What Is An Animal Consumer
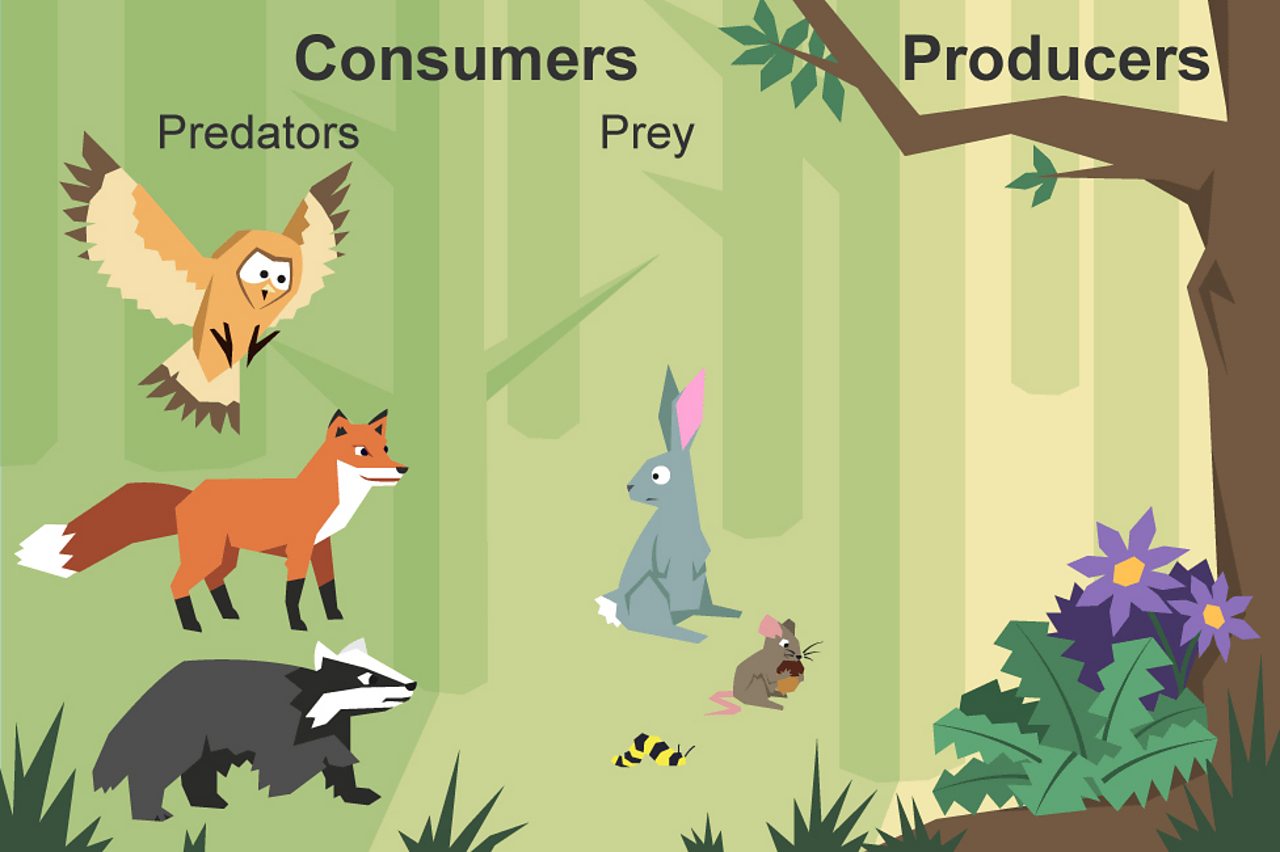
What Is A Food Chain Bbc Bitesize Consumer examples are plentiful, as every animal must consume food in order to live. consumers are grouped into four categories – primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. the category in which an animal is situated is defined by its food source within a specific food chain or food web, and not necessarily by its species or habits. Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores , from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals.
12 Examples Of Primary Consumers Pictures Diagram Wildlife Informer Scientific name: odocoileus virginianus. white tailed deer often forage on prairie grass and are prime examples of primary consumers. however, they can live in various habitats, from northern maine to the hammock swamps of florida. animals that eat white tailed deer include mountain lions, wolves, jaguars, and coyotes. A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores. Primary consumer definition. a primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers. organisms of this type make up the second trophic level and are consumed or predated by secondary consumers, tertiary consumers or apex predators. primary consumers are usually herbivores that feed on autotrophic plants, which produce their own food. Consumer is a category that belongs inside an ecosystem’s food chain. it primarily refers to animals. consumers cannot generate their own energy and must rely on the intake and digestion of producers, other consumers, or both in order to survive. in food chains, consumers are found alongside two additional groups: producers and decomposers.

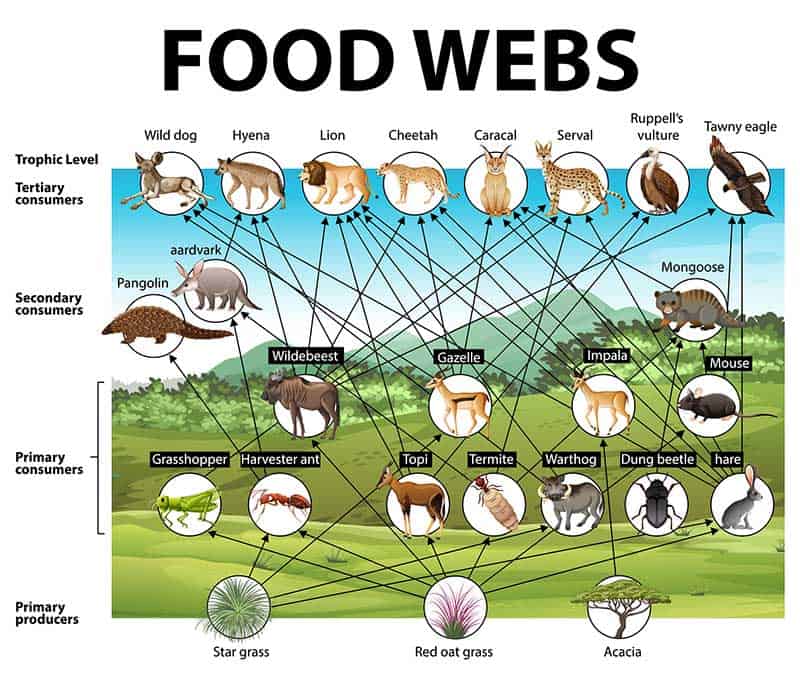
Consumer Biology Britannica Primary consumer definition. a primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers. organisms of this type make up the second trophic level and are consumed or predated by secondary consumers, tertiary consumers or apex predators. primary consumers are usually herbivores that feed on autotrophic plants, which produce their own food. Consumer is a category that belongs inside an ecosystem’s food chain. it primarily refers to animals. consumers cannot generate their own energy and must rely on the intake and digestion of producers, other consumers, or both in order to survive. in food chains, consumers are found alongside two additional groups: producers and decomposers. Camels. a camel is a mammal that is a primary consumer. they are herbivores and eat mostly vegetation. camels are adapted to living in desert conditions with long eyelashes and two rows of eyelashes to protect their eyes from the sand. in the food chain, there are different levels of consumers. the first level is the primary consumer. Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat.
Primary Consumer Animals Camels. a camel is a mammal that is a primary consumer. they are herbivores and eat mostly vegetation. camels are adapted to living in desert conditions with long eyelashes and two rows of eyelashes to protect their eyes from the sand. in the food chain, there are different levels of consumers. the first level is the primary consumer. Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat.

Comments are closed.