What Is Plastic Pollution Effects Of Plastic Pollution Plastic

Plastic Pollution Definition Sources Effects Solutions Facts Impacts of plastic pollution. plastic pollution has become ubiquitous in natural and built environments, raising concerns about potential harm to humans and nature alike. once in the environment, research shows that plastic pollution is persistent and may take between 100 to 1,000 years or more to decompose, depending on environmental conditions. Overall, 46 per cent of plastic waste is landfilled, while 22 per cent is mismanaged and becomes litter. unlike other materials, plastic does not biodegrade. this pollution chokes marine wildlife, damages soil and poisons groundwater, and can cause serious health impacts. is pollution the only problem with plastic?.
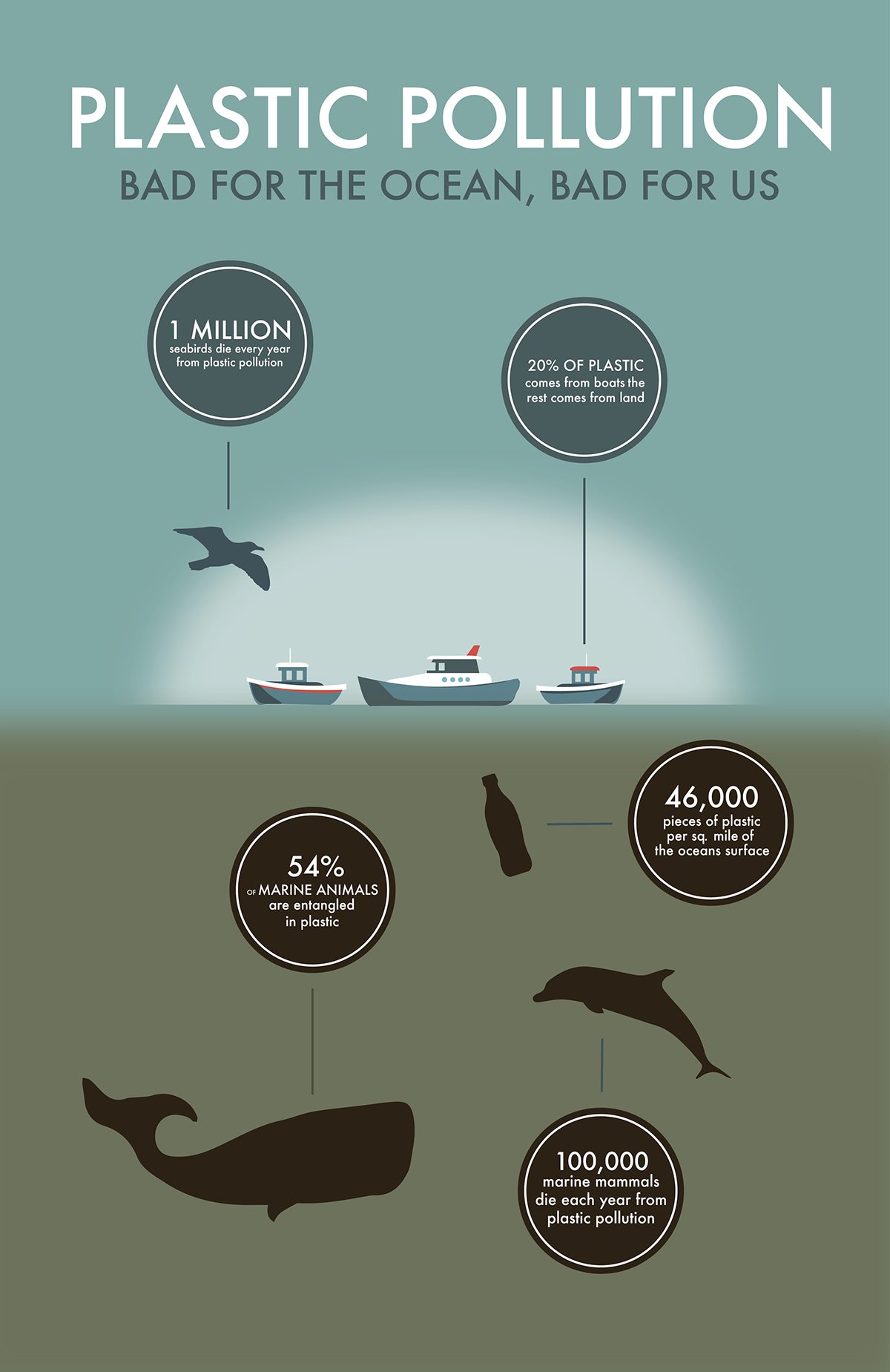
Plastic Pollution Infographic On Behance Plastic debris can contain toxic chemicals, which can leach into food and water supplies. ingesting these chemicals can cause a range of health problems, from endocrine disruption to reproductive problems and cancer. reducing the amount of plastic pollution is essential to protecting human health. economic losses. Plastic pollution, harmful accumulation of synthetic plastic products in the environment. plastics are persistent large scale pollutants, and plastic debris (such as bottles, straws, containers, and plastic wrap) and particulates have been found in many environmental niches, from mount everest to the bottom of the sea. The world's plastic pollution crisis, explained. raising new questions about the effects of plastics on fish populations. stopping plastic pollution. once in the ocean, it is difficult—if. Plastic pollution. every day, the equivalent of 2,000 garbage trucks full of plastic are dumped into the world's oceans, rivers, and lakes. plastic pollution is a global problem. every year 19 23 million tonnes of plastic waste leaks into aquatic ecosystems, polluting lakes, rivers and seas. plastic pollution can alter habitats and natural.

Plastic Pollution Definition Sources Effects Solutions Facts The world's plastic pollution crisis, explained. raising new questions about the effects of plastics on fish populations. stopping plastic pollution. once in the ocean, it is difficult—if. Plastic pollution. every day, the equivalent of 2,000 garbage trucks full of plastic are dumped into the world's oceans, rivers, and lakes. plastic pollution is a global problem. every year 19 23 million tonnes of plastic waste leaks into aquatic ecosystems, polluting lakes, rivers and seas. plastic pollution can alter habitats and natural. Even just in the last two decades, global plastic production has doubled. the world produces around 350 million tonnes of plastic waste each year. estimates vary, but recent high quality studies suggest that between 1 and 2 million tonnes of plastic enter the oceans annually. 1. that means 0.5% of plastic waste ends up in the ocean. Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles (e.g. plastic bottles, bags and microbeads) in the earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat. [1][2] plastics that act as pollutants are categorized by size into micro , meso , or macro debris. [3] plastics are inexpensive and durable.

Comments are closed.