Why Cmos Consumes Less Power

Power Consumption In Cmos Circuits Intechopen Cmos is fast, has a large fan out and uses less power than other technologies. other families are ttl (transistor transistor logic, npn pnp still used), ecl (emitter coupled logic fast but consumes a lot power still used in varying forms) dtl (diode transistor logic old), and rtl (resistor transistor logic (older). In this chapter, we explain the two types of power consumption found in a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) circuit. in general, a cmos circuit tends to dissipate power at all times—be it active or inactive. the power consumed by the circuit when it is performing computational tasks is known as dynamic power. on the contrary, the power lost due to current leakage during which.

Cmos Vlsi Design Consumes Less Power Actual Reason With Logic This is because the short circuit path will be active for a longer period of time. to minimize the total average short circuit current, it is desirable to have equal input and output edge times [2]. in this case, the power consumed by the short circuit currents is typically less than 10% of the total dynamic power. Reduced power dissipation in cmos circuits is a vital challenge in this cutting edge technology. it is most important when the size of transistors is scaled down to enhance transistor density over the silicon chip. power dissipation reduction is another essential goal in the designs. in a cmos circuit, overall power dissipation may be stated as. Here’s a simple way to understand it: when a cmos circuit is in a static state (not switching), it consumes almost no power because there is no continuous path from the power supply to ground. Body of the transistor is often connected to the source (no body bias) introducing a body bias modulates threshold voltage. forward body bias (fbb): increases threshold voltage. reverse body bias (rbb): reduces threshold voltage. h = h0 −. bulk cmos: effect of body bias decreases for technologies below 100nm.
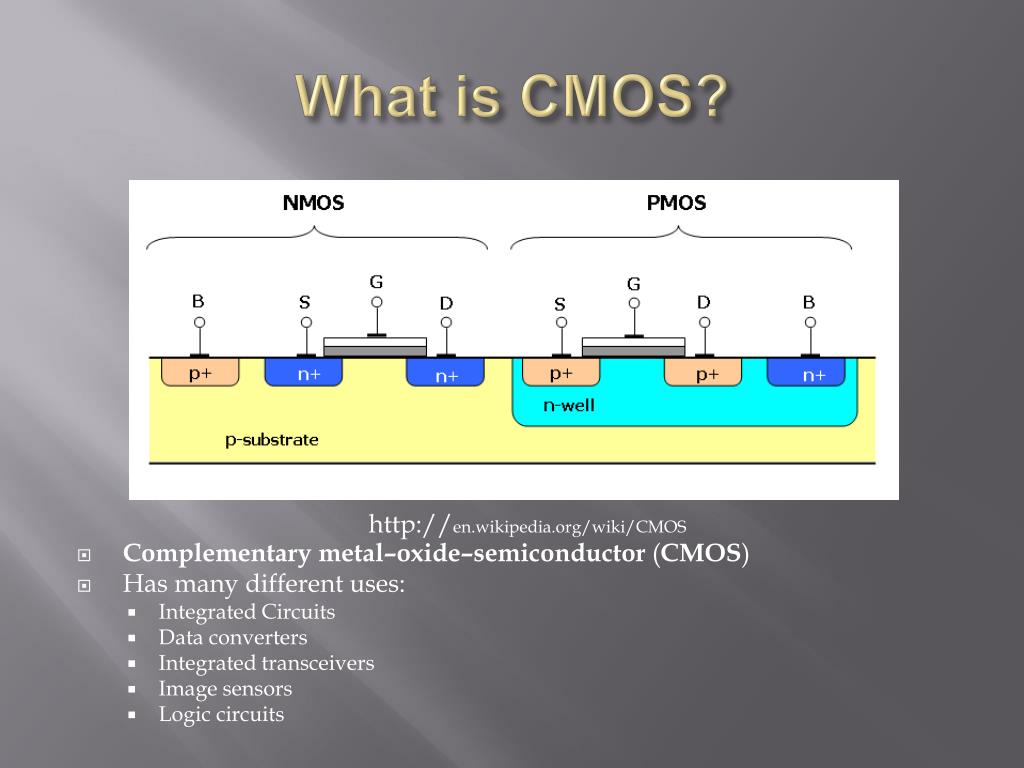
