What Is The Difference Between Primary Secondary And Tertiary Consumersођ

What Is The Difference Between Primary Secondary And Tertiary Consumers 5 min read. the main difference between primary secondary and tertiary consumers is that primary consumers are the herbivores that feed on plants, and secondary consumers can be either carnivores, which prey on other animals, or omnivores, which feed on both animals and plants, whereas tertiary consumers are the apex predators that feed on both. Primary sources include the original raw evidence or data that you collect yourself in a study. for example, interview transcripts or statistical data. secondary sources include distilled analyses and interpretations of primary data that someone else collected in their study. for example, journal articles and critical analysis pieces.
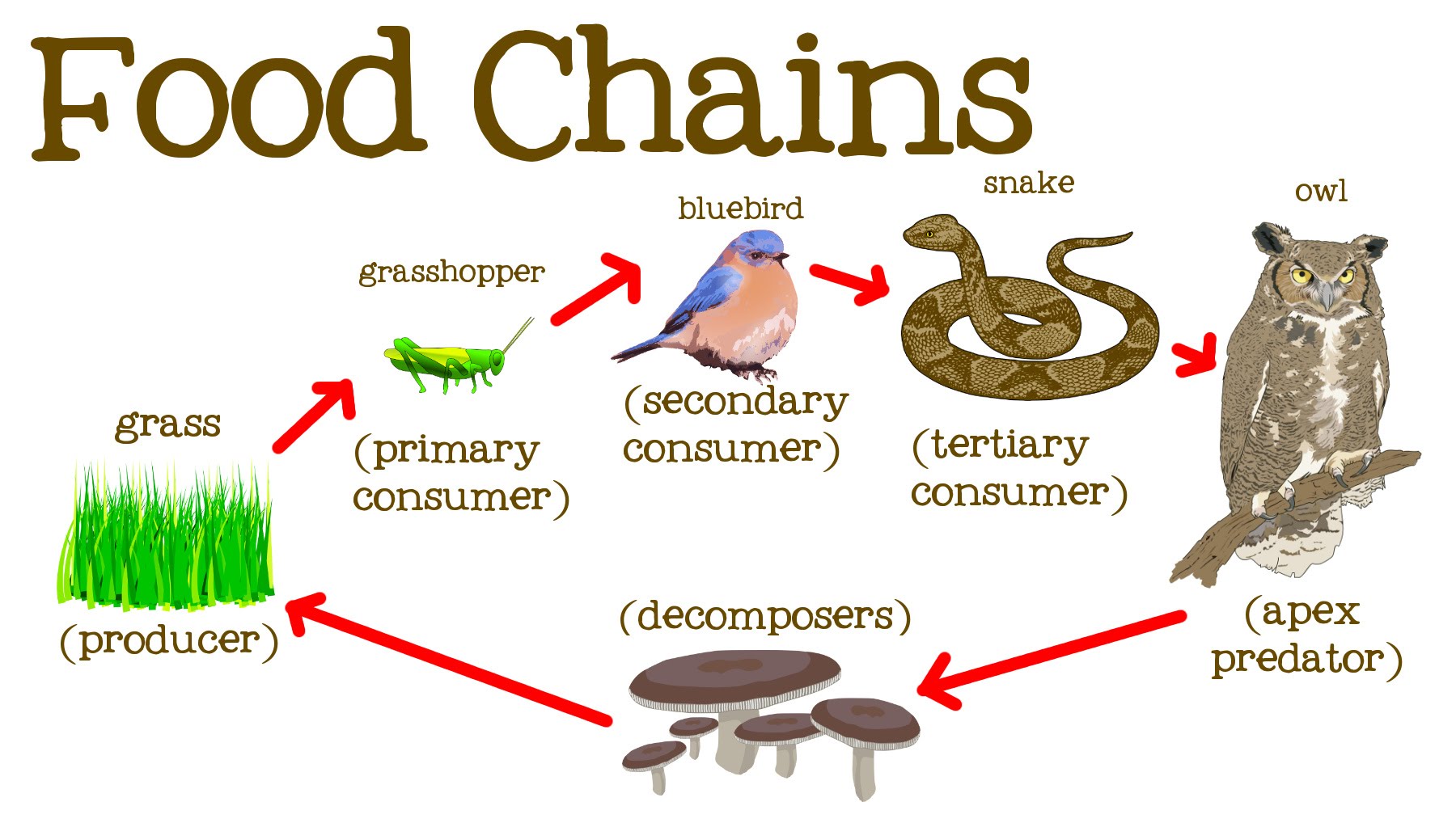
What Is The Difference Between A Producer Secondary Consumer Primary Here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. as every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web. In some formats, several of these common tertiary sources may qualify as secondary sources. just remember that tertiary materials are seldom attributed to a specific author. when in doubt, consider the questions for determining primary and secondary sources. what are the main differences between primary, secondary, and tertiary sources?. Sources of information or evidence are often categorized as primary, secondary, or tertiary material. these classifications are based on the originality of the material and the proximity of the source or origin. this informs the reader as to whether the author is reporting information that is first hand or is conveying the experiences and. The three labels for information sources in this category are, respectively, primary sources, secondary sources, and tertiary sources. here are examples to illustrate the first handedness, second handedness, and third handedness of information: j.d. salinger’s novel catcher in the rye.

