What Is A Secondary Consumer
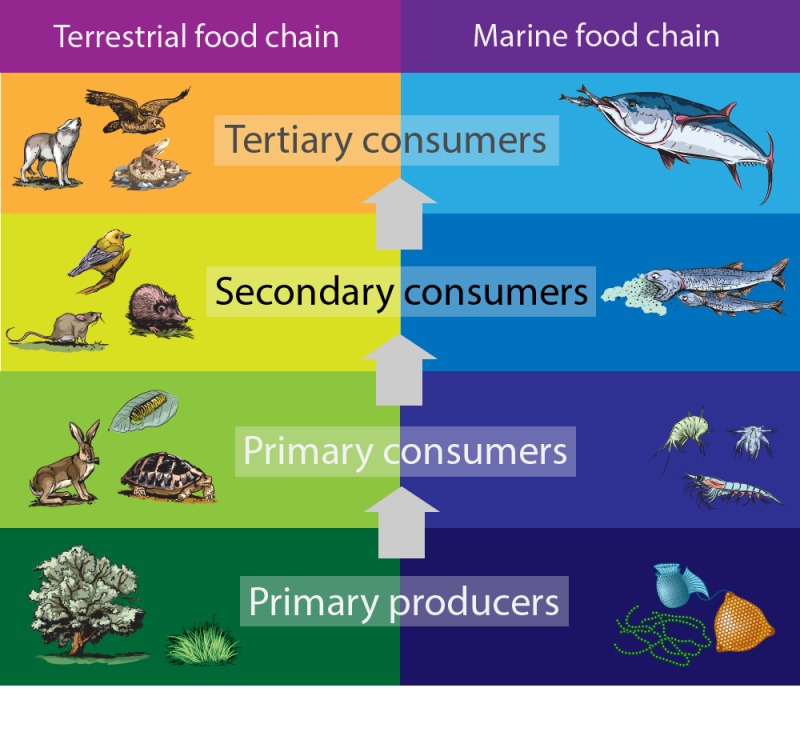
Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples A secondary consumer is an organism that eats primary consumers for energy. primary consumers are herbivores that only eat plants. secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores, and they regulate the population of primary consumers and provide energy to tertiary consumers. Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain and play a vital role in transferring energy and maintaining balance in an ecosystem.

Secondary Consumers Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers, such as herbivores or insects. they regulate populations, influence food webs, and contribute to biodiversity and ecosystem stability. learn about their types, adaptations, and impacts in different ecosystems. A secondary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary consumers for nutrients and energy. they can be carnivores or omnivores and play a key role in regulating the populations of primary consumers and tertiary consumers in an ecosystem. Published oct 23, 2024. secondary consumers are essential in maintaining ecosystem balance. these organisms, including carnivores and omnivores that feed on primary consumers, regulate populations and ensure energy flow through food webs. without them, ecosystems could face imbalances, leading to overpopulation or depletion of certain species. Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores or omnivores. learn more about their role, diversity, and importance in ecosystems.
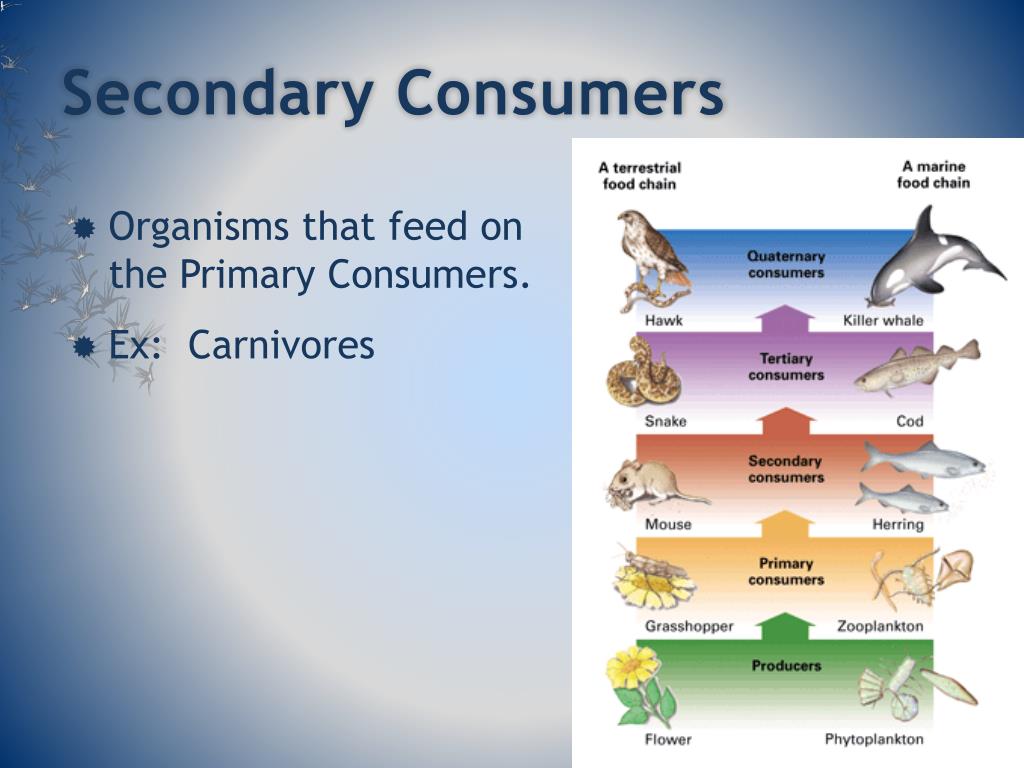
Secondary Consumers In A Forest Published oct 23, 2024. secondary consumers are essential in maintaining ecosystem balance. these organisms, including carnivores and omnivores that feed on primary consumers, regulate populations and ensure energy flow through food webs. without them, ecosystems could face imbalances, leading to overpopulation or depletion of certain species. Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores or omnivores. learn more about their role, diversity, and importance in ecosystems. A secondary consumer is an animal that eats primary consumers, which are herbivorous animals that eat plants. learn the difference between omnivores and carnivores, and see examples of secondary consumers in nature and food chains. A secondary consumer is any organism that obtains energy by consuming a primary consumer, whether that primary consumer is an insect that eats berries, a cow that eats grass, or plankton that feed on algae underwater. secondary consumers include owls, bears, lions and humans – along with many other organisms, and can be considered the.
