Why Are Monopolies Bad Reduce Consumer Choice Increase Product Price

Why Are Monopolies Bad Reduce Consumer Choice Increase Product Price Disadvantages of monopolies. higher prices than in competitive markets – monopolies face inelastic demand and so can increase prices – giving consumers no alternative. for example, in the 1980s, microsoft had a monopoly on pc software and charged a high price for microsoft office. a decline in consumer surplus. Monopolies are generally considered to be bad for consumers and the economy. when markets are dominated by a small number of big players, there’s a danger that these players can abuse their power to increase prices to customers. this kind of excessive market power can also lead to less innovation, losses in quality, and higher inflation.
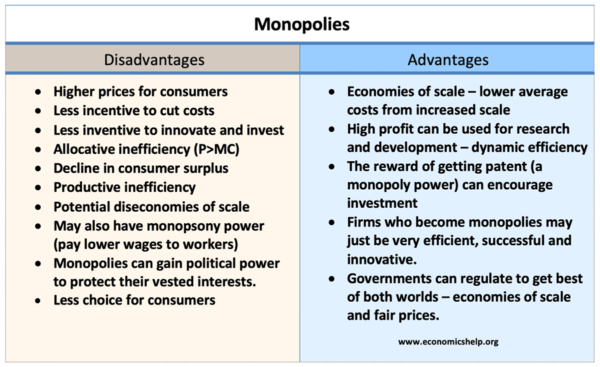
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Monopolies Economics Help The bottom line. monopolies contribute to market failure because they limit efficiency, innovation, and healthy competition. in an efficient market, prices are controlled by all players in the. The bottom line. monopolies are generally considered bad because they have vast control over one market, which is rarely in the best interests of the consumer. this is largely due to a lack of. Monopolies limit consumer choice. consumers are forced to accept the price and quality of goods offered by the single dominant company. additionally, monopolies can lead to less responsive customer service, as the company faces no competitive pressure to keep consumers satisfied. beyond the impact on the individual consumer, monopolies can have. In the standard theory of monopoly found in textbooks, the monopolist is a single seller of a good who increases his or her price above competitive levels, leading to reduced output. the key cost of monopoly is the restriction of industry production. two basic assumptions, or tenets, underlie this theory.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/monopoly-4-reasons-it-s-bad-and-its-history-3305945_final-1425bfcd84d94db6bc7e26c539259c22-5ef1039a953c4ae0a5cafdbc5b96ef1f.jpg)
What Is A Monopoly Monopolies limit consumer choice. consumers are forced to accept the price and quality of goods offered by the single dominant company. additionally, monopolies can lead to less responsive customer service, as the company faces no competitive pressure to keep consumers satisfied. beyond the impact on the individual consumer, monopolies can have. In the standard theory of monopoly found in textbooks, the monopolist is a single seller of a good who increases his or her price above competitive levels, leading to reduced output. the key cost of monopoly is the restriction of industry production. two basic assumptions, or tenets, underlie this theory. Monopoly profit maximization. monopoly is the only producer of the good (e.g. apple i phone) monopoly faces a demand curve d(p) that decreases with p (from consumers’ choices) monopoly has a curve of marginal cost of production mc. monopoly chooses the price p that maximizes its profits: profits = p × q c(q) with q=d(p). Entry forces economic profit to zero in the long run. because entry is blocked, a monopoly firm can sustain an economic profit in the long run. efficiency. the equilibrium solution is efficient because price equals marginal cost. the equilibrium solution is inefficient because price is greater than marginal cost.
The Graph Below Shows The Relationship Between The Various Costs And Monopoly profit maximization. monopoly is the only producer of the good (e.g. apple i phone) monopoly faces a demand curve d(p) that decreases with p (from consumers’ choices) monopoly has a curve of marginal cost of production mc. monopoly chooses the price p that maximizes its profits: profits = p × q c(q) with q=d(p). Entry forces economic profit to zero in the long run. because entry is blocked, a monopoly firm can sustain an economic profit in the long run. efficiency. the equilibrium solution is efficient because price equals marginal cost. the equilibrium solution is inefficient because price is greater than marginal cost.

Comments are closed.