Trophic Levels Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Sources of information or evidence are often categorized as primary, secondary, or tertiary material. these classifications are based on the originality of the material and the proximity of the source or origin. this informs the reader as to whether the author is reporting information that is first hand or is conveying the experiences and. The three labels for information sources in this category are, respectively, primary sources, secondary sources, and tertiary sources. here are examples to illustrate the first handedness, second handedness, and third handedness of information: j.d. salinger’s novel catcher in the rye. Tertiary sources sometimes include a bibliography, works cited, or reference list that can act as a directory to important primary and secondary sources. because tertiary sources often aim to provide a broad overview, they generally rely on groups of authors for content. editors then review and organize the material prior to publication. some. Telling the difference between primary, secondary, and tertiary sources can often be confusing because the difference is more about the content of the source than the published format. the format may be a first indicator of whether or not a source is primary, but evaluating the content will be the ultimate judgement call.
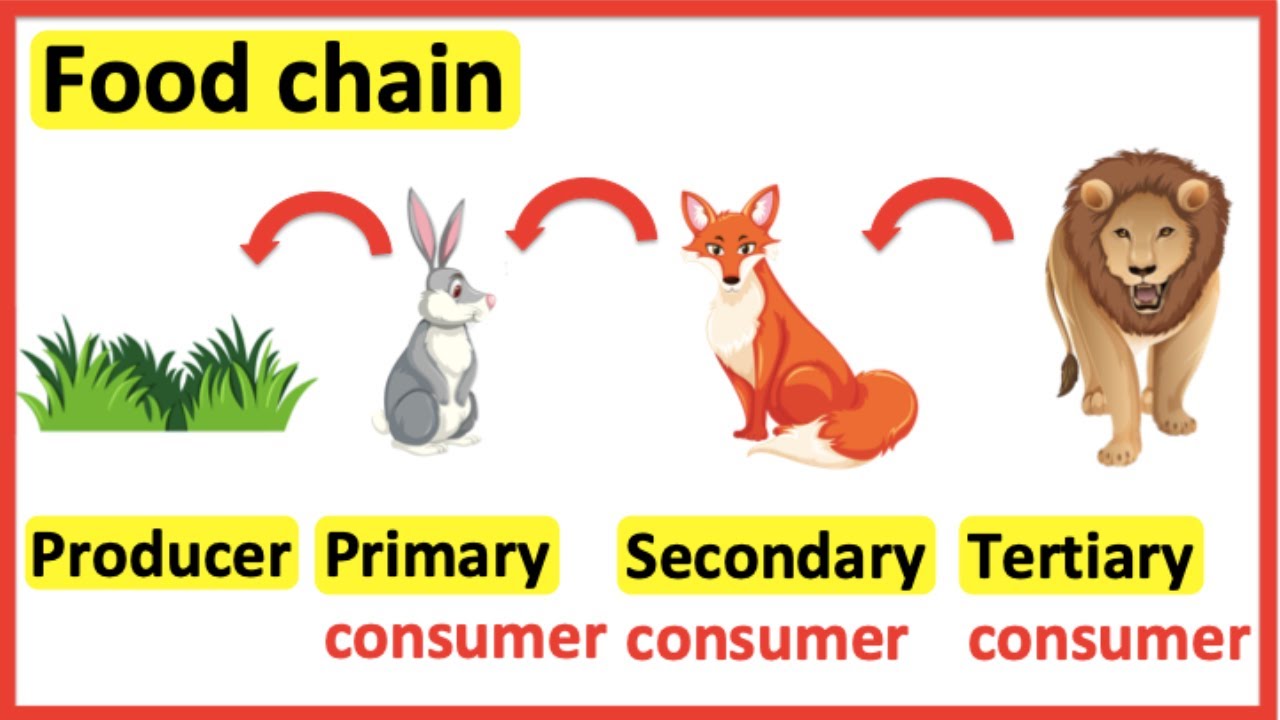
Food Chains Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Tertiary sources sometimes include a bibliography, works cited, or reference list that can act as a directory to important primary and secondary sources. because tertiary sources often aim to provide a broad overview, they generally rely on groups of authors for content. editors then review and organize the material prior to publication. some. Telling the difference between primary, secondary, and tertiary sources can often be confusing because the difference is more about the content of the source than the published format. the format may be a first indicator of whether or not a source is primary, but evaluating the content will be the ultimate judgement call.
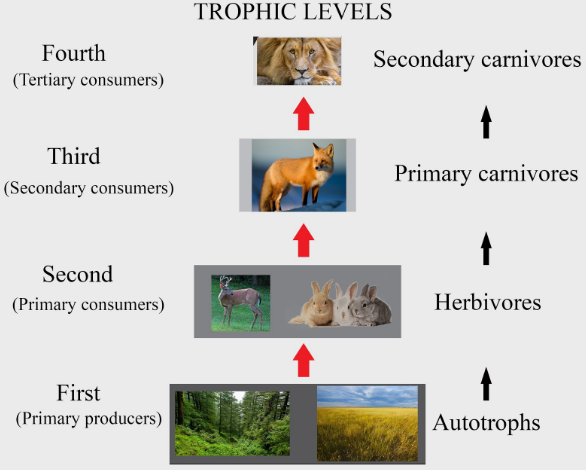
What Is The Difference Between A Producer Secondary Consumer Primary

Secondary Consumers Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript

Comments are closed.