What Is A Workover Rig Fracslap Explains
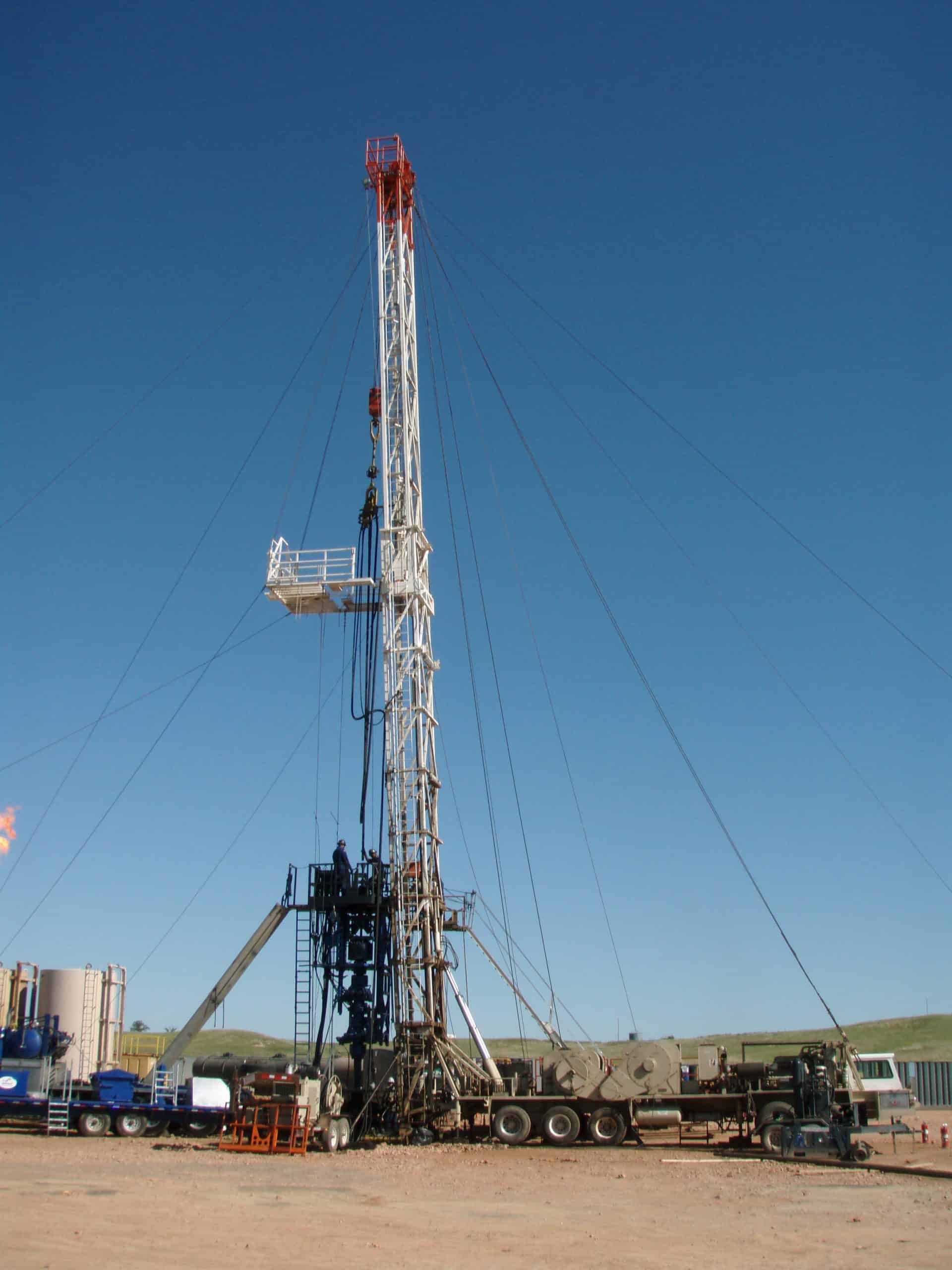

