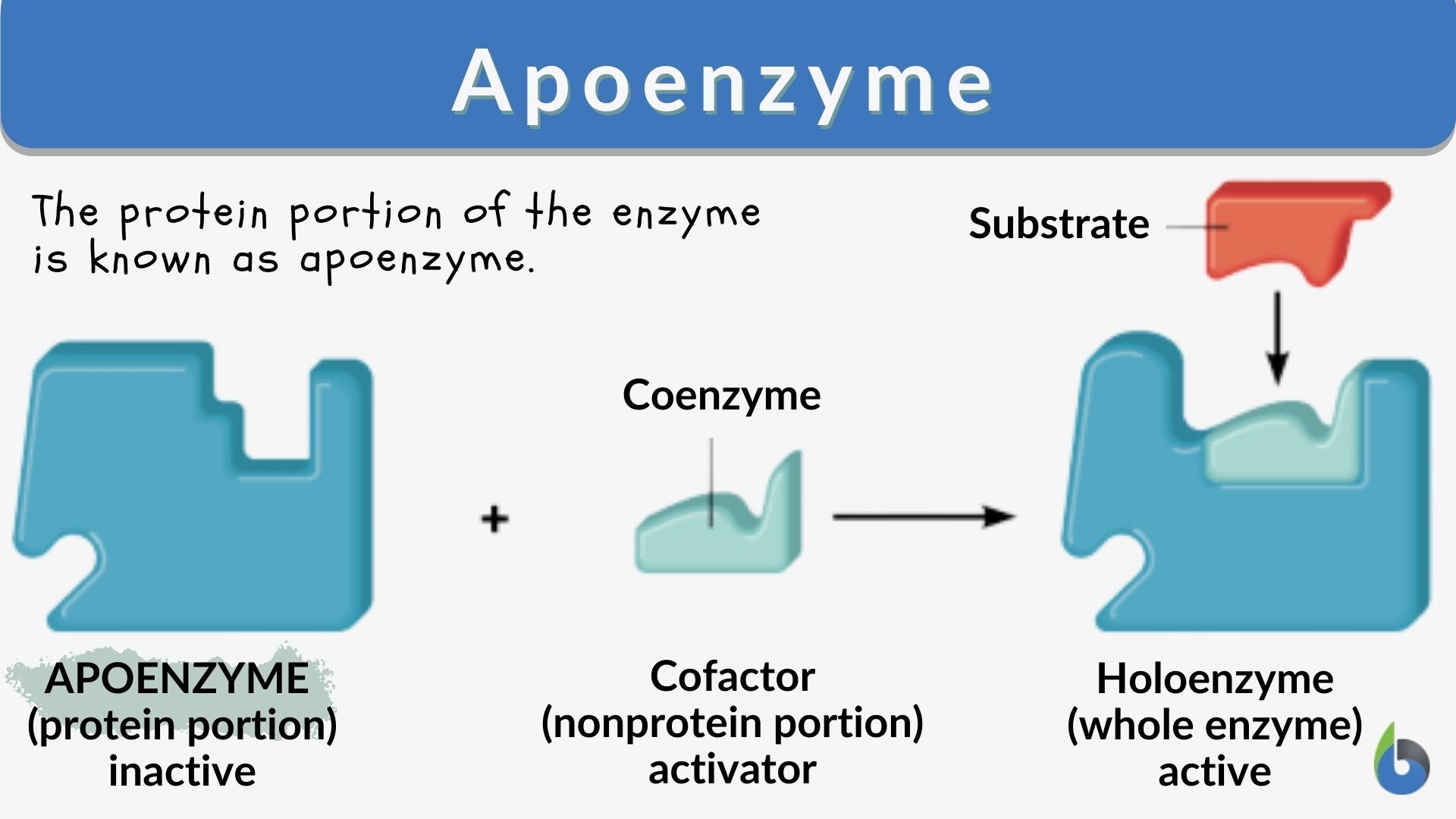
Apoenzyme Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary There are two types of cofactors: inorganic ions [e.g., zinc or cu (i) ions, also known as minerals] and organic molecules known as coenzymes. most coenzymes are vitamins or are derived from vitamins. when the cofactor is tightly bonded to the polypeptide chain through a covalent bond is called a prosthetic group. A cofactor is a non protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's activity as a catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of. In this video, learn about importance of enzymes, what they are, factors affecting enzyme activity, terms such as cofactor, coenzyme, apoenzyme, prosthetic g. Prosthetic group: prosthetic groups are a type of cofactors that are tightly bound to the enzymes or proteins. coenzyme: cofactor is a non protein chemical compound that is tightly and loosely bound to an enzyme or other protein molecules.
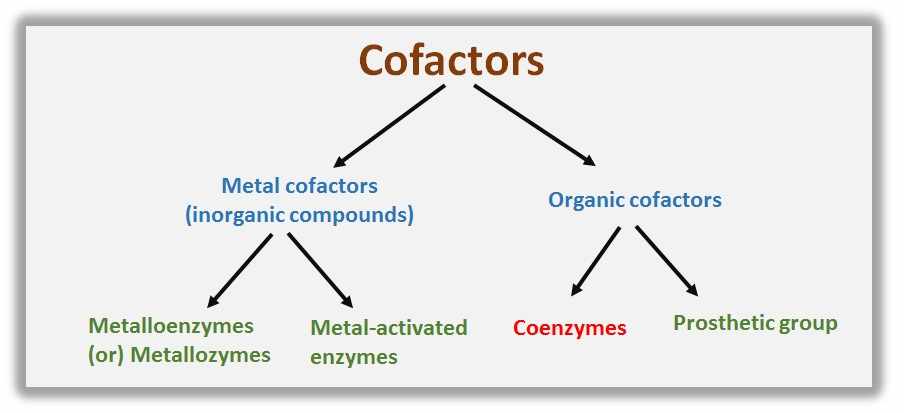
Examples Of Cofactors And Coenzymes Biology Brain In this video, learn about importance of enzymes, what they are, factors affecting enzyme activity, terms such as cofactor, coenzyme, apoenzyme, prosthetic g. Prosthetic group: prosthetic groups are a type of cofactors that are tightly bound to the enzymes or proteins. coenzyme: cofactor is a non protein chemical compound that is tightly and loosely bound to an enzyme or other protein molecules. Cofactor, coenzyme, and holoenzyme: cofactor may be an organic compound (e.g. flavin) or an inorganic compound (e.g. metal ion). the organic cofactor may either be a coenzyme or a prosthetic group. a coenzyme is a cofactor that is loosely bound to the enzyme and therefore may be released readily from the active site of the enzyme. Apoenzyme is the name given to an inactive enzyme that lacks its coenzymes or cofactors. holoenzyme is the term used to describe an enzyme that is complete with its coenzymes and cofactors. holoprotein is the word used for a protein with a prosthetic group or cofactor.

Comments are closed.