Why Monopolies Are Bad For Consumers A Graphical Example
The Graph Below Shows The Relationship Between The Various Costs And The highest level of output is achieved during the competitive market outcome where marginal benefit (shown by the consumer demand) is equal to marginal cost. the lower quantity is achieved when the firm has monopoly power, and restricts output. so this post has shown graphically why monopolies are bad for consumers. In today's post i will go over the basic economic interpretations for a monopoly and explain why a monopoly holds market power and what this means for the consumer. first it is important to recognize that monopolies only have power if they are the only seller of a good or service, and there are no close substitutes, check out this most for more.

Why Monopolies Are Bad For Customers Disadvantages of monopolies. higher prices than in competitive markets – monopolies face inelastic demand and so can increase prices – giving consumers no alternative. for example, in the 1980s, microsoft had a monopoly on pc software and charged a high price for microsoft office. a decline in consumer surplus. Monopoly graph. a monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where mr = mc. this will be at output qm and price pm. compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output. red area = supernormal profit (ar ac) * q. blue area = deadweight welfare loss (combined loss of producer and consumer surplus. Monopolies are generally considered to be bad for consumers and the economy. when markets are dominated by a small number of big players, there’s a danger that these players can abuse their power to increase prices to customers. this kind of excessive market power can also lead to less innovation, losses in quality, and higher inflation. The bottom line. monopolies are generally considered bad because they have vast control over one market, which is rarely in the best interests of the consumer. this is largely due to a lack of.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/monopoly-4-reasons-it-s-bad-and-its-history-3305945_final-1425bfcd84d94db6bc7e26c539259c22-5ef1039a953c4ae0a5cafdbc5b96ef1f.jpg)
What Is A Monopoly Monopolies are generally considered to be bad for consumers and the economy. when markets are dominated by a small number of big players, there’s a danger that these players can abuse their power to increase prices to customers. this kind of excessive market power can also lead to less innovation, losses in quality, and higher inflation. The bottom line. monopolies are generally considered bad because they have vast control over one market, which is rarely in the best interests of the consumer. this is largely due to a lack of. Intuitively, it makes sense that area e f represents the economic inefficiency created because it is bounded horizontally by the units that aren't being produced by the monopoly and vertically by the amount of value that would have been created for consumers and producers if those units had been produced and sold. 08. The bottom line. monopolies contribute to market failure because they limit efficiency, innovation, and healthy competition. in an efficient market, prices are controlled by all players in the.
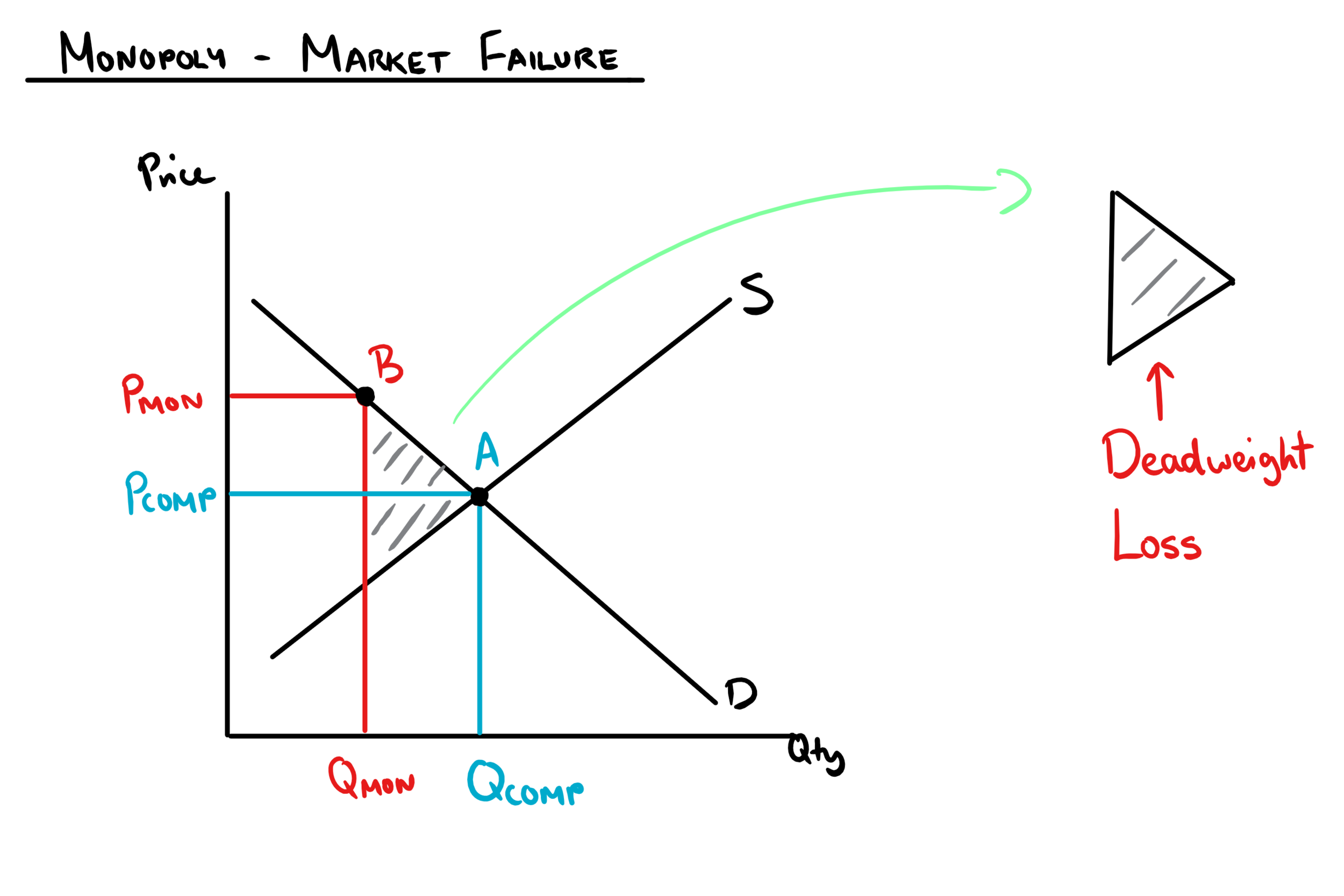
Monopolies Market Failure Mr Banks Economics Hub Resources Intuitively, it makes sense that area e f represents the economic inefficiency created because it is bounded horizontally by the units that aren't being produced by the monopoly and vertically by the amount of value that would have been created for consumers and producers if those units had been produced and sold. 08. The bottom line. monopolies contribute to market failure because they limit efficiency, innovation, and healthy competition. in an efficient market, prices are controlled by all players in the.

Why Monopolies Are Bad For Consumers A Graphical Example Youtube

Can You Use A Diagram To Explain Why A Monopoly When Compared To

Comments are closed.