What Is A Workover Rig Another common question i get is "what is a workover rig?" you may have also heard the term tripping pipe, elevators, and tongs when it comes to workover rig. Workover is a term used in the oil and gas industry to describe the maintenance and repair of existing wells. this process is used to restore production from a well that has decreased or stopped flowing, and it is an important part of the lifecycle of an oil or gas well. these tasks are performed using specialized equipment, such as workover rigs, and a team of skilled workers.there are.
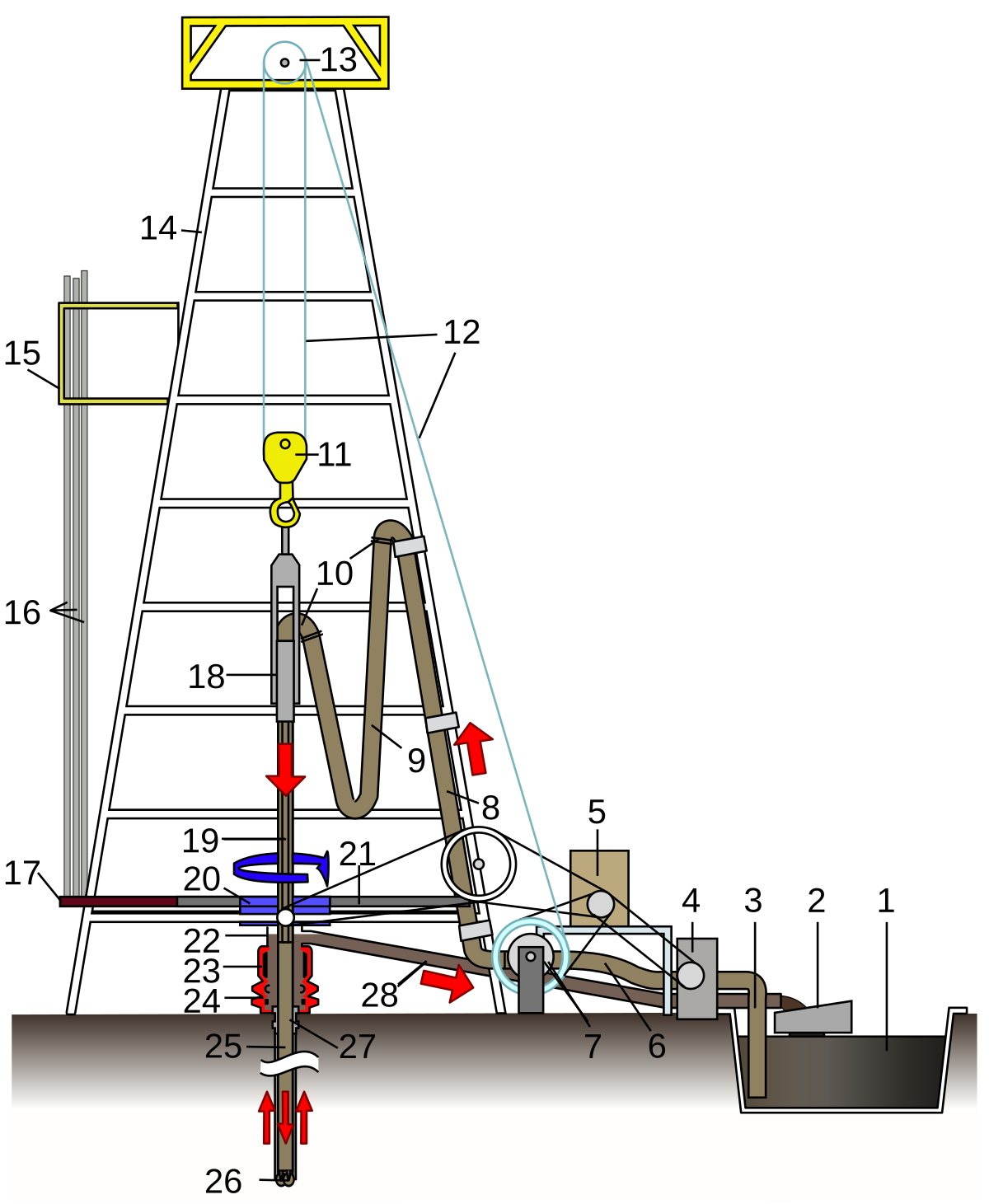
Workover Rig Diagram , the go to source for quick definitions, describes a workover rig in the following manner: “the term workover is used to refer to any oil well intervention involving invasive techniques, such as wireline, coiled tubing or snubbing. more specifically, though, it will refer to the expensive process of pulling and replacing a. A workover rig is like an abbreviated oil rig. when it is erected, it looks like an oil derrick with its steel tower and smaller base. however, it is called a "workover" rig for three reasons. one, when it is in use, you and your crew will "work over" the oil well with this rig. two, you and the crew are working over parts of the oil well that. Scope of work: the primary factor in determining whether a drilling rig or a workover rig is more suitable is the scope of the work required. if the goal is to create a new well, a drilling rig would be the appropriate choice. if the focus is on maintaining, servicing, or re entering an existing well, a workover rig would be the better option. Workover rigs. this phase of the completion is usually done with a “workover” rig. workover rigs are smaller rigs that more easily, efficiently and cheaply can deal with downhole operations both on tubing and wireline. this video shows a workover rig, and gives a good idea of the theory and scale of using workover rigs.

Workover Rig Scope of work: the primary factor in determining whether a drilling rig or a workover rig is more suitable is the scope of the work required. if the goal is to create a new well, a drilling rig would be the appropriate choice. if the focus is on maintaining, servicing, or re entering an existing well, a workover rig would be the better option. Workover rigs. this phase of the completion is usually done with a “workover” rig. workover rigs are smaller rigs that more easily, efficiently and cheaply can deal with downhole operations both on tubing and wireline. this video shows a workover rig, and gives a good idea of the theory and scale of using workover rigs. Workover rig. workover rig is known as the workover the different types of rigs include the offshore and onshore rig that range from 150 horsepower to 1000 horsepower. workover rigs have a surface depth that is equipped with diesel engines and transmissions and is available from 8000 ft to 30000 ft. workover rigs contain a full line of drilling. Workover rigs are used for interventions that boost productivity, such as stimulation techniques (like hydraulic fracturing or acidizing) and the installation of artificial lift systems. by increasing the flow rate and recoverable reserves, these operations improve the economic viability of wells. also, sidetracking operations with workover.

Workover Rig System Buckman Jet Drilling Workover rig. workover rig is known as the workover the different types of rigs include the offshore and onshore rig that range from 150 horsepower to 1000 horsepower. workover rigs have a surface depth that is equipped with diesel engines and transmissions and is available from 8000 ft to 30000 ft. workover rigs contain a full line of drilling. Workover rigs are used for interventions that boost productivity, such as stimulation techniques (like hydraulic fracturing or acidizing) and the installation of artificial lift systems. by increasing the flow rate and recoverable reserves, these operations improve the economic viability of wells. also, sidetracking operations with workover.

Comments are closed.