Ppt Cmos Fabrication Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 946155 Here’s a simple way to understand it: when a cmos circuit is in a static state (not switching), it consumes almost no power because there is no continuous path from the power supply to ground. Body of the transistor is often connected to the source (no body bias) introducing a body bias modulates threshold voltage. forward body bias (fbb): increases threshold voltage. reverse body bias (rbb): reduces threshold voltage. h = h0 −. bulk cmos: effect of body bias decreases for technologies below 100nm. Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) power consumption is the amount of electrical power consumed by cmos circuits during operation. cmos power consumption components can be broken down into static, dynamic, short circuit, and clock power consumption. cmos power consumption affects several aspects of pcb design, including power. Cmos power dissipation refers to the amount of power dissipated by complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) integrated circuits (ics) during operation. cmos is widely used in modern electronic devices, such as microprocessors, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits, due to its low power consumption, high noise immunity, and.
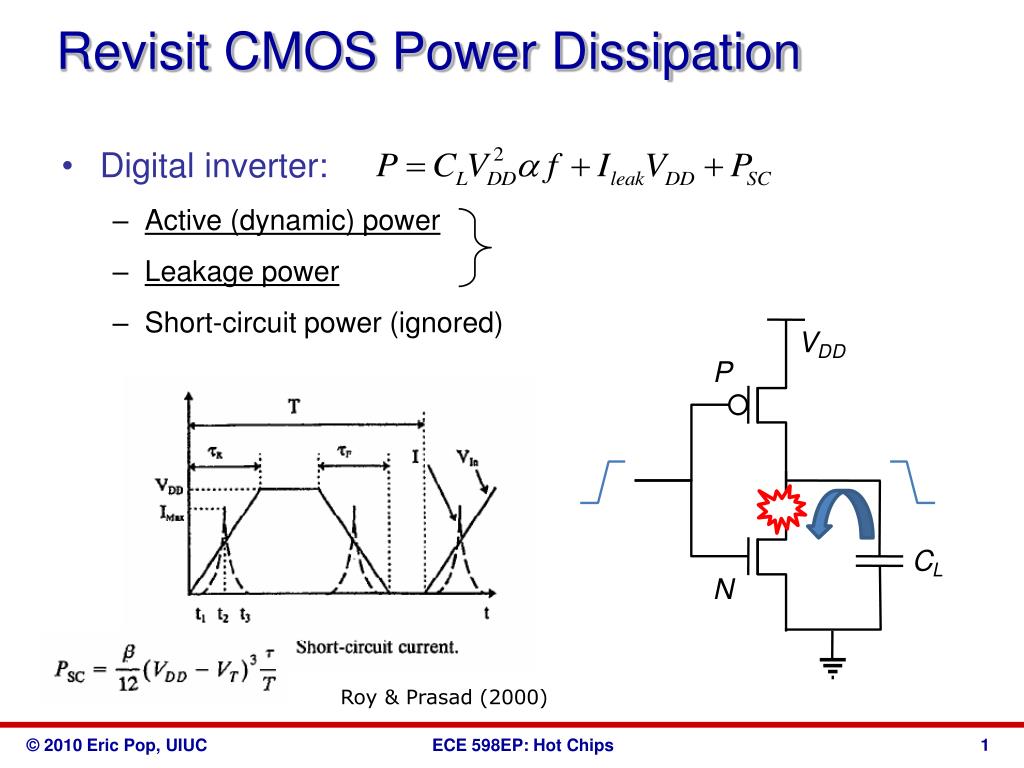
Ppt Revisit Cmos Power Dissipation Powerpoint Presentation Free Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) power consumption is the amount of electrical power consumed by cmos circuits during operation. cmos power consumption components can be broken down into static, dynamic, short circuit, and clock power consumption. cmos power consumption affects several aspects of pcb design, including power. Cmos power dissipation refers to the amount of power dissipated by complementary metal oxide semiconductor (cmos) integrated circuits (ics) during operation. cmos is widely used in modern electronic devices, such as microprocessors, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits, due to its low power consumption, high noise immunity, and.

Power Consumption In Cmos Circuits Intechopen

Comments are closed.