You Are Generally Considered A Consumer In The Food Chain
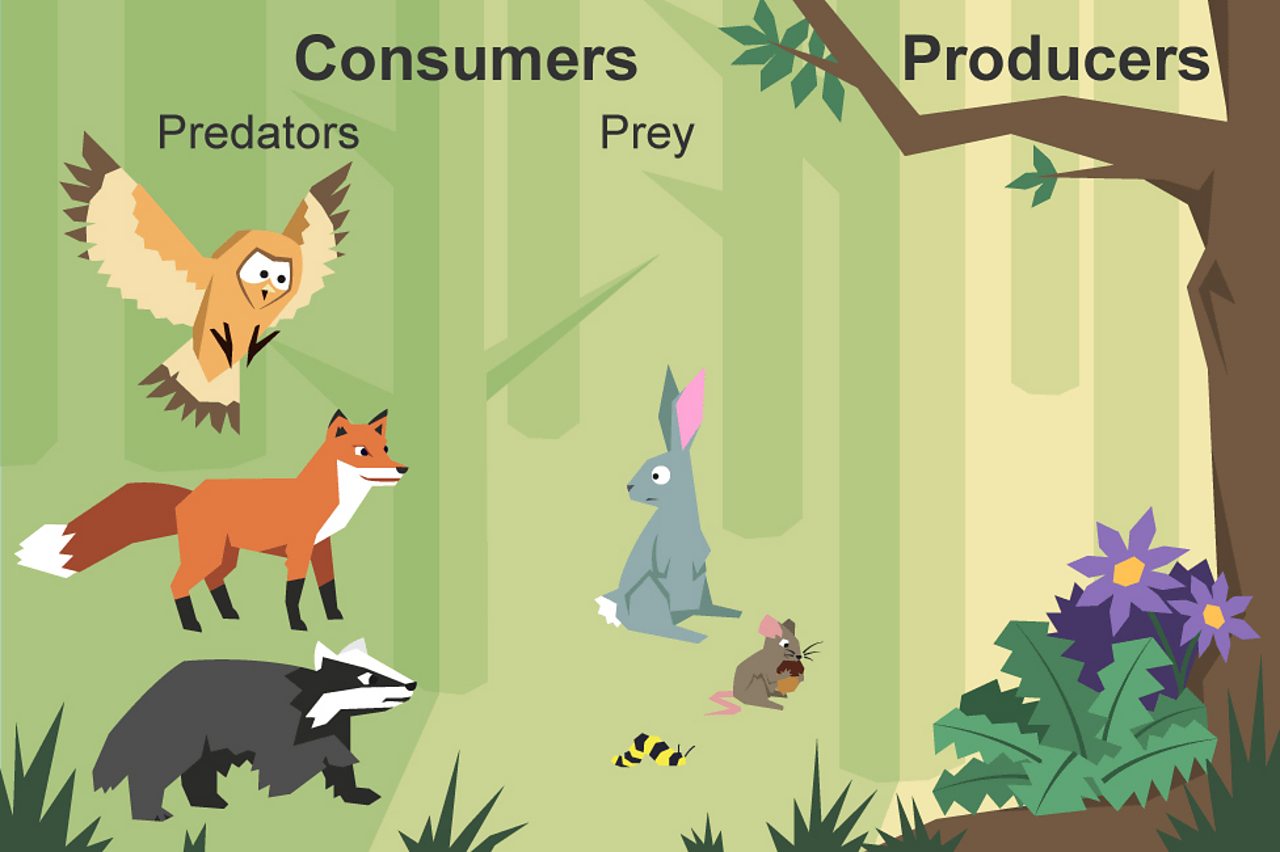
What Is A Food Chain Bbc Bitesize A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.

Food Chain Definition Consumers At Evelyn Oller Blog In the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{g}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. some communities have additional trophic levels (quaternary consumers, fifth order consumers, etc.). finally, detritivores and decomposers break down dead and decaying organisms from any trophic level. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, non linear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 3). figure 3. this food web shows the interactions between organisms across trophic levels in the lake ontario ecosystem. Higher level consumers feed on the next lower tropic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain shown in figure 1, the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. one major factor that limits the length of food chains is energy. Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those.
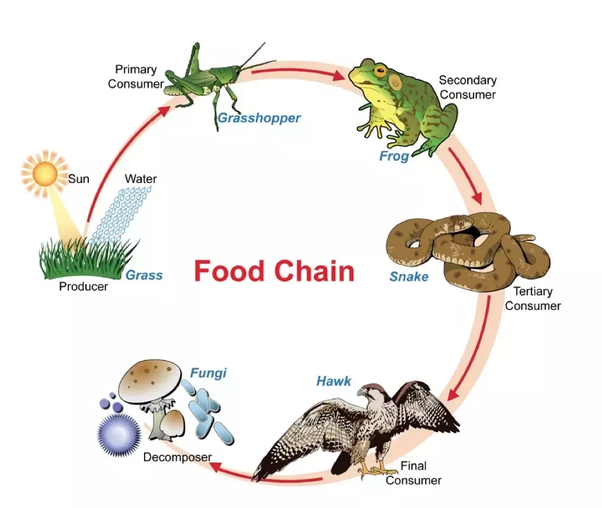
Food Chain Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Higher level consumers feed on the next lower tropic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain shown in figure 1, the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. one major factor that limits the length of food chains is energy. Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those. The food chain is a series of creatures that begins with producer organisms, having consumers at various levels in between, and ends with decomposer species. a food web connects numerous food chains. the food chain takes a single path, whereas the food web takes several paths. the food chain teaches us about the relationships between creatures. The cow and human are consumers. a food chain is a list of organisms in a. habitat. that shows their feeding relationship, i.e what eats what. the organisms are joined by arrows which show the.

Food Chain Pyramid Examples The food chain is a series of creatures that begins with producer organisms, having consumers at various levels in between, and ends with decomposer species. a food web connects numerous food chains. the food chain takes a single path, whereas the food web takes several paths. the food chain teaches us about the relationships between creatures. The cow and human are consumers. a food chain is a list of organisms in a. habitat. that shows their feeding relationship, i.e what eats what. the organisms are joined by arrows which show the.

Comments are closed.