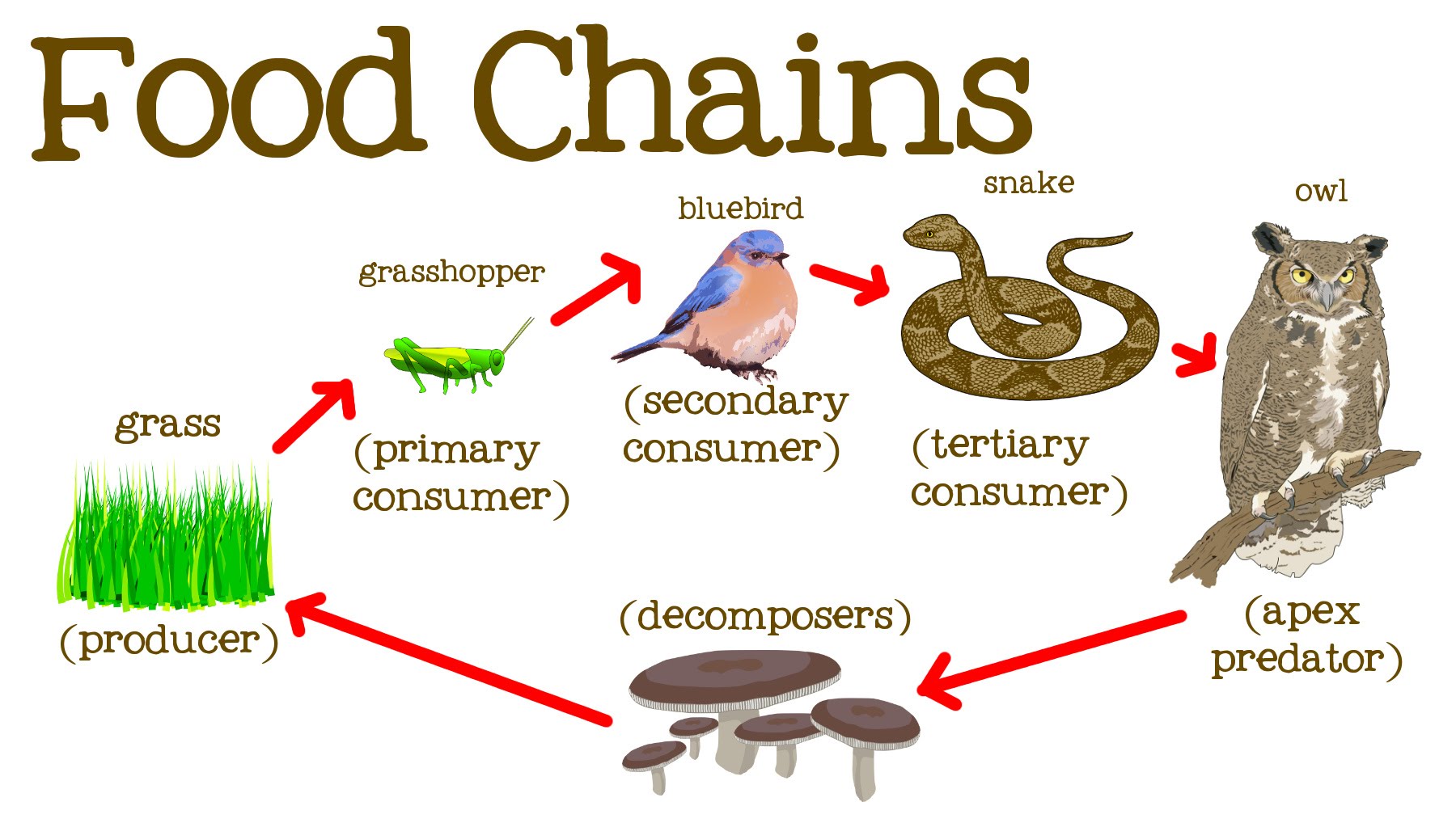
What Is The Difference Between A Producer Secondary Consumer Primary A secondary consumer is an animal that eats primary consumers, which are herbivorous animals that eat plants. learn the difference between omnivores and carnivores, and see examples of secondary consumers in nature and food chains. A secondary consumer is any organism that obtains energy by consuming a primary consumer, whether that primary consumer is an insect that eats berries, a cow that eats grass, or plankton that feed on algae underwater. secondary consumers include owls, bears, lions and humans – along with many other organisms, and can be considered the.

Comments are closed.