What Are Secondary Consumers
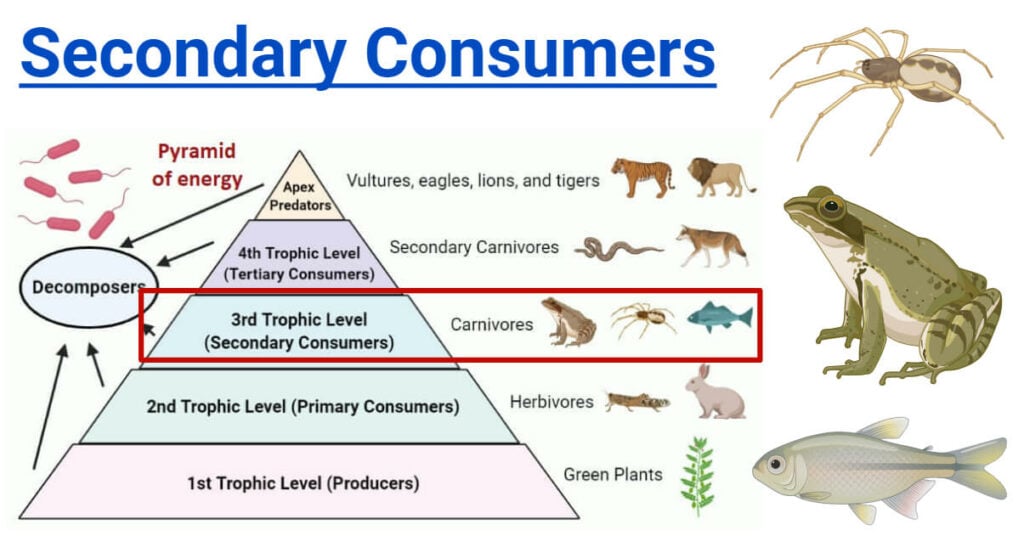
Secondary Consumers Types Food Chain Examples Roles Secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers for energy. they can be carnivores or omnivores, and they regulate the population of primary consumers and provide energy to tertiary consumers. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores.
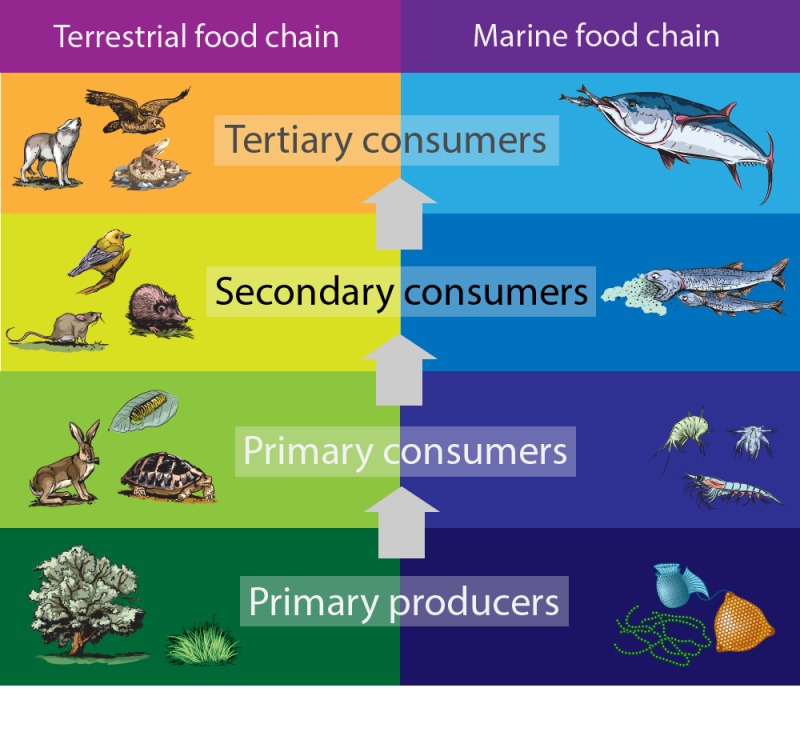
Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples Functions of secondary consumers. secondary consumers have an integral role to play in the food network. they are deeply involved in the regulation of the primary consumers’ populations in an ecosystem as they eat them for energy. moreover, secondary consumers also act as a source of nutrients and energy to the tertiary consumers. Secondary consumers are those that predate upon primary consumers, and tertiary consumers predate upon secondary consumers. secondary consumers are either carnivores (which eat meat) or omnivores. Definition of secondary consumers. secondary consumers are organisms that primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores, who eat only other animals, or omnivores, who consume both animal and plant matter. their role is vital in transferring energy. Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores , from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals.

Secondary Consumer Definition Examples Food Chain Lesson Study Definition of secondary consumers. secondary consumers are organisms that primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores, who eat only other animals, or omnivores, who consume both animal and plant matter. their role is vital in transferring energy. Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores , from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals. Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers, which are plants or herbivores. they are either carnivores or omnivores, and they play a role in controlling the population of primary consumers and providing energy to tertiary consumers. Secondary consumers are pivotal in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. they play a crucial role by regulating populations of primary consumers, thus ensuring that plant life is not overexploited. understanding their impact helps us appreciate the complexity and interdependence within food webs. these organisms contribute significantly to.

Secondary Consumers Heterotrophs Omnivores Education Notes Youtube Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers, which are plants or herbivores. they are either carnivores or omnivores, and they play a role in controlling the population of primary consumers and providing energy to tertiary consumers. Secondary consumers are pivotal in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. they play a crucial role by regulating populations of primary consumers, thus ensuring that plant life is not overexploited. understanding their impact helps us appreciate the complexity and interdependence within food webs. these organisms contribute significantly to.

Comments are closed.